At the train station in Bruneck, South Tyrol, looking east.
ChatGPT is a miracle of rare device. Here’s how I’m thinking about it.
ChatGPT is based on the same underlying computational architecture as GPT-3, which was released in the summer of 2020. That’s when I started  reading “GPT for Dummies” articles. Some were more useful than others, but none of them gave me what I wanted. So I started poking around in the technical literature. I picked up a thing or two, enough to issue a working paper, GPT-3: Waterloo or Rubicon? Here be Dragons. [GPT = Generative Pretrained Transformer]
reading “GPT for Dummies” articles. Some were more useful than others, but none of them gave me what I wanted. So I started poking around in the technical literature. I picked up a thing or two, enough to issue a working paper, GPT-3: Waterloo or Rubicon? Here be Dragons. [GPT = Generative Pretrained Transformer]
Then three months ago OpenAI let ChatGPT loose on the web. WOOSH! The sky’s on fire, the ice caps are melting, the oceans are rising, and baby needs a new pair of shoes. Badly.
I started all over, reading those “Dummy” articles and poking around in the technical literature. But, and this is important, I also spent an enormous time playing around with ChatGPT and blogging about it, writing almost 70 blog posts and four working papers. That taught me a great deal. If only I knew how to read the tea leaves.
All that time and effort, and I still don’t know what’s going on. “This is not good,” says I to myself, “not good at all. If no one’s going to tell me how this puppy works, I’m just going to have to figure it out for myself.”
That’s what I’m doing now. I’m going to write until the last sentence is finished. Then I’m going to send the article off to Abbas, go for a walk, eat dinner, go to bed, wake up Monday morning, and see if it makes sense. There’s a reasonable chance that it will, in which case I’ll feel satisfied for a day and then start all over again, revising my ideas, coming up with new ones, getting frustrated, laughing myself silly, and in general having a grand old time making sense of these strange new machines, these artificial intelligences, these chatbots, these miracles of rare device. Read more »
Is it finally time to care about the metaverse?
by Sarah Firisen
 Google the phrase “is it time to care about the metaverse?” and there are a wealth of articles, mostly claiming that the answer is yes! Are they right?
Google the phrase “is it time to care about the metaverse?” and there are a wealth of articles, mostly claiming that the answer is yes! Are they right?
In the next six months, I’m going to start on a home-building project. While I’ve done home renovations before, building a house from the ground up is a new and scary experience. I’m not a good visualizer; during the home renovation project, I couldn’t look at a bathroom tile and imagine what an entire bathroom would look like using that design. Given this, it was great that our architect used 3D software that enabled us to “walk through” the house plan. But how much more effective would it be if I could really “live” in a virtual copy of the house for a while? If there was a digital twin of the house design in the metaverse, my avatar could inhabit it for a while and get a real feel for whether that kitchen is big enough and whether the tile for the floor is a bit much or just right.
As I’ve written before, my ex-husband and I were very into Second Life about 16 years ago. He was a Senator in the ROMA sim, while I used my software development skills to learn the language for building and scripting to become a fashion designer. Dabbling in virtual architecture and construction, I built my own stores, and I also built my ex-husband a villa on a plot of virtual land he bought in the ROMA sim. Way back then, virtual worlds were mostly escapes from the real world. There was the occasional brand that set up a Second Life store, but they never really seemed to know what to do with the technology. Read more »
Monday, February 20, 2023
Growing up with chatGPT (and some lessons from Harry Truman)
by Ashutosh Jogalekar
 Like most people, I have been baffled, mystified, unimpressed and fascinated by chatGPT, the new AI engine that has taken the world by storm over the last few months. I cannot remember any time that a new AI development got so much attention, led to so much mockery and caused so much alarm. As the writer Ted Chiang wrote, chatGPT – and what would inevitably be its subsequent versions and spinoffs – represent a blurry, lossy, version of the Internet, containing all the unique strengths and gory flaws of that medium. There is little doubt that chatGPT is not intelligent the way humans are based on the complete lack of nuance and and elementary factual errors it still makes as it cobbles together patterns from data without high-level understanding. But there is also no doubt that it creates an illusion of human intelligence that is beguiling, endlessly fascinating, addictive and frankly disturbing and potentially dangerous. Dangerous not because the machine is intelligent but because humans will no longer be able to distinguish between intelligence and the illusion of intelligence.
Like most people, I have been baffled, mystified, unimpressed and fascinated by chatGPT, the new AI engine that has taken the world by storm over the last few months. I cannot remember any time that a new AI development got so much attention, led to so much mockery and caused so much alarm. As the writer Ted Chiang wrote, chatGPT – and what would inevitably be its subsequent versions and spinoffs – represent a blurry, lossy, version of the Internet, containing all the unique strengths and gory flaws of that medium. There is little doubt that chatGPT is not intelligent the way humans are based on the complete lack of nuance and and elementary factual errors it still makes as it cobbles together patterns from data without high-level understanding. But there is also no doubt that it creates an illusion of human intelligence that is beguiling, endlessly fascinating, addictive and frankly disturbing and potentially dangerous. Dangerous not because the machine is intelligent but because humans will no longer be able to distinguish between intelligence and the illusion of intelligence.
Some people think that AI engines like chatGPT herald a global threat of artificial general intelligence (AGI) because of their unprecedented ability to generate misinformation and the illusion of intelligence. AGI is AI that escapes from its narrowly defined applications to become all-encompassing. We should grapple with the challenges that AGI would pose, even if the probability of a true AGI remains slim. But as the parent of a 2-year-old, I feel an even more urgent question looming over the horizon: what are chatGPT or AGI going to do to our children’s generation? How can we try to ensure that they can handle the challenges posed by these unprecedented technological developments?
We don’t know how to answer this question yet since the impact of technology on society is inherently unpredictable – who would have predicted that social media would drive us apart by cocooning us in our echo chambers instead of triggering a global open exchange of ideas – but some lessons from history combined with old-fashioned, boring common sense might help us make sense of the brave new AI world that chatGPT represents. When the new becomes unpredictable and risky, the old-fashioned and boring may not look too bad. Read more »
The Joy of Abstraction
by Jonathan Kujawa

On “The Joy of Abstraction” by Eugenia Cheng.
Category theory has variously been called “abstract nonsense,” “diagram chasing,” or the “mathematics of mathematics.” Some mathematicians find it a useful language, some a crucial tool for developing insights and obtaining new results, and more than a few have no use for it at all. I am currently teaching one of our first-year graduate courses. Because of the topic and my tastes, the students have seen a smattering of category theory. Another professor might skip that point of view entirely. This is all to say that even serious students of mathematics are unlikely to see category theory until graduate school.
Eugenia Cheng wrote a Ph.D. thesis entitled “Higher-Dimensional Category Theory: Opetopic Foundations”, has written more than a dozen research papers on all sorts of serious categorical topics, and was formerly a tenured professor at the University of Sheffield, UK. A decade or so ago, Dr. Cheng decided to give up the traditional academic track and put her energy into bringing mathematics to a broad audience. Dr. Cheng is now a Scientist in Residence at the School of the Art Institute of Chicago, a writer of popular math books, a frequent guest on TV shows, and an all-around evangelizer for thinking about math in novel and humanistic ways.
Eugenia Cheng recently wrote a most peculiar book. It is an introduction to category theory for people whose math education might have stopped with high school. With such modest prerequisites it is remarkable that by the end of the book you are wrestling with advanced topics that my first-year graduate students still haven’t seen! It sounds ambitious and even a little nuts. Dr. Cheng is about the only person in the world with the very particular set of skills needed to write such a book. Read more »
Monday Poem
Fugitive
big brown bison walks the white line
of a two-lane, black eyes scanning for a sign,
regarding asphalt he wonders
what happened to the grass
how did this black ribbon come to bisect
my meadow between talus and hundred-foot pines
and where are the columbine?
he asks no one in particular because
not even the alpha male in a herd would know
as a car crawls slowly up behind
capturing the remains of a wilderness,
and smart phones gripped in the hands of small
homos sapiens click & snap at the ends of arms
thrust through windows catching
an outlaw bison who broke from a farm,
whose humped shade steps like a rope-walker
down the white line’s length wondering
where the stillness went
where are the laurel and clover?
what are these beasts
that glide like murmuring ghosts along
this scar in my pasture clicking like crickets
trailing a burnt Cenozoic scent?
Jim Culleny
© Oct 31, 2010
Is the Simulation Argument an Improvement on the Dream Argument?
by Tim Sommers

“Suddenly he woke up and there he was, solid and unmistakable Zhuang Zhou. But he didn’t know if he was Zhuang Zhou who had dreamt he was a butterfly, or a butterfly dreaming that he was Zhuang Zhou.” — Zhuangzi (translation by Burton Watson)
“We are almost certainly living in a computer simulation.” – Nick Bostrom*
Is the hypothesis that we live in a computer simulation an improvement, in some way, on the classic skeptical argument that life is but a dream? The dream argument seems to show that life could be a dream. Some claim that the simulation argument shows that not only is it possible that we live in a computer simulation, but that we almost certainly do live in a simulation.
I’ll argue that the simulation argument does not make it any more likely than the dream argument does that this is not reality. Furthermore, the simulation argument might even be worse (as a skeptical argument) in one way. If I am dreaming, there is not just another world, but, in some sense, another me, out there beyond the dream. But if I am a being that only exists in a simulation, it follows that there is no other me out there – and challenges the very idea that this scenario is really “skeptical,” in the same way, as the dream argument.
From Zhuangzi to Descartes to The Matrix, people have worried and wondered over global epistemological skeptical scenarios like these. Let’s call them GESSes.
They are global because they cover all knowledge from our senses, they are epistemological because they raise the question of what we can know, skeptical because they answer, ‘we can’t know anything,’ and scenarios in the sense that they offer a story about why our senses systemically fail to make contact with reality.
So, how do you know whether we are currently being deceived about everything around us by an evil demon or dreaming it all, as Descartes says, or if we live in some kind of simulation? Read more »
Lost in Vocalization: Adventures in Listening
by Brooks Riley
 1. In nature the act of listening is primarily a survival strategy. More intense than hearing, listening is a proactive tool, affording animals a skill with which to detect predators nearby (defense mechanism), but also for predators to detect the presence and location of prey (offense mechanism).
1. In nature the act of listening is primarily a survival strategy. More intense than hearing, listening is a proactive tool, affording animals a skill with which to detect predators nearby (defense mechanism), but also for predators to detect the presence and location of prey (offense mechanism).
My favorite listener of all time (FLOAT) is a predator, the magnificent great grey owl (Strix nebulosa), whose gorgeous fifty-shades-of-grey plumage serves as a soundproofing puffer coat over a surprisingly diminutive body, making the creature both the world’s largest owl in length and one of its lightest in weight. That sweet funny face serves a purpose far more practical than irresistible charm. What happens up there in the frozen arctic latitudes where the great grey owl lives is a match between two well-equipped, cunning adversaries—both good listeners—the owl high up in a tree and the vole deep under a blanket of snow.
If evolution were music, this owl’s hunting technique would be one of nature’s greatest hits, a masterpiece of carefully designed and calibrated physical traits functioning in sync like an orchestra—to enable the owl to hear, locate and capture the unseen vole under two feet of snow from up to a hundred feet away. Read more »
Perceptions
Fire Alarm
by Chris Horner

The alarm bells are deafening, and the evidence is irrefutable: greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuel burning and deforestation are choking our planet and putting billions of people at immediate risk.…[…] We are sleepwalking to climate catastrophe. […] It is a a “code red for humanity. —António Guterres, United Nations Secretary General.
The world is moving ever closer to catastrophic climate crisis and yet the economies of the world are still going for growth, while the major fossil fuel extractors row back on their pledges to switch to renewables instead of dragging out yet more oil and gas. Automobiles are everywhere; planes fly across the globe to all destinations. And the weather gets more and more extreme: flood, fire, hurricane and drought. And still we continue down the mad path to an unliveable planet.
A catastrophe is developing, not in the future, nor in some distant scenario but right now. And it is clear that far too little, too late, is being done in response. What is less obvious is why this should be so. The reasons for the slowness and inadequacy of the measures taken can, of course, be identified as lying in the kind of political log jams that characterise the present time, along with bureaucratic inertia, weak leadership and the influence of special interest groups in delaying and obfuscating. Yet if we really are on the edge of an abyss, as Guitterez says, one might expect more to be happening.
If nothing less than war time measures need to be taken, why are we not taking them? Read more »
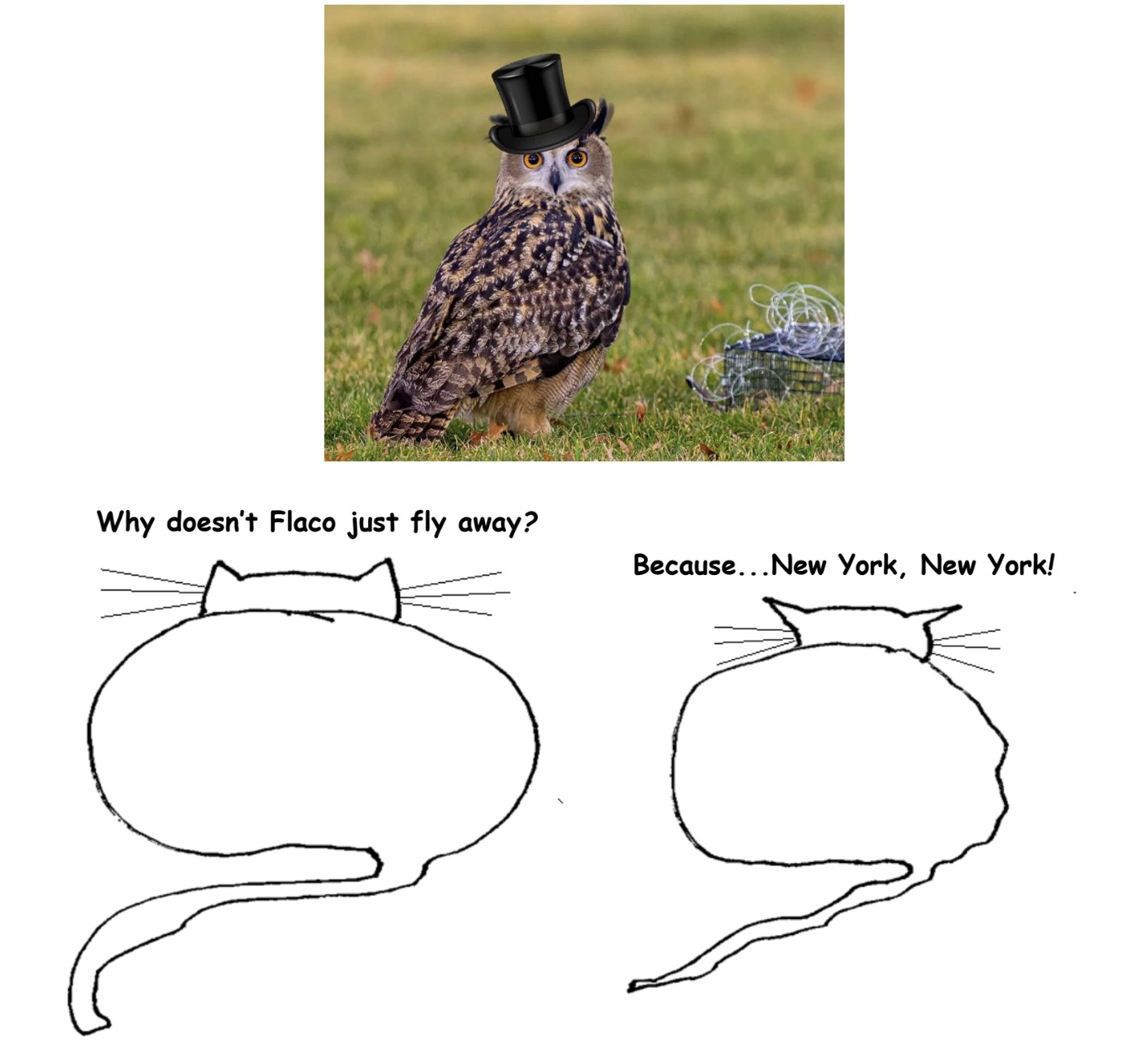
Catspeak
by Brooks Riley

A Bedroom Autopsy
by Ethan Seavey
 A metal bucket with a snowman on it; a plastic faux-neon Christmas tree; a letter from Alexandra; an unsent letter to Alexandra; a small statuette of a world traveler missing his little plastic map; a snow globe showcasing a large white skull, with black sand floating around it.
A metal bucket with a snowman on it; a plastic faux-neon Christmas tree; a letter from Alexandra; an unsent letter to Alexandra; a small statuette of a world traveler missing his little plastic map; a snow globe showcasing a large white skull, with black sand floating around it.
When I was much younger, there was this vague idea that my death (however randomly it may come about) would result in the total autopsy of my bedroom, which would allow loved ones and biographers the opportunity to analyze my psyche. I planned for them to find my journals and publish my stories posthumously; and it was nice to think about, because I would do none of the work of publishing myself and I would receive all the fame from the grave. For most of the stories I was writing, I would have been similarly satisfied if a thief had stolen them from me to publish under my name while I was still breathing, but as a little boy I had secrets in abundance. It would be absolutely asinine of myself to have secrets lying around my room, ready to be discovered. At least, not without making them work for it first.
One such object is a small book with the title 99. It’s a book you might pick up as a gift for someone you might not know very well. It was given to me by some friends who knew me extremely well and who knew I liked pretty (but practically unreadable) books to leave around as decoration. This book had a pure white cover. Its pages contained 99 “activities” to “do” when you’re bored. Both of these words are in quotes because they wrongly imply that you will be doing something. Some examples: sign up for a class (an activity of waiting which is not immediately invigorating enough to satisfy my boredom); try out an instrument you’ve never played before (an activity I will immediately become discouraged in); set up your single friend with your other single friend (an activity that would not service my own boredom but other people’s).
The one that matters here, though, was a page labeled “flip something familiar upside down.” If you open to the page where the black ribbon sits comfortably, near the middle of the book, you’ll see that the ribbon is fixed with a large sewing pin. Certainly the quest-taker would take notice of this page in particular and realize that it is a clue. Read more »
Monday Photo
A Piece of “A Piece of Chalk”
by Eric Bies
 I liked to play with chalk when I was little. Little kids did then. As far as I can tell they still do now. I walk and jog and drive around town for every other reason. Inevitably, I end up spotting many (maybe not as many, but a good many) of them doing as I did: crouching between buildings, hunkering down on driveways and sidewalks to draw mommies and daddies and monsters; moons and suns; circles and squares. One minute they’re sketching their darling doggy; the next, they’re dreaming up cross sections of skyscrapers to hop across their faces. A very little one down the block, crab-walking with a piece of pink clasped in his left hand, practices divination with squiggles like the entrails of a bird. Recently, the rain has washed it all away, but only for the moment.
I liked to play with chalk when I was little. Little kids did then. As far as I can tell they still do now. I walk and jog and drive around town for every other reason. Inevitably, I end up spotting many (maybe not as many, but a good many) of them doing as I did: crouching between buildings, hunkering down on driveways and sidewalks to draw mommies and daddies and monsters; moons and suns; circles and squares. One minute they’re sketching their darling doggy; the next, they’re dreaming up cross sections of skyscrapers to hop across their faces. A very little one down the block, crab-walking with a piece of pink clasped in his left hand, practices divination with squiggles like the entrails of a bird. Recently, the rain has washed it all away, but only for the moment.
The Englishman G. K. Chesterton, one of those writers who wrote a lot of everything—novels about men with names like Thursday and Innocent Smith, biographies of Francis and Aquinas, a long poem about the Battle of Lepanto, detective stories Borges loved—also liked to play with chalk.
In “A Piece of Chalk,” one of many memorable articles written for the Daily News in the first years of the last century, Chesterton recounts a morning outing while on vacation. Read more »
Monday, February 13, 2023
Some Comments on Writing Popular Mathematics
by John Allen Paulos
Intelligibility or precision: to combine the two is impossible. ―Bertrand Russell.
Please forgive the long letter; I didn’t have time to write a short one. ―Blaise Pascal

I have always resonated with the two quotes above and believe they’re particularly germane to writing popular mathematics. Let me start with Russell. If his remark is taken literally, I would disagree with it, but if we take it merely as pointing out the often inevitable trade-off between precision and intelligibility, I find it rather profound. In my books I’ve certainly tried to be both precise and intelligible and hope that for the most part I have succeeded, as have so many other popular author of mathematics. The fact remains that combining the two is often a difficult task that at times depends on extra-mathematical understandings.
Take, for example, the notion of a continuous function in mathematics. Perhaps as a first approximation we might say that a function is continuous of we can graph it without lifting our pencil off the page. No breaks. This is intelligible, but is hardly precise and is, in fact, not what we mean by a continuous function. As generations of calculus students have understood (or misunderstood), the standard definition is simply not intuitive, involving as it does a complex statement involving the function in question and deltas and epsilons, Greek letters measuring distances along x- and y-axes. Unfortunately, immediately insisting on precision is a good way to discourage students from taking calculus. Read more »
Ted Bundies I Have Known
by Deanna K. Kreisel [Doctor Waffle Blog]

I really don’t understand those podcasts where young women with their whole lives ahead of them spend an hour each week obsessing over serial killers. There are between one and 87 of these shows—I don’t know their names, I’ve never listened to them, and frankly I don’t want to know more than I already do. I am resisting Googling. But I’m aware of their existence because middle-aged women with half their lives ahead of them keep urging me to listen. The last time this happened, I was at a dinner party where I was regaled with a description of a podcast’s description of the Golden State Killer (do not Google!) over pasta carbonara and a nice Soave Classico. I spent the next few months obsessively checking and re-checking the door and window locks every night, then huddling under the covers in fear as I waited for sleep. I’m pretty sure there’s still a knife under the mattress “just in case.”
To be clear: I understand the pleasure of these shows. In fact, I understand it all too well—which is why I have no desire to start listening. I too have found myself crawling out of a Wikipedia rabbit hole of an evening, blinking in confusion and wondering why I just spent two hours of my time on earth compulsively reading about the exploits of Robert Pickton (do not Google!). What I don’t understand is how people can wallow in gruesome descriptions of psychopathy, gleefully taking in all the grisly details of murders, rapes, cannibalism, and the rest of it, and then calmly go about their daily lives. I’m not sure if my problem is mild undiagnosed OCD or just a hyper-sensitive nervous system, but once I get those images in my head I cannot get them out. Even the movie Titanic was too much for me—I left the theater shaking and sick with crying, watching in amazement as people around me in the lobby chatted about where to go for dinner. Avoiding images and descriptions of murderous mayhem is a discipline I follow that allows me to continue functioning as a moderately productive member of society.
But I think there’s something else going on with these serial killers, at least for me. Read more »
Monday Poem
Now Only Knocks Now
Add 30 seconds to anytime,
what’s that interval?
Hell, double it
what’s that?
Have you ever had a day that lasts three
or one that goes so fast it’s past instantly?
Are those durations short or long, if
hours mean anything?
Subtract five hours from anytime
do we really think we’ve minced minutes,
as we tick them off are they really not there?
There’s a continuum called now
outside of which is guesswork
because our instruments only work here,
slice it anyway you want
it remains……… still ………. whole
our clocks do not
affect it.
Now is never what it was before
because things change
and will change again, now,
not yesterday or tomorrow
it only happens now
now is the only thing we have to work with
now only knocks now
by Jim Culleny
9/5/14
Artificial Intelligence [sic: Machine Learning] and The Best Game in Town; Or How Some Philosophers, and the BBS, Missed a Step
by David J. Lobina
Where was I? Last month I made the point that Artificial Intelligence (AI) – or, more appropriately, Machine Learning and Deep Learning, the actual paradigms driving the current hype in AI – is doomed to be forever inanimate (i.e., lack sentience) and dumb (i.e., not smart in the sense that humans can be said to be “smart”; maybe “Elon Musk” smart, though).[i] And I did so by highlighting two features of Machine Learning that are relevant to any discussion of these issues: that the processes involved in building the relevant mathematical models are underlain by the wrong kind of physical substrate for sentience; and that these processes basically calculate correlations between inputs and outputs – the patterns an algorithm finds within the dataset it is fed – and these are not the right sort of processing mechanisms for (human) sapience.
These were technical points, in a way, and as such their import need not be very extensive. In fact, last time around I also claimed that the whole question of whether AI can be sentient or sapient was probably moot to begin with. After all, when we talk about AI [sic] these days, what we are really talking about is, on the one hand, some (mathematical) models of the statistical distributions of various kinds of data (tokens, words, images, what have you), and on the other, and much more commonly, the computer programs that we actually use to interact with the models – for instance, conversational agents such as ChatGPT, which accesses a Large Language Model (LLM) in order to respond to the prompts of a given user. From the point of view of cognition, however, neither the representations (or symbols) nor the processes involved in any of the constructs AI practitioners usually mention – models, programs, algorithms – bear much resemblance to any of the properties we know about (human) cognition – or, indeed, about the brain, despite claims that the neural networks of Machine/Deep Learning mimic brain processes. Read more »
Now That The End Is Here
by Mike Bendzela

While changing keys during a recent old time jam session, a friend asked for my thoughts about this new ChatGPT thing, seeing as I teach writing to college students and the fear is that this text-generating gadget will disrupt how such courses are taught. I had to answer that I did not have any thoughts about it, because I was assured early on, AI is coming and there is absolutely nothing you can do about it! Thus, safely relieved of the burden of having to dwell on the inevitable, I have chosen to ignore it instead. As a famous Republican once said, “Why should I waste my beautiful mind on something like that?” Besides, I am an adjunct and not paid to worry about pedagogy. I can worry about more important things, such as the low tire pressure light that will not go off on my dashboard. How to deal with techno tyranny with aplomb is something I can put off. I will be retiring in a few short years anyhow.
This friend* who asked me about ChatGPT technology seemed about as ignorant in it as I am: “Do you know how it works?”
He was trying to tune his banjo. This could take a while, and I was afraid I would have to . . . chat about ChatGPT in the meantime. Read more »
Catspeak
by Brooks Riley
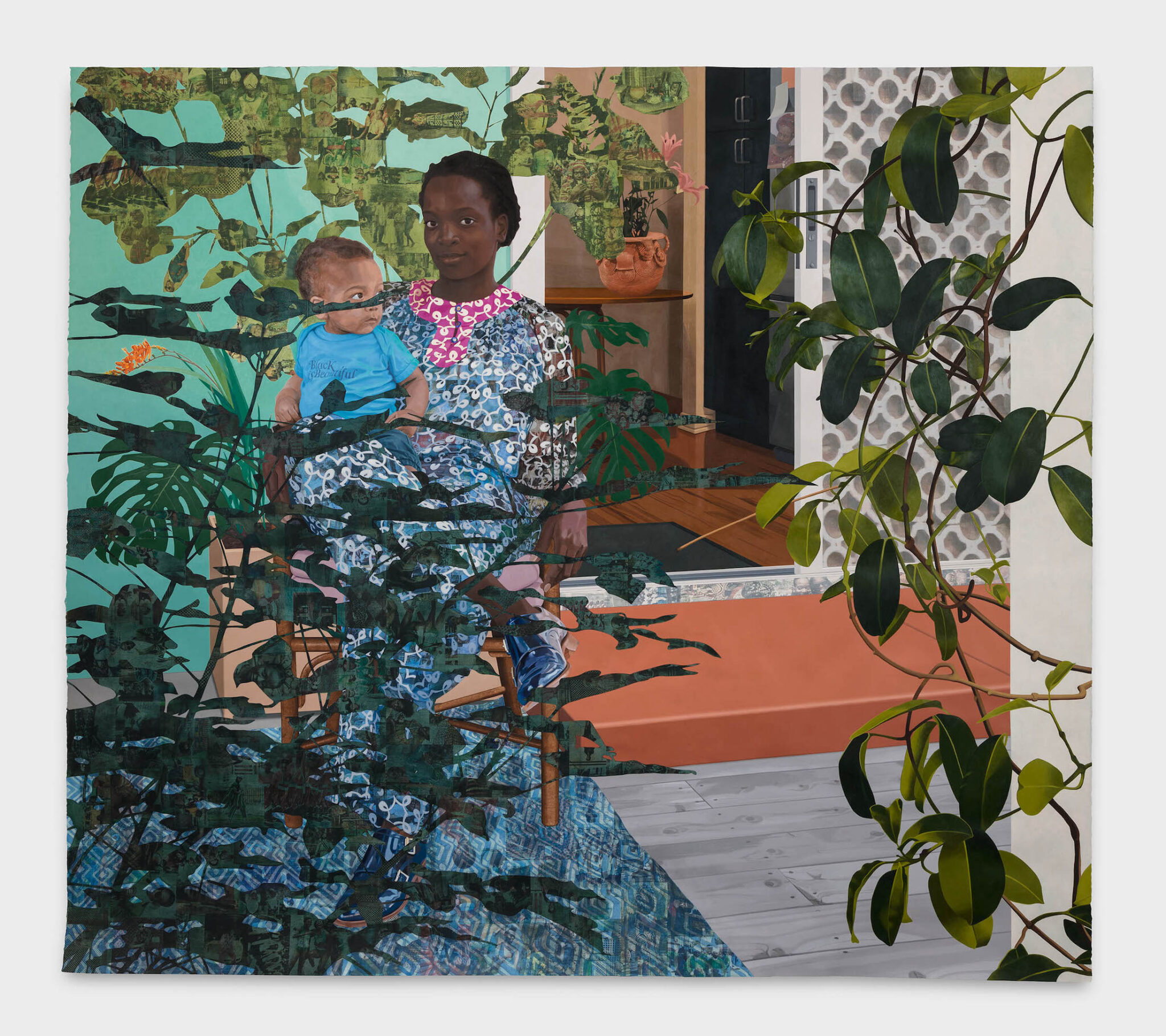


 Njideka Akunyili Crosby. Still You Bloom in This Land of No Gardens, 2021.
Njideka Akunyili Crosby. Still You Bloom in This Land of No Gardens, 2021.