by Ethan Seavey

You know this feeling. The formation of words to open the conversation, the gravity of this dull walk with your father. The deals you make with the devil inside yourself: tell him by the time you reach the end of this street, the middle of this bridge, and definitely before you reach Sainte-Chapelle.
You’re coming out, because you’ll collapse if you don’t. And when the words are about to boil over on your tongue, you’re cut off by your own voice pointing out a French bus with the word «Toot» on it.
You’ve done this before. It’s harder, now.
A few years ago you went on walks like this one all the time. You’d structure the beginning of the conversation over and over, memorize it, say, “Dad, I need to tell you something important: I’m gay.” Even in your mind the last word would come out as a raspy quietness.
Today, these are the words you rehearse like a pop song echoing in your head: “Dad, I think I need to get help. I don’t know how to manage my mental health anymore. I deal with daily anxiety, and I’m really struggling with the idea of spending the next year across the world from everything I know.”
The parks are bigger here. And the people speak too quickly a language you can just barely understand. And their crows are blacker; and street smart like your pigeons. The fathers here smile wider as they run, pushing their children on scooters. The hot is mild and so is the cold, and the rain is only falling dew. Read more »

 Andrea Chung. From the series Vex, 2020.
Andrea Chung. From the series Vex, 2020.
 The day I began writing this essay, Portland Oregon braced for yet another round of uncharacteristic heat. Over several months of preparation, as I had been reading and pondering Kim Stanley Robinson’s big, detailed, hyper-realistic science-fiction book The Ministry for the Future, our normally cool northwest town had found itself repeatedly facing drought and high temperatures. Now we were about to be trapped under a “heat dome” of 115 degrees Fahrenheit (46° C) – Las Vegas temperatures, Abu-Dhabi temperatures – for days on end.
The day I began writing this essay, Portland Oregon braced for yet another round of uncharacteristic heat. Over several months of preparation, as I had been reading and pondering Kim Stanley Robinson’s big, detailed, hyper-realistic science-fiction book The Ministry for the Future, our normally cool northwest town had found itself repeatedly facing drought and high temperatures. Now we were about to be trapped under a “heat dome” of 115 degrees Fahrenheit (46° C) – Las Vegas temperatures, Abu-Dhabi temperatures – for days on end.

 Theories that specify which properties are essential for an object to be a work of art are perilous. The nature of art is a moving target and its social function changes over time. But if we’re trying to capture what art has become over the past 150 years within the art institutions of Europe and the United States, we must make room for the central role of creativity and originality. Objects worthy of the honorific “art” are distinct from objects unsuccessfully aspiring to be art by the degree of creativity or originality on display. (I am understanding “art” as a normative concept here.)
Theories that specify which properties are essential for an object to be a work of art are perilous. The nature of art is a moving target and its social function changes over time. But if we’re trying to capture what art has become over the past 150 years within the art institutions of Europe and the United States, we must make room for the central role of creativity and originality. Objects worthy of the honorific “art” are distinct from objects unsuccessfully aspiring to be art by the degree of creativity or originality on display. (I am understanding “art” as a normative concept here.)
 Even though I arrived at Economics with the aim of interpreting history, it soon gave me a more general perspective. First, it showed me the value of precision and empirical testing in thinking about socially important issues. This immediately appealed to me, as two of the first courses I liked in college were on Deductive and Inductive Logic. More importantly, Economics gave me a deeper understanding of the incentive mechanisms that sustain social institutions. It made me think why some of the glib solutions suggested by my leftist friends were difficult to sustain in the real world, unless based on motivations/norms and constraints of people in that world. Why are cooperatives and nationalized industries, suggested as substitutes for private enterprise, often (not always) dysfunctional? Economics asks the question: if there is a social problem, why does it not get resolved by the people on their own, and if your answer is that it is the ‘system’ that is to blame—which was the main message of many leftist stories I read and plays/movies I watched—Economics teaches us to go beyond and look into the underlying mechanism through which that ‘system’ is perpetuated or occasionally broken.
Even though I arrived at Economics with the aim of interpreting history, it soon gave me a more general perspective. First, it showed me the value of precision and empirical testing in thinking about socially important issues. This immediately appealed to me, as two of the first courses I liked in college were on Deductive and Inductive Logic. More importantly, Economics gave me a deeper understanding of the incentive mechanisms that sustain social institutions. It made me think why some of the glib solutions suggested by my leftist friends were difficult to sustain in the real world, unless based on motivations/norms and constraints of people in that world. Why are cooperatives and nationalized industries, suggested as substitutes for private enterprise, often (not always) dysfunctional? Economics asks the question: if there is a social problem, why does it not get resolved by the people on their own, and if your answer is that it is the ‘system’ that is to blame—which was the main message of many leftist stories I read and plays/movies I watched—Economics teaches us to go beyond and look into the underlying mechanism through which that ‘system’ is perpetuated or occasionally broken. Recently I came upon this photo of my friend Eric, me, and his father, tucked into a book that I was trying to place in the correct place on my shelves as a part of a recent book-organizing effort and it made me think about one of the scarier events in my life. It was 2004. It was also only a couple of years after 9/11 and by then the Patriot Act was in full effect and I personally knew completely innocent people who had been caught up in the “bad Muslim” dragnet and had been detained, deported from America, etc. It was in this atmosphere that I was invited to attend my good friend Eric’s wedding on a lake in Michigan. I found the cheapest ticket possible which would involve a stopover in Pittsburgh on the way to Detroit from NYC and a stop in Philadelphia on the way back. I also reserved a rental car at the Detroit airport to get to the rural lake where the wedding was going to be.
Recently I came upon this photo of my friend Eric, me, and his father, tucked into a book that I was trying to place in the correct place on my shelves as a part of a recent book-organizing effort and it made me think about one of the scarier events in my life. It was 2004. It was also only a couple of years after 9/11 and by then the Patriot Act was in full effect and I personally knew completely innocent people who had been caught up in the “bad Muslim” dragnet and had been detained, deported from America, etc. It was in this atmosphere that I was invited to attend my good friend Eric’s wedding on a lake in Michigan. I found the cheapest ticket possible which would involve a stopover in Pittsburgh on the way to Detroit from NYC and a stop in Philadelphia on the way back. I also reserved a rental car at the Detroit airport to get to the rural lake where the wedding was going to be. Philosophers are prone to define
Philosophers are prone to define 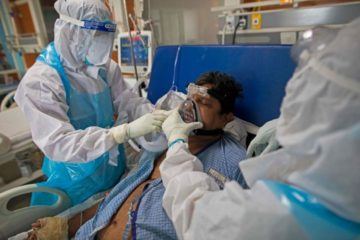 This week I had planned to present the 3 Quarks Daily readership with a fluffy little piece about my memories of a grade school foreign language teacher. It was poignant, it was heartfelt, it was funny (if I do say so myself). Above all, it was intended as a brief respite from the nonstop parade of horrors scrolling past our screens every day—a parade in which my own recent writings have occupied a lavishly decorated float. We all deserve a break, I thought. It would be nice to look at some baton twirlers for a minute, listen to an oompa band.
This week I had planned to present the 3 Quarks Daily readership with a fluffy little piece about my memories of a grade school foreign language teacher. It was poignant, it was heartfelt, it was funny (if I do say so myself). Above all, it was intended as a brief respite from the nonstop parade of horrors scrolling past our screens every day—a parade in which my own recent writings have occupied a lavishly decorated float. We all deserve a break, I thought. It would be nice to look at some baton twirlers for a minute, listen to an oompa band.
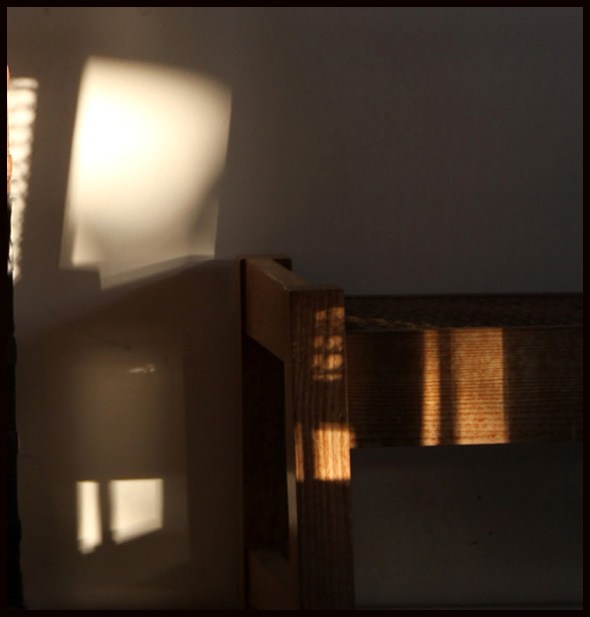 Sughra Raza. Karachi Afternoon Sun, 2010.
Sughra Raza. Karachi Afternoon Sun, 2010.




