by Jerry Cayford
I was always attracted to that old dichotomy: people must be either stupid or lying when they claim to believe some obvious falsehood. This dichotomy is a staple of Democratic theorizing about our political culture. (Sometimes the choice is between stupid and evil, which amounts to the same.) For example, Adam-Troy Castro’s social media classic “Why Do Liberals Think Trump Supporters Are Stupid?” has been circulating since halfway through Trump’s first term. But this simple dichotomy is losing its appeal. It is just not plausible that tens of millions of ordinary Republicans—our neighbors, friends, and families—are stupid or evil. There have been many proposed explanations of this puzzle: information siloes hide the obvious from otherwise intelligent people; tribalism exerts a powerful evolutionary draw. I believe, though, that there is a different and hidden complexity here.
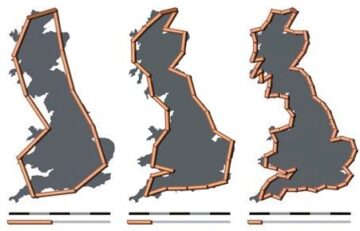
I use the word “complexity” deliberately, because my argument draws on one of the icons of chaos theory (aka complexity theory) known as the “Coastline Paradox.” That name refers to a 1967 paper, “How Long Is the Coast of Britain?” by one of the pioneers of chaos theory, Benoit Mandelbrot. James Gleick provides a quick introduction to the topic in “The Man Who Reshaped Geometry” (1985), and a thorough treatment in his book Chaos: Making a New Science (1987). But the Coastline Paradox itself is easy to understand.
Imagine you measure the coast of Britain by putting markers every ten miles and summing the distances between them. You get a certain result. If you put markers every mile, you get a larger result. Measure the coast with a yardstick: longer still. With an inch ruler: longer. The coast will continue to get longer as you trace it around ever-smaller irregularities, around every grain of sand. So, how long is the coast? As Gleick says in his article, “In fact, it depends on the length of your ruler. As the scale becomes finer and finer, bays and peninsulas reveal new subbays and subpeninsulas, and the length—truly—increases without limit, at least down to atomic scales.” In a sense, physical length does not exist. Or, physical lengths are all infinite. Or, better, length depends on your method of measuring.
Examining length gives us a glimpse into a new picture of how the things we say and believe relate to reality. Read more »


 Nirmal Raja. Entangled / The Weight of Our Past, 2022.
Nirmal Raja. Entangled / The Weight of Our Past, 2022.


 Words, so many words. Words that inspire “Ask Not,” and those that call upon our resolve “[A] date that will live in infamy.” Words that warn about the future “[W]e must guard against the acquisition of unwarranted influence, whether sought or unsought, by the military-industrial complex,” and those that express optimism about it “I’ve been to the mountaintop.” Words that deny their own importance “[T]he world will little note nor long remember what we say here,” while elevating themselves and the dead they honor to immortality.
Words, so many words. Words that inspire “Ask Not,” and those that call upon our resolve “[A] date that will live in infamy.” Words that warn about the future “[W]e must guard against the acquisition of unwarranted influence, whether sought or unsought, by the military-industrial complex,” and those that express optimism about it “I’ve been to the mountaintop.” Words that deny their own importance “[T]he world will little note nor long remember what we say here,” while elevating themselves and the dead they honor to immortality.


 Dhingra’s book is built on many months of Sundays spent walking the market, talking to traders and readers, and mapping the bazaar’s assemblages and syncopations. I was lucky enough to tag along on one of these expeditions in July 2023. Arriving empty-handed, we traced a circuitous route between tables piled high with dog-eared paperbacks under billowing canopies. I departed clutching lucky finds: a 1950s Urdu story collection and a strange out-of-print children’s novel called
Dhingra’s book is built on many months of Sundays spent walking the market, talking to traders and readers, and mapping the bazaar’s assemblages and syncopations. I was lucky enough to tag along on one of these expeditions in July 2023. Arriving empty-handed, we traced a circuitous route between tables piled high with dog-eared paperbacks under billowing canopies. I departed clutching lucky finds: a 1950s Urdu story collection and a strange out-of-print children’s novel called 

 In 2007, at the Munich Security Conference, Vladimir Putin announced that the current world order had changed. The unipolar world order, with one centre of power, force and decision-making, was unacceptable to the leader in the Kremlin. Yet, more than that, Putin’s speech prepared the replacement of the unipolar world order, a replacement, he would later come back to, over and over again: multipolarity.
In 2007, at the Munich Security Conference, Vladimir Putin announced that the current world order had changed. The unipolar world order, with one centre of power, force and decision-making, was unacceptable to the leader in the Kremlin. Yet, more than that, Putin’s speech prepared the replacement of the unipolar world order, a replacement, he would later come back to, over and over again: multipolarity.






 One argument for the existence of a creator /designer of the universe that is popular in public and academic circles is the fine-tuning argument. It is argued that if one or more of nature’s physical constants as mathematically accounted for in subatomic physics had varied just by an infinitesimal amount, life would not exist in the universe. Some claim, for example, with an infinitesimal difference in certain physical constants the Big Bang would have collapsed upon itself before life could form or elements like carbon essential for life would never have formed. The specific settings that make life possible seem to be set to almost incomprehensible infinitesimal precision. It would be incredibly lucky to have these settings be the result of pure chance. The best explanation for life is not physics alone but the existence of a creator/designer who intentionally fine-tuned physical laws and fundamental constants of physics to make life physically possible in the universe. In other words, the best explanation for the existence of life in general and ourselves in particular, is not chance but a theistic version of a designer of the universe.
One argument for the existence of a creator /designer of the universe that is popular in public and academic circles is the fine-tuning argument. It is argued that if one or more of nature’s physical constants as mathematically accounted for in subatomic physics had varied just by an infinitesimal amount, life would not exist in the universe. Some claim, for example, with an infinitesimal difference in certain physical constants the Big Bang would have collapsed upon itself before life could form or elements like carbon essential for life would never have formed. The specific settings that make life possible seem to be set to almost incomprehensible infinitesimal precision. It would be incredibly lucky to have these settings be the result of pure chance. The best explanation for life is not physics alone but the existence of a creator/designer who intentionally fine-tuned physical laws and fundamental constants of physics to make life physically possible in the universe. In other words, the best explanation for the existence of life in general and ourselves in particular, is not chance but a theistic version of a designer of the universe.