by Joseph Shieber
The traditional assumption in the United States has been that each person is individually responsible for their own health care. In other words, the US has a system in which the wealthy are able to afford more or better care (with the understanding that more care does not always lead to better health outcomes!), and the poor are able to afford less or no care.
There is something intuitively appealing about the idea that you should be rewarded in relation to the work that you’ve done or the results that you’ve achieved. It’s the basis of the well-known children’s fable, “The Little Red Hen”, in which the hen tries to get her fellow barnyard animals (dog, goose, etc.) to help her sow the seeds, reap the wheat, grind the grain, and bake the bread. Since none of the other animals are willing to help, when the bread is done the hen eats it all herself. In fact, the fable is so intuitively plausible that folksy free-market hero Ronald Reagan — pre-Presidency — used it himself.
The idea behind “The Little Red Hen” is so intuitively appealing that it’s not just limited to free market views. Even socialist thinkers from pre-Marxists like Ricardian socialists to later theorists like Lenin and Trotsky embraced the formula, “To each according to his works”, rather than Marx’s “To each according to his needs”.
Indeed, in a very useful paper, Luc Bovens and Adrien Lutz trace back the dual threads of “to each according to his works” and “to each according to his needs” to the New Testament. So, for example, in Romans 2:6, we see that God “will render to each one according to his works” (compare Matthew 16:27, 1 Corinthians 3:8).
In contrast, in Acts 4:35, we read that “There was not a needy person among them, for as many as were owners of lands or houses sold them and brought the proceeds of what was sold … and it was distributed to each as any had need” (compare Acts 2:45).
The deep textual roots of these two rival maxims suggests that each exerts a strong intuitive pull — though perhaps not equally strong to everyone.
Public health emergencies, however, reveal the fragility inherent in the motto of “to each according to his works” when it comes to health systems. Everyone’s health is interconnected, and that the ability of each individual to fight infection depends in part on everyone else’s having done their part. Read more »

 Socrates, snub-nosed, wall-eyed, paunchy, squat,
Socrates, snub-nosed, wall-eyed, paunchy, squat,


 Over the past week, Pakistan has been consumed by the Aurat (Women’s) March, which was held today, March 8, International Women’s Day, in all the major cities of the country. The march’s aim is to highlight the continued discrimination, inequality, and harassment suffered by women. There are some people against it who argue that the march should not be allowed, but the Islamabad High Court has rejected the petition that asked for its cancellation. So the march happened.
Over the past week, Pakistan has been consumed by the Aurat (Women’s) March, which was held today, March 8, International Women’s Day, in all the major cities of the country. The march’s aim is to highlight the continued discrimination, inequality, and harassment suffered by women. There are some people against it who argue that the march should not be allowed, but the Islamabad High Court has rejected the petition that asked for its cancellation. So the march happened. During a recent visit to Paris, I squeezed through the crowded bookshelves of the famous Shakespeare and Company bookstore, a stone’s throw from Notre Dame, whose charred heights sat masked in scaffolding just across the Seine. It has become something of a Parisian tourist hotspot, mostly because of its association with our favorite Modernist expat writers, immortalized and gilded in a cosmopolitan, angsty, and glamorous mystique through the canonization of their works and, some might argue, the award-winning Woody Allen film Midnight in Paris.
During a recent visit to Paris, I squeezed through the crowded bookshelves of the famous Shakespeare and Company bookstore, a stone’s throw from Notre Dame, whose charred heights sat masked in scaffolding just across the Seine. It has become something of a Parisian tourist hotspot, mostly because of its association with our favorite Modernist expat writers, immortalized and gilded in a cosmopolitan, angsty, and glamorous mystique through the canonization of their works and, some might argue, the award-winning Woody Allen film Midnight in Paris. 

 Research by linguists
Research by linguists
 There was this one moment. A sunny June day in Nebraska. No one was around. I dribbled the basketball over the warm blacktop, moving towards a modest hoop erected at the end of a Lutheran church parking lot. I picked up my dribble, took two steps, sprung lightly from my left foot, up and forward, my right arm extending as my hand gracefully served the ball to the white backboard. Its upward angle peaked, bounced softly, and descended back through the netless hoop.
There was this one moment. A sunny June day in Nebraska. No one was around. I dribbled the basketball over the warm blacktop, moving towards a modest hoop erected at the end of a Lutheran church parking lot. I picked up my dribble, took two steps, sprung lightly from my left foot, up and forward, my right arm extending as my hand gracefully served the ball to the white backboard. Its upward angle peaked, bounced softly, and descended back through the netless hoop.
 What is commonsense to most people who received a K-12 public education in the United States is that every formal system of state schooling throughout the modern world is designed to educate its students to develop, what Charles Lemert calls “sociologically competencies” within whatever ideological system is dominating at the time of their schooling. People correctly assume that children going to school during the Weimar Republic, for example, were educated to function competently within that ideological system. Children who were in school during the reign of Chairman Mao in the People’s Republic of China were educated to function competently within that system. Children in China today are educated to be sociologically competent in China’s current government and economic system. Children in France, Spain, Portugal, Israel, Mexico, Argentina, Brazil, and Iran likewise are educated to function competently in those systems. In the Soviet Union, children were educated to function within its version of communism. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, children were required to learn different civic knowledge and skills in order to be competent within the newly emerging political ideologies of reformed nation states.
What is commonsense to most people who received a K-12 public education in the United States is that every formal system of state schooling throughout the modern world is designed to educate its students to develop, what Charles Lemert calls “sociologically competencies” within whatever ideological system is dominating at the time of their schooling. People correctly assume that children going to school during the Weimar Republic, for example, were educated to function competently within that ideological system. Children who were in school during the reign of Chairman Mao in the People’s Republic of China were educated to function competently within that system. Children in China today are educated to be sociologically competent in China’s current government and economic system. Children in France, Spain, Portugal, Israel, Mexico, Argentina, Brazil, and Iran likewise are educated to function competently in those systems. In the Soviet Union, children were educated to function within its version of communism. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, children were required to learn different civic knowledge and skills in order to be competent within the newly emerging political ideologies of reformed nation states.
 Notwithstanding the spread of English as a global lingua franca, translation continues to be a vital component of international relations, whether political, commercial, or cultural. In certain cases, translation is also necessary nationally, for instance in countries comprising more than one significant linguistic group. This is so in Switzerland, which voted by an overwhelming majority in 1938 to add a fourth national tongue to thwart the irredentist aspirations of its Italian neighbor, and which in certain contexts is obliged to use a Latin version of its own name (Confoederatio Helvetica) to avoid favoring one language group over another.
Notwithstanding the spread of English as a global lingua franca, translation continues to be a vital component of international relations, whether political, commercial, or cultural. In certain cases, translation is also necessary nationally, for instance in countries comprising more than one significant linguistic group. This is so in Switzerland, which voted by an overwhelming majority in 1938 to add a fourth national tongue to thwart the irredentist aspirations of its Italian neighbor, and which in certain contexts is obliged to use a Latin version of its own name (Confoederatio Helvetica) to avoid favoring one language group over another. If you listen to that track as featured in the mix, my judgment may seem a little harsh. The track is on the static side, but that’s hardly a fault in the context: the textures are lovely, and there’s plenty of movement; and at under four minutes it can’t really be said to overstay its welcome. A minor work, perhaps, but as a brief linking interlude it works perfectly well. So what’s the problem?
If you listen to that track as featured in the mix, my judgment may seem a little harsh. The track is on the static side, but that’s hardly a fault in the context: the textures are lovely, and there’s plenty of movement; and at under four minutes it can’t really be said to overstay its welcome. A minor work, perhaps, but as a brief linking interlude it works perfectly well. So what’s the problem?
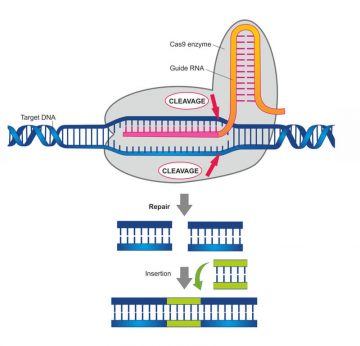 front of some her UC Berkeley colleagues, Doudna shared, “a story … about some research … that led in an unexpected direction … ” producing “ … some science that has profound implications going forward…but also makes us really think about what it means to be human and what it means to have the power to manipulate the very code of life …”
front of some her UC Berkeley colleagues, Doudna shared, “a story … about some research … that led in an unexpected direction … ” producing “ … some science that has profound implications going forward…but also makes us really think about what it means to be human and what it means to have the power to manipulate the very code of life …”