by Akim Reinhardt
 There’s a lot we can learn about today’s America by observing the Mormon Church.
There’s a lot we can learn about today’s America by observing the Mormon Church.
Last month the Church of Latter Day Saints, as its officially known, issued a strong, positive directive to its 16.5 million members. Vaccines had been proven safe and effective, it reminded them. And please wear a mask in public gatherings, it implored them. The statement’s language was uplifting and unifying: “We can win this war if everyone will follow the wise and thoughtful recommendations of medical experts and government leaders,”
It led to a backlash.
Despite this urging from the LDS’ top ranks, nearly a fifth of church members say they will not get vaccinated. Another 15% are hesitant. Some anti-vax and anti-mask members complain the church is restricting their freedoms. In response, some Mormon vaccination and mask supporters are accusing the mask and vaccine holdouts of apostasy. Even bishops (regional church leaders) are divided. In one Idaho church, bishops stood in front of their congregation unmasked to read the official proclamation encouraging masks.
The Church of Latter Day Saints has one of the most loyal constituencies of any large social organization in America. There is no unanimity of course; small splinter groups have always existed, and as with any religion, some people are always distancing themselves from the church or leaving it altogether. Nonetheless, for two centuries practicing Mormons have been bound together by faith; a history of persecution; geography; relative cultural homogeneity here in the U.S.; a rigorous schedule of activities in the home, at church, and elsewhere, all designed to reinforce membership and belonging; and by a highly organized, hierarchical, patriarchal, and doctrinaire leadership that has wielded tremendous influence over its loyal followers, who typically follow specific dictates such as no alcohol, coffee, or tea.
So if even the Mormon Church is having trouble getting its truehearted constituents to follow simple health directives overwhelmingly backed by science and designed for their own benefit, then you know this about something much bigger than masks and shots. This is about what has happened in America during the last four decades. Read more »




 I was there when they first went up. From my south-facing bedroom on Morton Street in the village, I watched them grow, floor by floor, to a height unimaginable for that time. When they were finished, I began to measure their height against their distance from my bedroom. If they fell over, would they reach me? Not only was I ignorant of structural engineering, I never gave a thought to what would happen to the people inside if they did fall over. Years later I would learn that they didn’t fall over, they fell down. This time my thoughts were with those people inside.
I was there when they first went up. From my south-facing bedroom on Morton Street in the village, I watched them grow, floor by floor, to a height unimaginable for that time. When they were finished, I began to measure their height against their distance from my bedroom. If they fell over, would they reach me? Not only was I ignorant of structural engineering, I never gave a thought to what would happen to the people inside if they did fall over. Years later I would learn that they didn’t fall over, they fell down. This time my thoughts were with those people inside. Sachin Chaudhuri, who lived in Bombay, came to know, I think from Binod Chaudhuri, about my teenage forays into writing political pieces, and he asked me to share them with him, and sent back detailed (handwritten) comments on them. A little later he started encouraging me to write for EW (copies of which he sent me every week). But I was too diffident; I was a neophyte Economics student, and I knew of EW’s sky-high reputation (Prime Minister Nehru had a standing instruction to his assistants that as soon as the weekly comes out it should immediately be at his desk). Many years later in my MIT days when I met Paul Samuelson, the great American economist, he once told me that he thought EW was a unique magazine, having topical columns on every week’s events and at the same time publishing specialized analytical articles, some quite technical. I found out that he, like many stalwart economists and other social scientists in the world at that time, had himself written for EW—this was partly a tribute to the magnetic personality of Sachin Chaudhuri which attracted some of the finest minds and created a rich intellectual aura around the magazine.
Sachin Chaudhuri, who lived in Bombay, came to know, I think from Binod Chaudhuri, about my teenage forays into writing political pieces, and he asked me to share them with him, and sent back detailed (handwritten) comments on them. A little later he started encouraging me to write for EW (copies of which he sent me every week). But I was too diffident; I was a neophyte Economics student, and I knew of EW’s sky-high reputation (Prime Minister Nehru had a standing instruction to his assistants that as soon as the weekly comes out it should immediately be at his desk). Many years later in my MIT days when I met Paul Samuelson, the great American economist, he once told me that he thought EW was a unique magazine, having topical columns on every week’s events and at the same time publishing specialized analytical articles, some quite technical. I found out that he, like many stalwart economists and other social scientists in the world at that time, had himself written for EW—this was partly a tribute to the magnetic personality of Sachin Chaudhuri which attracted some of the finest minds and created a rich intellectual aura around the magazine.
 In these dying days of summer, as I steel myself for the onslaught of an uncertain term ahead, I’ve been reading
In these dying days of summer, as I steel myself for the onslaught of an uncertain term ahead, I’ve been reading  The Italian author Sandro Veronesi’s latest novel, his ninth, The Hummingbird, is a clever book that offers the reader both literary pleasure and serious thought. The novel is essentially a family saga, and like all family histories and stories it has a complexity of interpersonal relationships and human emotions all woven into the story. It sounds so typical of life and the reader might begin to think that the novel is a family saga that could be tedious, but that is far from the truth. Veronesi has skilfully used structure to fracture any complacency or perception of the characters and the story, and his novel is a superb piece of skilled writing with unexpected twists and turns.
The Italian author Sandro Veronesi’s latest novel, his ninth, The Hummingbird, is a clever book that offers the reader both literary pleasure and serious thought. The novel is essentially a family saga, and like all family histories and stories it has a complexity of interpersonal relationships and human emotions all woven into the story. It sounds so typical of life and the reader might begin to think that the novel is a family saga that could be tedious, but that is far from the truth. Veronesi has skilfully used structure to fracture any complacency or perception of the characters and the story, and his novel is a superb piece of skilled writing with unexpected twists and turns.
 Andrea Chung. From the series Vex, 2020.
Andrea Chung. From the series Vex, 2020.
 The day I began writing this essay, Portland Oregon braced for yet another round of uncharacteristic heat. Over several months of preparation, as I had been reading and pondering Kim Stanley Robinson’s big, detailed, hyper-realistic science-fiction book The Ministry for the Future, our normally cool northwest town had found itself repeatedly facing drought and high temperatures. Now we were about to be trapped under a “heat dome” of 115 degrees Fahrenheit (46° C) – Las Vegas temperatures, Abu-Dhabi temperatures – for days on end.
The day I began writing this essay, Portland Oregon braced for yet another round of uncharacteristic heat. Over several months of preparation, as I had been reading and pondering Kim Stanley Robinson’s big, detailed, hyper-realistic science-fiction book The Ministry for the Future, our normally cool northwest town had found itself repeatedly facing drought and high temperatures. Now we were about to be trapped under a “heat dome” of 115 degrees Fahrenheit (46° C) – Las Vegas temperatures, Abu-Dhabi temperatures – for days on end.

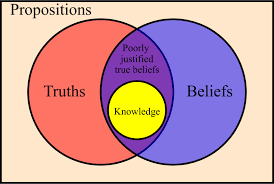
 Theories that specify which properties are essential for an object to be a work of art are perilous. The nature of art is a moving target and its social function changes over time. But if we’re trying to capture what art has become over the past 150 years within the art institutions of Europe and the United States, we must make room for the central role of creativity and originality. Objects worthy of the honorific “art” are distinct from objects unsuccessfully aspiring to be art by the degree of creativity or originality on display. (I am understanding “art” as a normative concept here.)
Theories that specify which properties are essential for an object to be a work of art are perilous. The nature of art is a moving target and its social function changes over time. But if we’re trying to capture what art has become over the past 150 years within the art institutions of Europe and the United States, we must make room for the central role of creativity and originality. Objects worthy of the honorific “art” are distinct from objects unsuccessfully aspiring to be art by the degree of creativity or originality on display. (I am understanding “art” as a normative concept here.)