by Michael Liss
I am not the Catholic candidate for president. I am the Democratic Party’s candidate for president, who happens also to be a Catholic. I do not speak for my church on public matters, and the church does not speak for me. —JFK

September 12, 1960. Just eight weeks before the 1960 election, and the Democratic candidate for President, John Fitzgerald Kennedy, finds himself before a crowd of roughly 300 Protestant clerics at a meeting of the Greater Houston Ministerial Association. He has been invited to explain his views on religion, more particularly, his religion.
To modern eyes, there is something surreal about this. Watch the clip in grainy black and white, read the speech, and you can’t help but be mesmerized. Why is he here? Kennedy was a war hero; he’d been a Congressman, a Senator, and a Pulitzer Prize winner. While it certainly could be argued that there might be better men for the job, surely JFK had achieved enough in his life to meet the qualifications for being a President.
Unless (and certainly many in the audience believed this) Kennedy could never be qualified. Unless, to use his own words on this day, he was just one of “40 million Americans [who] lost their chance of being president on the day they were baptized.”
Whatever his feelings, Kennedy and his team knew this moment, and moments like it, were inevitable. They had always known it, even before he entered the race. It was a reflection of what the journalist Theodore White called “the largest and most important division in American society, that between Protestants and Catholics.” Read more »

 As forced migration in the wake of war and climate change continues, and various administrations attempt to additionally restrict the movement of people while further “freeing” the flow of capital, national borders, nativism, and a sense of cultural rootedness have re-emerged as acceptable topics in a globalized order that had until recently believed itself post-national. In the German-speaking world, where refugees have been met with varying degrees of enthusiasm depending on their provenance, national pride, long taboo following the Second World War, at least in Germany, is enjoying a comeback. As the last generation of perpetrators and victims dies and a newly self-confident, unproblematically nationalist generation comes to consciousness, it is again becoming possible to use a romantic, symbolically charged term like Heimat.
As forced migration in the wake of war and climate change continues, and various administrations attempt to additionally restrict the movement of people while further “freeing” the flow of capital, national borders, nativism, and a sense of cultural rootedness have re-emerged as acceptable topics in a globalized order that had until recently believed itself post-national. In the German-speaking world, where refugees have been met with varying degrees of enthusiasm depending on their provenance, national pride, long taboo following the Second World War, at least in Germany, is enjoying a comeback. As the last generation of perpetrators and victims dies and a newly self-confident, unproblematically nationalist generation comes to consciousness, it is again becoming possible to use a romantic, symbolically charged term like Heimat.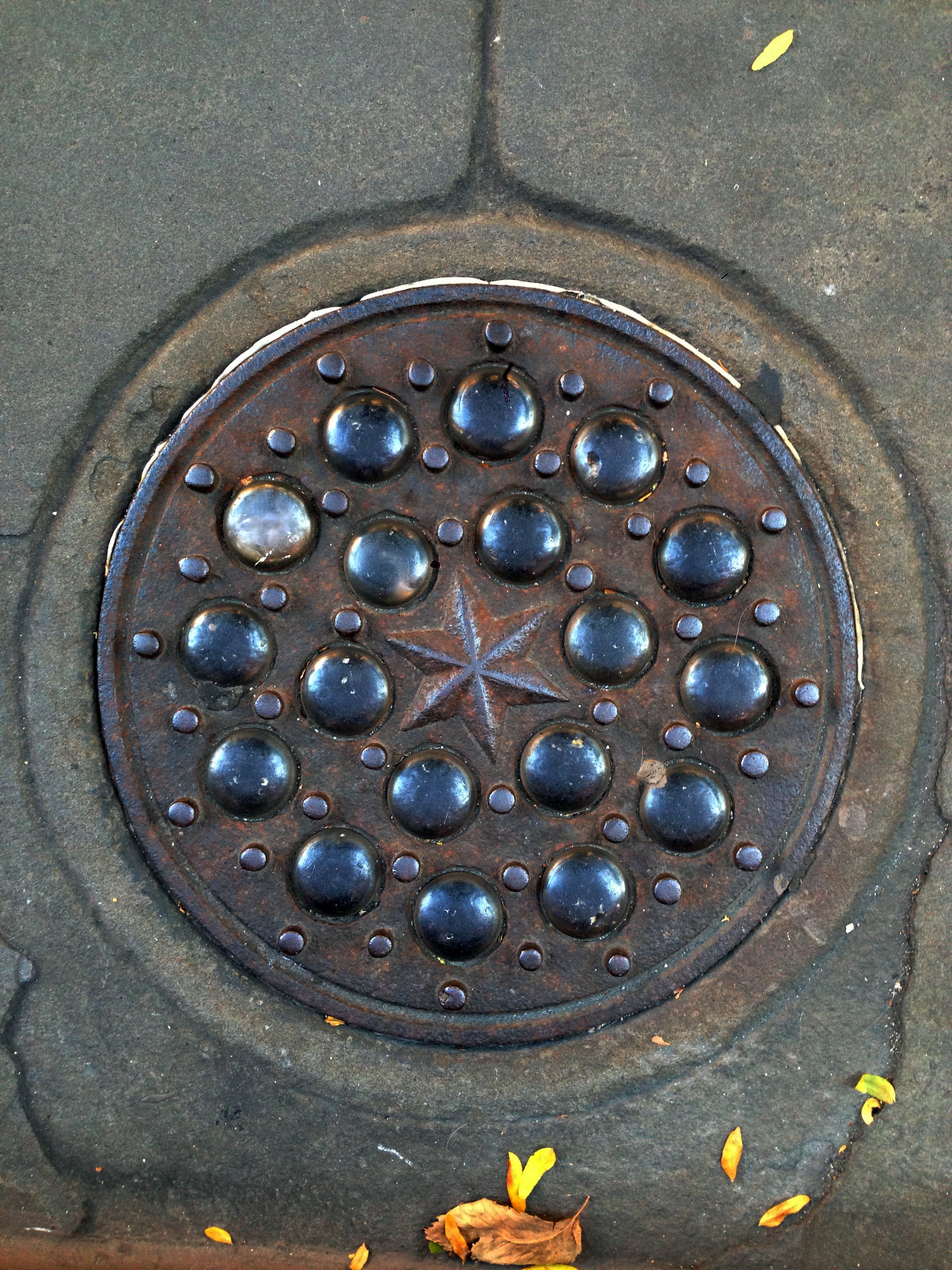 Sughra Raza. Don’t Step On The Jewels, 2014.
Sughra Raza. Don’t Step On The Jewels, 2014.
 technology will somehow amplify itself into a superintelligence and proceed to eliminate the human race, either inadvertently – as a side effect of some other project, such as creating paper clips (a standard example), or deliberately.
technology will somehow amplify itself into a superintelligence and proceed to eliminate the human race, either inadvertently – as a side effect of some other project, such as creating paper clips (a standard example), or deliberately.

 About eight years ago, I was in downtown Manhattan and went into a Warby Parker store, an eyewear retailer. I didn’t post anything on social media about it, but I did have location services enabled on Facebook. Later that day, Facebook started showing me ads for eyewear (something it had never done before.) How and why it did that wasn’t a giant leap of understanding, and I immediately turned location services off for Facebook. But of course, this was sticking one thumb in the crumbling dam that is my data privacy. I own an Alexa, and I have an iPhone, an Apple watch, and an iPad. And that’s just for starters. I use Google all day long, subscribe to multiple online publications, use Amazon regularly, have used Instacart in the past, and the list goes on.
About eight years ago, I was in downtown Manhattan and went into a Warby Parker store, an eyewear retailer. I didn’t post anything on social media about it, but I did have location services enabled on Facebook. Later that day, Facebook started showing me ads for eyewear (something it had never done before.) How and why it did that wasn’t a giant leap of understanding, and I immediately turned location services off for Facebook. But of course, this was sticking one thumb in the crumbling dam that is my data privacy. I own an Alexa, and I have an iPhone, an Apple watch, and an iPad. And that’s just for starters. I use Google all day long, subscribe to multiple online publications, use Amazon regularly, have used Instacart in the past, and the list goes on.
 In the middle 1990’s my friend from the September Group, Sam Bowles, and I were invited by the Chicago-based MacArthur Foundation to form an inter-disciplinary and international research network to study the effects of Economic Inequality, with the two of us as co-Directors. I have known Sam for nearly four decades now. He is one of the brightest economists I know, with a large vision and wide-ranging interests that are often lacking in many bright economists. His landmark 2013 book Cooperative Species with his frequent co-author Herb Gintis uses experimental data and evolutionary science to show how genetic and cultural evolution has produced a human species where large numbers make sacrifices to uphold cooperative social norms. He himself has been socially alert and active in public causes all through his life, starting from writing background papers for Martin Luther King’s 1968 Poor People’s March to most recently providing leadership in the revamping of undergraduate Economics curriculum to include upfront non-standard issues like inequality, the environment and reciprocity and altruism in human behavior, and making it available free online worldwide. He is also one of the most generous and genial people I know.
In the middle 1990’s my friend from the September Group, Sam Bowles, and I were invited by the Chicago-based MacArthur Foundation to form an inter-disciplinary and international research network to study the effects of Economic Inequality, with the two of us as co-Directors. I have known Sam for nearly four decades now. He is one of the brightest economists I know, with a large vision and wide-ranging interests that are often lacking in many bright economists. His landmark 2013 book Cooperative Species with his frequent co-author Herb Gintis uses experimental data and evolutionary science to show how genetic and cultural evolution has produced a human species where large numbers make sacrifices to uphold cooperative social norms. He himself has been socially alert and active in public causes all through his life, starting from writing background papers for Martin Luther King’s 1968 Poor People’s March to most recently providing leadership in the revamping of undergraduate Economics curriculum to include upfront non-standard issues like inequality, the environment and reciprocity and altruism in human behavior, and making it available free online worldwide. He is also one of the most generous and genial people I know.
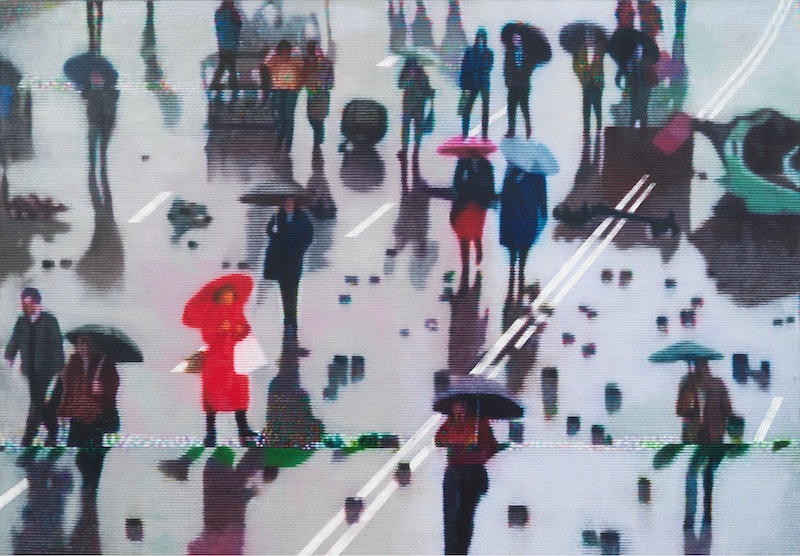



 Kon Trubkovich. The Antepenultimate End, 2019.
Kon Trubkovich. The Antepenultimate End, 2019. It seems we’re always tinkering with those eternities, not just to cherish their value or find their meaning, but to transform them into something else. Maybe that’s what creative writing ultimately is—momentary eternities arranged so that they somehow move the reader the way a perfect arrangement of musical notes might do. Reading is a compelling pastime for millions because words function as artfully selected indicators of events and images that readers will complete in their own minds, as they follow verbal guideposts for the imagination to begin to do its work.
It seems we’re always tinkering with those eternities, not just to cherish their value or find their meaning, but to transform them into something else. Maybe that’s what creative writing ultimately is—momentary eternities arranged so that they somehow move the reader the way a perfect arrangement of musical notes might do. Reading is a compelling pastime for millions because words function as artfully selected indicators of events and images that readers will complete in their own minds, as they follow verbal guideposts for the imagination to begin to do its work.
