William Nakabayashi at The Believer:
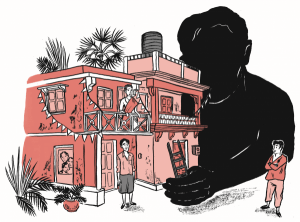 Filmistan Studios occupies five acres in Goregaon, India, which is technically an outer suburb of Mumbai, but denser than most New York City neighborhoods. If you take the train from the city proper and fight the foot traffic that crowds the bazaar area around the station, you’ll reach a pair of steel gates. Just on the other side are Filmistan’s soundstages, which have been in continuous operation since 1943. In the Golden Age of Hindi Film, up to the 1960s, the industry worked along lines similar to those of the old Hollywood studio system, with each production house fielding its own stable of talent. Unlike most of its former rivals, Filmistan has remained open for business as a production facility, and the grounds now accommodate eight stages and several outdoor shooting areas, including a Hindu temple, a jailhouse exterior, and a village. But Filmistan is more than a collection of sets. Behind the scenes, there are real people living there. I came to Filmistan as an anthropologist in training, with a research project that looked solid enough, on paper, to win a Fulbright grant. One thing about ethnography they don’t teach you in school, though, is how awkward it can be getting started. Reaching out to people to do research with—soliciting “informants”—can feel like approaching strangers for a date. Left to myself in Mumbai, with my sun-glasses and clumsy Hindi, I was a field-work wallflower
Filmistan Studios occupies five acres in Goregaon, India, which is technically an outer suburb of Mumbai, but denser than most New York City neighborhoods. If you take the train from the city proper and fight the foot traffic that crowds the bazaar area around the station, you’ll reach a pair of steel gates. Just on the other side are Filmistan’s soundstages, which have been in continuous operation since 1943. In the Golden Age of Hindi Film, up to the 1960s, the industry worked along lines similar to those of the old Hollywood studio system, with each production house fielding its own stable of talent. Unlike most of its former rivals, Filmistan has remained open for business as a production facility, and the grounds now accommodate eight stages and several outdoor shooting areas, including a Hindu temple, a jailhouse exterior, and a village. But Filmistan is more than a collection of sets. Behind the scenes, there are real people living there. I came to Filmistan as an anthropologist in training, with a research project that looked solid enough, on paper, to win a Fulbright grant. One thing about ethnography they don’t teach you in school, though, is how awkward it can be getting started. Reaching out to people to do research with—soliciting “informants”—can feel like approaching strangers for a date. Left to myself in Mumbai, with my sun-glasses and clumsy Hindi, I was a field-work wallflower
more here.

 R
R Alvinella pompejana, a type of deep sea worm, can thrive at temperatures that would kill most living organisms. It has been used in skin creams — and sequences of its genes appear in 18 patents from not only BASF, but also a French research institution. Genetic prospectors — a term some find offensive, while acknowledging there’s not a great alternative — have a range of motivations. Some are hoping to develop a novel treatment for cancer. Others want to create the next Botox. Most are looking for organisms with exceptional traits that might offer the missing piece in their new product. That is why patents are filled with“extremophiles,” known for doing well in extreme darkness, cold, acidity and other harsh environments, said Robert Blasiak, a researcher from the Stockholm Resilience Centre who was involved in the patent study.
Alvinella pompejana, a type of deep sea worm, can thrive at temperatures that would kill most living organisms. It has been used in skin creams — and sequences of its genes appear in 18 patents from not only BASF, but also a French research institution. Genetic prospectors — a term some find offensive, while acknowledging there’s not a great alternative — have a range of motivations. Some are hoping to develop a novel treatment for cancer. Others want to create the next Botox. Most are looking for organisms with exceptional traits that might offer the missing piece in their new product. That is why patents are filled with“extremophiles,” known for doing well in extreme darkness, cold, acidity and other harsh environments, said Robert Blasiak, a researcher from the Stockholm Resilience Centre who was involved in the patent study. In 1933, with Hitler and the Nazis boycotting Jewish businesses, many powerful Jews in Germany and the powerful American Jewish charities opposed retaliation, advocating negotiation instead. Some viewed Hitler as a “weak man” and wanted to “strengthen his hand”: “Once the Nazis had cleansed Germany of opposition parties and ended parliamentary government, they turned their attention to the Jews. By mid-March, the rank-and-file were storming department stores and demanding a boycott of Jewish businesses. As much to guide as to incite these volatile emotions. Hitler and Goebbels championed the idea of a boycott. In a March 27 radio broadcast, the government announced that on the morning of April 1st, at the stroke of ten, SA and SS members would take up positions outside Jewish stores and warn the public not to enter. This offense was portrayed as a defensive measure against ‘Jewish atrocity propaganda abroad.’ To add further terror, Göring told Jewish community leaders that they would be held responsible for any anti-German propaganda appearing abroad. Eager to create jobs through exports, Hitler wanted to minimize adverse publicity overseas.
In 1933, with Hitler and the Nazis boycotting Jewish businesses, many powerful Jews in Germany and the powerful American Jewish charities opposed retaliation, advocating negotiation instead. Some viewed Hitler as a “weak man” and wanted to “strengthen his hand”: “Once the Nazis had cleansed Germany of opposition parties and ended parliamentary government, they turned their attention to the Jews. By mid-March, the rank-and-file were storming department stores and demanding a boycott of Jewish businesses. As much to guide as to incite these volatile emotions. Hitler and Goebbels championed the idea of a boycott. In a March 27 radio broadcast, the government announced that on the morning of April 1st, at the stroke of ten, SA and SS members would take up positions outside Jewish stores and warn the public not to enter. This offense was portrayed as a defensive measure against ‘Jewish atrocity propaganda abroad.’ To add further terror, Göring told Jewish community leaders that they would be held responsible for any anti-German propaganda appearing abroad. Eager to create jobs through exports, Hitler wanted to minimize adverse publicity overseas. He flew so fast and so close to the sun that it took an entire lifetime to fall back to Earth.
He flew so fast and so close to the sun that it took an entire lifetime to fall back to Earth. I recently read Simone Weil for the first time after having come across numerous references to her over the past year. I broke down and bought Waiting for God despite the intimidating and frankly confusing title. I was not disappointed. One of her essays in particular, “Reflections on the Right Use of School Studies in View of the Love of God,” has opened and focused my thinking on education and learning in general, whether for children or later in life for the rest of us.
I recently read Simone Weil for the first time after having come across numerous references to her over the past year. I broke down and bought Waiting for God despite the intimidating and frankly confusing title. I was not disappointed. One of her essays in particular, “Reflections on the Right Use of School Studies in View of the Love of God,” has opened and focused my thinking on education and learning in general, whether for children or later in life for the rest of us. 

 Opera as resistance? Music as re-enchantment?
Opera as resistance? Music as re-enchantment?
 When it comes to evil, nobody beats Hitler. He committed the biggest mass murder of innocent humans in all of history.
When it comes to evil, nobody beats Hitler. He committed the biggest mass murder of innocent humans in all of history.

 Many years ago in 1991, in my first job out of college, I worked for a small investment bank. By 1994, I was working in its IT department. One of my tasks was PC support and I had a modem attached to my computer so that I could connect to Compuserve for research on technical issues. Yes, this was the heydey of Compuserve, the year that the first web browser came out and a time when most people had very little idea, if any, what this Internet thing was.
Many years ago in 1991, in my first job out of college, I worked for a small investment bank. By 1994, I was working in its IT department. One of my tasks was PC support and I had a modem attached to my computer so that I could connect to Compuserve for research on technical issues. Yes, this was the heydey of Compuserve, the year that the first web browser came out and a time when most people had very little idea, if any, what this Internet thing was. 
 Novels set in New York and Berlin of the 1980s and 1990s, in other words, just as subculture was at its apogee and the first major gentrification waves in various neighborhoods of the two cities were underway—particularly when they also try to tell the coming-of-age story of a young art student maturing into an artist—these novels run the risk of digressing into art scene cameos and excursions on drug excess. In her novel A Lesser Day (Spuyten Duyvil, second edition 2018), Andrea Scrima purposely avoids effects of this kind. Instead, she concentrates on quietly capturing moments that illuminate her narrator’s ties to the locations she’s lived in and the lives she’s lived there.
Novels set in New York and Berlin of the 1980s and 1990s, in other words, just as subculture was at its apogee and the first major gentrification waves in various neighborhoods of the two cities were underway—particularly when they also try to tell the coming-of-age story of a young art student maturing into an artist—these novels run the risk of digressing into art scene cameos and excursions on drug excess. In her novel A Lesser Day (Spuyten Duyvil, second edition 2018), Andrea Scrima purposely avoids effects of this kind. Instead, she concentrates on quietly capturing moments that illuminate her narrator’s ties to the locations she’s lived in and the lives she’s lived there. In the fall of 1971, I set out from the small New Hampshire town where I’d spent the first 17 years of my life and rode a Greyhound bus to New Haven. I had a trunk of clothes, a portable stereo housed in a red Samsonite suitcase, and a couple dozen vinyl albums—Bob Dylan, Joni Mitchell, Leonard Cohen, the Rolling Stones—that I hauled up three flights of stairs to a fourth-floor dormitory room. Yale had gone coed two years before, but ours was the first class in which women would complete the full four years.
In the fall of 1971, I set out from the small New Hampshire town where I’d spent the first 17 years of my life and rode a Greyhound bus to New Haven. I had a trunk of clothes, a portable stereo housed in a red Samsonite suitcase, and a couple dozen vinyl albums—Bob Dylan, Joni Mitchell, Leonard Cohen, the Rolling Stones—that I hauled up three flights of stairs to a fourth-floor dormitory room. Yale had gone coed two years before, but ours was the first class in which women would complete the full four years.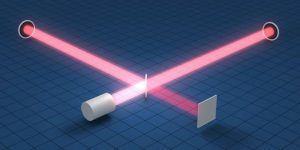 Light always moves at the same, constant speed: c, or 299,792,458 m/s. That’s the speed of light in a vacuum, and LIGO has vacuum chambers inside both arms. The thing is, when a gravitational wave passes through each arm, lengthening or shortening the arm, it also lengthens or shortens the wavelength of the light within it by a corresponding amount.
Light always moves at the same, constant speed: c, or 299,792,458 m/s. That’s the speed of light in a vacuum, and LIGO has vacuum chambers inside both arms. The thing is, when a gravitational wave passes through each arm, lengthening or shortening the arm, it also lengthens or shortens the wavelength of the light within it by a corresponding amount. After the crash of 2008, the language of inequality began to trickle into the popular discourse. Then the Occupy movement launched it into the mainstream; the fall of 2011 was the first time in generations that concerns about distributive justice drove crowds into the streets and made front-page news. Scholars, pundits, and politicians all took note, and before long, Gornick and her colleagues found themselves at the center of what President Barack Obama
After the crash of 2008, the language of inequality began to trickle into the popular discourse. Then the Occupy movement launched it into the mainstream; the fall of 2011 was the first time in generations that concerns about distributive justice drove crowds into the streets and made front-page news. Scholars, pundits, and politicians all took note, and before long, Gornick and her colleagues found themselves at the center of what President Barack Obama  In his appearance before the Senate Judiciary Committee last week, Brett Kavanaugh put on a prodigious display of vacuity and mendacity. Kavanaugh is the retrograde jurist picked by Donald Trump to fill the Supreme Court vacancy that arose when the Court’s “swing vote,” Anthony Kennedy, retired. His politics is god awful, but that is hardly news. It was a sure thing that Trump would nominate someone with god-awful politics. Because he knows little and cares less about the judicial system, except when it impinges on his financial shenanigans, and because, as part of his pact with “conservatives” Trump outsourced judicial appointments to the Federalist Society, anyone he would nominate was bound to come with god-awful politics. At least, this particular god-awful jurist is well schooled, well spoken (in the way that lawyers are), and intelligent enough to talk like a lawyer or judge, while dissembling shamelessly and saying nothing of substance. That puts him leagues ahead of Trump. It also puts him head and shoulders above the average Republican. But let’s not praise him too much on that account; much the same could be said of Ted Cruz. Because politically the two of them are so much alike, it is instructive to compare Kavanaugh with that villainous Texas Senator.
In his appearance before the Senate Judiciary Committee last week, Brett Kavanaugh put on a prodigious display of vacuity and mendacity. Kavanaugh is the retrograde jurist picked by Donald Trump to fill the Supreme Court vacancy that arose when the Court’s “swing vote,” Anthony Kennedy, retired. His politics is god awful, but that is hardly news. It was a sure thing that Trump would nominate someone with god-awful politics. Because he knows little and cares less about the judicial system, except when it impinges on his financial shenanigans, and because, as part of his pact with “conservatives” Trump outsourced judicial appointments to the Federalist Society, anyone he would nominate was bound to come with god-awful politics. At least, this particular god-awful jurist is well schooled, well spoken (in the way that lawyers are), and intelligent enough to talk like a lawyer or judge, while dissembling shamelessly and saying nothing of substance. That puts him leagues ahead of Trump. It also puts him head and shoulders above the average Republican. But let’s not praise him too much on that account; much the same could be said of Ted Cruz. Because politically the two of them are so much alike, it is instructive to compare Kavanaugh with that villainous Texas Senator.