by Michael Liss
 The Machine has me in its tentacles. Some algorithm thinks I really want to buy classical sheet music, and it is not going to be discouraged. Another (or, perhaps it is the same) insists that now is the time to invest in toner cartridges, running shoes, dress shirts, and incredibly expensive real estate.
The Machine has me in its tentacles. Some algorithm thinks I really want to buy classical sheet music, and it is not going to be discouraged. Another (or, perhaps it is the same) insists that now is the time to invest in toner cartridges, running shoes, dress shirts, and incredibly expensive real estate.
Swinging over to the relative peace and quiet of my email box, I find an extraordinary number of politicians bidding against one another for my attention. It’s a little like Christmas come early: “Now, Stringer, now, Helen, now Andrew and Adams! On, Williams on, Loree! on, Kallos and Weprin!” Every single one of them vibrates with intensity, assuring me that he or she is ready to serve me, my family, my community, and the world. Oh, and, by the way, brother, can I spare a dime?
I need my dimes right now. I’m not moving to a deluxe apartment in the sky, and I’ll buy more dress shirts when the world gets back to normal and I ditch this pandemic-related beard. So, back to Schirmer’s Selected Piano Masterpieces (Intermediate Level). I know my sin. My daughter and I were talking about the accompaniment in Schubert’s Lieder and I (foolishly, without going into a private viewing mode) did a quick search. This was more than two weeks ago, and The Machine will keep at me until it is convinced I absolutely, positively, won’t give in. Machine, if you are reading (and I know you must be), please trust me, I can’t play the piano, and I definitely can’t sing. I’d be happy to post something to YouTube to prove it. Or ask my friends to confirm—after all, you know who they are. Read more »


 Two profound horrors have plagued the world in recent times: the Covid-19 pandemic and the Trump presidency. And after years of dread, their recent decline has brought me a brief respite of peace.
Two profound horrors have plagued the world in recent times: the Covid-19 pandemic and the Trump presidency. And after years of dread, their recent decline has brought me a brief respite of peace. Whenever I discover a band that sports an accordion in the lineup, I’m ready to listen.
Whenever I discover a band that sports an accordion in the lineup, I’m ready to listen. An empty space sits where I once sat. I miss it. I miss the strangers I shared it with, and a few regulars with whom I achieved a nodding relationship. A couple of baristas I might greet and chat up. Very briefly.
An empty space sits where I once sat. I miss it. I miss the strangers I shared it with, and a few regulars with whom I achieved a nodding relationship. A couple of baristas I might greet and chat up. Very briefly.
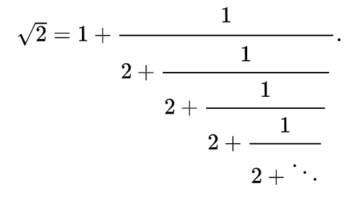

 There is a story that Clemenceau, the Prime Minister of France, was in conversation with some German representatives during the Paris peace negations in 1919 that led to the Treaty of Versailles. One of the Germans said something to the effect that in a hundred years time historians would wonder what had really been the cause of the Great War and who had been really responsible. Clemenceau, so the story goes, retorted that one thing was certain: ‘the historians will not say that Belgium invaded Germany’.
There is a story that Clemenceau, the Prime Minister of France, was in conversation with some German representatives during the Paris peace negations in 1919 that led to the Treaty of Versailles. One of the Germans said something to the effect that in a hundred years time historians would wonder what had really been the cause of the Great War and who had been really responsible. Clemenceau, so the story goes, retorted that one thing was certain: ‘the historians will not say that Belgium invaded Germany’.
 We are not where we were one year ago—or have we just returned?
We are not where we were one year ago—or have we just returned? In the part of my life when I was most actively trying to invent myself as a writer, I was working as a high school teacher and was desperately unhappy. (Notice the way that I put this: “I was working as a high school teacher,” not “I was a high school teacher”; the notion that a job defines a person still disgusts me.) In the evenings, I left work and wrote magazine pitches, not as many, I realize in retrospect, as could have brought me success, but enough to keep me talkative in the teacher’s lounge. I had the impression, back then, that a writer could make a name for himself on the basis of a single strong piece, and since my work was deeply derivative—I was, after all, inexperienced—I hatched a plan.
In the part of my life when I was most actively trying to invent myself as a writer, I was working as a high school teacher and was desperately unhappy. (Notice the way that I put this: “I was working as a high school teacher,” not “I was a high school teacher”; the notion that a job defines a person still disgusts me.) In the evenings, I left work and wrote magazine pitches, not as many, I realize in retrospect, as could have brought me success, but enough to keep me talkative in the teacher’s lounge. I had the impression, back then, that a writer could make a name for himself on the basis of a single strong piece, and since my work was deeply derivative—I was, after all, inexperienced—I hatched a plan.




 Abstract: This article, written by the Digital Philosophy Group of TU Delft is inspired by the Netflix documentary The Social Dilemma. It is not a review of the show, but rather uses it as a lead to a wide-ranging philosophical piece on the ethics of digital technologies. The underlying idea is that the documentary fails to give an impression of how deep the ethical and social problems of our digital societies in the 21st century actually are; and it does not do sufficient justice to the existing approaches to rethinking digital technologies. The article is written, we hope, in an accessible and captivating style. In the first part (“the problems”), we explain some major issues with digital technologies: why massive data collection is not only a problem for privacy but also for democracy (“nothing to hide, a lot to lose”); what kind of knowledge AI produces (“what does the Big Brother really know”) and is it okay to use this knowledge in sensitive social domains (“the risks of artificial judgement”), why we cannot cultivate digital well-being individually (“with a little help from my friends”), and how digital tech may make persons less responsible and create a “digital Nuremberg”. In the second part (“The way forward”) we outline some of the existing philosophical approaches to rethinking digital technologies: design for values, comprehensive engineering, meaningful human control, new engineering education, and a global digital culture.
Abstract: This article, written by the Digital Philosophy Group of TU Delft is inspired by the Netflix documentary The Social Dilemma. It is not a review of the show, but rather uses it as a lead to a wide-ranging philosophical piece on the ethics of digital technologies. The underlying idea is that the documentary fails to give an impression of how deep the ethical and social problems of our digital societies in the 21st century actually are; and it does not do sufficient justice to the existing approaches to rethinking digital technologies. The article is written, we hope, in an accessible and captivating style. In the first part (“the problems”), we explain some major issues with digital technologies: why massive data collection is not only a problem for privacy but also for democracy (“nothing to hide, a lot to lose”); what kind of knowledge AI produces (“what does the Big Brother really know”) and is it okay to use this knowledge in sensitive social domains (“the risks of artificial judgement”), why we cannot cultivate digital well-being individually (“with a little help from my friends”), and how digital tech may make persons less responsible and create a “digital Nuremberg”. In the second part (“The way forward”) we outline some of the existing philosophical approaches to rethinking digital technologies: design for values, comprehensive engineering, meaningful human control, new engineering education, and a global digital culture. 
 Religion has always had an uneasy relationship with money-making. A lot of religions, at least in principle, are about charity and self-improvement. Money does not directly figure in seeking either of these goals. Yet one has to contend with the stark fact that over the last 500 years or so, Europe and the United States in particular acquired wealth and enabled a rise in people’s standard of living to an extent that was unprecedented in human history. And during the same period, while religiosity in these countries varied there is no doubt, especially in Europe, that religion played a role in people’s everyday lives whose centrality would be hard to imagine today. Could the rise of religion in first Europe and then the United States somehow be connected with the rise of money and especially the free-market system that has brought not just prosperity but freedom to so many of these nations’ citizens? Benjamin Friedman who is a professor of political economy at Harvard explores this fascinating connection in his book “Religion and the Rise of Capitalism”. The book is a masterclass on understanding the improbable links between the most secular country in the world and the most economically developed one.
Religion has always had an uneasy relationship with money-making. A lot of religions, at least in principle, are about charity and self-improvement. Money does not directly figure in seeking either of these goals. Yet one has to contend with the stark fact that over the last 500 years or so, Europe and the United States in particular acquired wealth and enabled a rise in people’s standard of living to an extent that was unprecedented in human history. And during the same period, while religiosity in these countries varied there is no doubt, especially in Europe, that religion played a role in people’s everyday lives whose centrality would be hard to imagine today. Could the rise of religion in first Europe and then the United States somehow be connected with the rise of money and especially the free-market system that has brought not just prosperity but freedom to so many of these nations’ citizens? Benjamin Friedman who is a professor of political economy at Harvard explores this fascinating connection in his book “Religion and the Rise of Capitalism”. The book is a masterclass on understanding the improbable links between the most secular country in the world and the most economically developed one.