by Thomas R. Wells

But countries are not anymore than that.
Firstly and most obviously, countries are merely a social construction. They are collectively produced fictions (like money or religions) rather than mind-independent objects (like stones). Being fictional does not mean that countries do not matter, but it does mean that they only exist so long as enough people agree to act as if they do.
Secondly and more significantly, countries are locations, not organisations. Organisations are things like armies or corporations that convert groups of human individuals into a coordinated and powerful actor. Unlike countries, organisations are a kind of collectively produced fiction that can actually do things, often very significant things. What we call governments are a particular kind of organisation, one that has achieved the power to make and enforce rules over the inhabitants of a country, for example by hurting those who persist in daring to disagree and by preventing outsiders from entering. (In Max Weber’s famous definition, it “successfully claims a monopoly of the legitimate use of violence”.) This power is called sovereignty and it is an attribute of governments, not countries.
A common mistake is to confuse a country with its inhabitants with its government. This leads to statements that are strictly meaningless at best and deeply misleading at worst because they are category errors on the order of ‘Green ideas sleep furiously’. Read more »
 Sughra Raza. Self-portrait With Trees. Seattle, February, 2022.
Sughra Raza. Self-portrait With Trees. Seattle, February, 2022.
 On 4 October 1957, in my mind’s eye, I was playing alone in the back yard when the radio in the breezeway broadcast a special news bulletin that changed my life. We had moved from Chicago to Minneapolis in 1951 and my parents had bought a recently built house on a dead-end street in a relatively cheap residential area out near the airport. The house was built in the modern suburban style that people called a ranch-style bungalow and its most interesting post-war feature was the breezeway, a screened-in patio attached to the house. The screens that kept flies and mosquitos at bay in warm weather were swapped for glass panels when the weather turned cold and we changed our window screens for storm widows.
On 4 October 1957, in my mind’s eye, I was playing alone in the back yard when the radio in the breezeway broadcast a special news bulletin that changed my life. We had moved from Chicago to Minneapolis in 1951 and my parents had bought a recently built house on a dead-end street in a relatively cheap residential area out near the airport. The house was built in the modern suburban style that people called a ranch-style bungalow and its most interesting post-war feature was the breezeway, a screened-in patio attached to the house. The screens that kept flies and mosquitos at bay in warm weather were swapped for glass panels when the weather turned cold and we changed our window screens for storm widows.


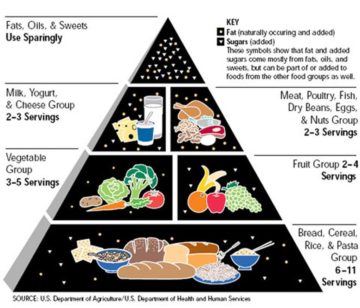 We have many choices when deciding what to eat. For most of human history, however, there has likely been little to no choice at all: people ate what was available to them or what their culture led them to eat. Now things are not so simple. As I mentioned in
We have many choices when deciding what to eat. For most of human history, however, there has likely been little to no choice at all: people ate what was available to them or what their culture led them to eat. Now things are not so simple. As I mentioned in 


 I enjoyed my days in Delhi School of Economics, but some aspects of the university’s policy in recruitment and promotion of teachers used to trouble me. Let me just give two examples. One is from DSE itself, but illustrative of a much more general problem in university life. We had a middle-aged colleague who had long wanted to be promoted to Readership (Associate Professorship), but failed in the usual process, because he had not done any serious research to speak of in many years. He was full of leftist clichés, and was popular with some sections of leftist students. He first started complaining that he was being passed over in promotion because his ‘right-wing’ colleagues (the term used in Economics those days was ‘neo-classical’—in the same pejorative way the term ‘neo-liberal’ is used nowadays) were biased in undervaluing his work. This after a time did not work, as even some leftist scholars in the Department shared views similar to those of the ‘right-wing’ colleagues on this matter. Then he tried a different tack.
I enjoyed my days in Delhi School of Economics, but some aspects of the university’s policy in recruitment and promotion of teachers used to trouble me. Let me just give two examples. One is from DSE itself, but illustrative of a much more general problem in university life. We had a middle-aged colleague who had long wanted to be promoted to Readership (Associate Professorship), but failed in the usual process, because he had not done any serious research to speak of in many years. He was full of leftist clichés, and was popular with some sections of leftist students. He first started complaining that he was being passed over in promotion because his ‘right-wing’ colleagues (the term used in Economics those days was ‘neo-classical’—in the same pejorative way the term ‘neo-liberal’ is used nowadays) were biased in undervaluing his work. This after a time did not work, as even some leftist scholars in the Department shared views similar to those of the ‘right-wing’ colleagues on this matter. Then he tried a different tack. It’s my oldest memory. I am three, standing harnessed between my parents, in a brand-new two-seater 1959 Jaguar convertible roadster. We are on an empty gravel road someplace in Virginia and my Dad decides to let his new baby fly. I can see In front of me the windshield and, below, a gray leather dashboard that has two things of great interest…a speedometer and a tachometer. The motor hmmmmmms as he takes the car through the forward gears, the tachometer first rising and then falling, the speed increasing. The big whitewall tires are crunching the rough road; cinders are flying; we hit 60 MPH, then 70, then 80; and I’m clapping my hands and piping out “Faster, Daddy! Faster!” My mom goes from worried to furious “Slow down, Ernie, slow down!” As he passes 90, I look down for a moment and she’s slapping her yellow shorts. I peek at the rearview mirror and see a huge cloud of dust. 95, 100, and finally 105. Then without warning, and without using the brakes, he starts to slow, gradually downshifting; the speedometer and tachometer fall; and that’s where my memory ends.
It’s my oldest memory. I am three, standing harnessed between my parents, in a brand-new two-seater 1959 Jaguar convertible roadster. We are on an empty gravel road someplace in Virginia and my Dad decides to let his new baby fly. I can see In front of me the windshield and, below, a gray leather dashboard that has two things of great interest…a speedometer and a tachometer. The motor hmmmmmms as he takes the car through the forward gears, the tachometer first rising and then falling, the speed increasing. The big whitewall tires are crunching the rough road; cinders are flying; we hit 60 MPH, then 70, then 80; and I’m clapping my hands and piping out “Faster, Daddy! Faster!” My mom goes from worried to furious “Slow down, Ernie, slow down!” As he passes 90, I look down for a moment and she’s slapping her yellow shorts. I peek at the rearview mirror and see a huge cloud of dust. 95, 100, and finally 105. Then without warning, and without using the brakes, he starts to slow, gradually downshifting; the speedometer and tachometer fall; and that’s where my memory ends. The peopling of Polynesia was an epic chapter in world exploration. Stirred by adventure and hungry for land, intrepid pioneers sailed for days or weeks beyond their known horizons to discover landscapes and living things never before seen by human eyes. Survival was never easy or assured, yet they managed to find and colonize nearly every spot of land across the entire southern Pacific Ocean. On each island, they forged new societies based on familiar Polynesian models of ranked patrilineages, family bonds and obligations, social care and cohesion, cooperation and duty. Each culture that arose was unique and changeable, as islanders continually adjusted to altered conditions, new information, and shifting political tides. Through trial and hardship, most of these civilizations—even on some of the tiniest islands, like
The peopling of Polynesia was an epic chapter in world exploration. Stirred by adventure and hungry for land, intrepid pioneers sailed for days or weeks beyond their known horizons to discover landscapes and living things never before seen by human eyes. Survival was never easy or assured, yet they managed to find and colonize nearly every spot of land across the entire southern Pacific Ocean. On each island, they forged new societies based on familiar Polynesian models of ranked patrilineages, family bonds and obligations, social care and cohesion, cooperation and duty. Each culture that arose was unique and changeable, as islanders continually adjusted to altered conditions, new information, and shifting political tides. Through trial and hardship, most of these civilizations—even on some of the tiniest islands, like 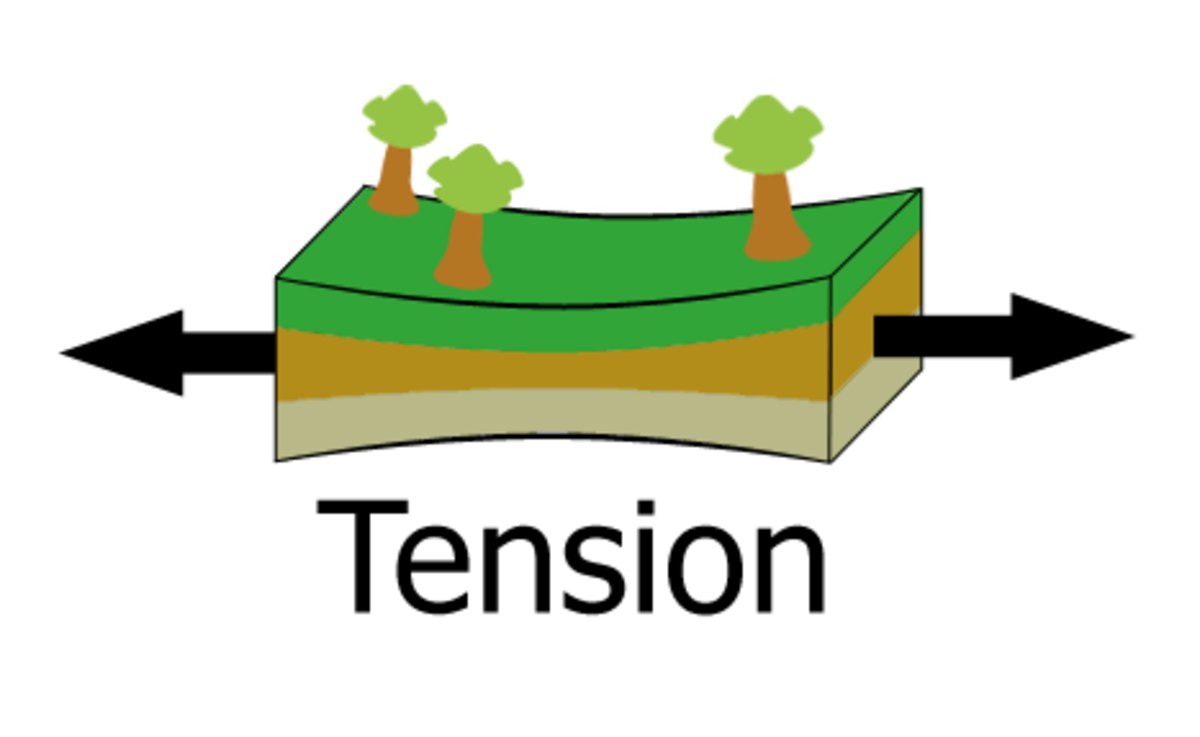 The United States has always faced a fundamental tension. On one side are those who champion, enforce, and/or profit from hierarchies of power: white supremacist racism, sexist patriarchy, Christian fundamentalism, and capital concentrations chief among them. Arrayed against these hierarchies of power are people who promote and work for racial equality, gender and sexual equality, cultural tolerance, the amelioration of poverty, and genuine freedom both for and from religious beliefs and practices.
The United States has always faced a fundamental tension. On one side are those who champion, enforce, and/or profit from hierarchies of power: white supremacist racism, sexist patriarchy, Christian fundamentalism, and capital concentrations chief among them. Arrayed against these hierarchies of power are people who promote and work for racial equality, gender and sexual equality, cultural tolerance, the amelioration of poverty, and genuine freedom both for and from religious beliefs and practices.


 By a happy chance, the section I was invited to read from, alongside Andreas Flückiger and William Brockman, two associates of the Foundation, at the
By a happy chance, the section I was invited to read from, alongside Andreas Flückiger and William Brockman, two associates of the Foundation, at the 