by Brooks Riley
Time is a double-jointed trickster, bending this way and that to elude the tempi of one’s needs.
 Time isn’t what it used to be. The pandemic has altered our perception of it. This is why time is no longer quite as valuable as it was before we were suddenly assaulted with too much of it. It used to be a commodity in short supply. It’s even been called a currency (time is money), but the reverse was never true. No matter how many billions Mr. Bezos has, he has no more hours in his day than I do.
Time isn’t what it used to be. The pandemic has altered our perception of it. This is why time is no longer quite as valuable as it was before we were suddenly assaulted with too much of it. It used to be a commodity in short supply. It’s even been called a currency (time is money), but the reverse was never true. No matter how many billions Mr. Bezos has, he has no more hours in his day than I do.
Utilization of time has also changed. Novels still require the same amount of time to read as they always have, but audiobooks actually slow down the storytelling process: Where eyes once flew over the page, a human voice now dictates the pace at which we enjoy the authorial content as we keep our eyes on the road and our hands on the wheel.
All this leads to the question of just how our grasp of time or time-passing has been altered aesthetically by the convergence of that motherlode of time, the pandemic, with the rising popularity of elongated storytelling formats like TV series—those time-indulgent, episodic ways to weave a tale, unhurried by a two-hour time limit. Where movies used to define—and confine—our consumption of a narrative, series now populate the streaming platforms, becoming increasingly dominant in the menu listings and more sophisticated in their dramaturgy.
They get no respect. Read more »

 The evidence that mass media can cause physiological responses in humans is so evident in our everyday experience that it’s easy to ignore. Subliminal muzak makes our fingers tap lightly on our grocery carts. Billboards with sexy models flush our cheeks during our daily commutes. But not all such stimuli are subtle. For those media products whose main purpose is to cause a physiological response, genre labels serve as warnings—e.g., we label items that make us laugh as comedy, items that turn us on as pornography, or items that trigger our fight-or-flight response as horror. Modern people have complex attitudes toward media that invoke a physiological response, and practitioners of such genres alternatively experience intense celebration and intense censure.
The evidence that mass media can cause physiological responses in humans is so evident in our everyday experience that it’s easy to ignore. Subliminal muzak makes our fingers tap lightly on our grocery carts. Billboards with sexy models flush our cheeks during our daily commutes. But not all such stimuli are subtle. For those media products whose main purpose is to cause a physiological response, genre labels serve as warnings—e.g., we label items that make us laugh as comedy, items that turn us on as pornography, or items that trigger our fight-or-flight response as horror. Modern people have complex attitudes toward media that invoke a physiological response, and practitioners of such genres alternatively experience intense celebration and intense censure. Some decades back the typical voting pattern in many democracies used to be that the rich and upper middle classes used to vote in general for right-leaning parties, while the relatively poor voted for left-leaning parties. But in recent decades this pattern has been shifting: many of the professional or more educated voters in some of those countries are increasingly going for left or green parties, while many of the poor working-class voters are turning to right-wing parties, sometimes led by populist demagogues. Thomas Piketty and his associates in a new paper issued by the World Inequality Lab have provided data to show that for 21 western democracies the more educated voters have over the years become more left supporters than the less-educated voters. Piketty has described this elite division between high-education and high-income people colorfully as that between the Brahmin Left and the Merchant (the corresponding Indian caste term would have been ‘bania’) Right. He does not go much into explaining this pattern but it is clear that as education expands (measured by average years of schooling of the adult population) the left or center-left parties now can have a viable base even in the relatively rich or upper middle classes. Education often makes one appreciate more liberal values, which may sometimes outweigh their worries about higher taxes that the left parties may inflict.
Some decades back the typical voting pattern in many democracies used to be that the rich and upper middle classes used to vote in general for right-leaning parties, while the relatively poor voted for left-leaning parties. But in recent decades this pattern has been shifting: many of the professional or more educated voters in some of those countries are increasingly going for left or green parties, while many of the poor working-class voters are turning to right-wing parties, sometimes led by populist demagogues. Thomas Piketty and his associates in a new paper issued by the World Inequality Lab have provided data to show that for 21 western democracies the more educated voters have over the years become more left supporters than the less-educated voters. Piketty has described this elite division between high-education and high-income people colorfully as that between the Brahmin Left and the Merchant (the corresponding Indian caste term would have been ‘bania’) Right. He does not go much into explaining this pattern but it is clear that as education expands (measured by average years of schooling of the adult population) the left or center-left parties now can have a viable base even in the relatively rich or upper middle classes. Education often makes one appreciate more liberal values, which may sometimes outweigh their worries about higher taxes that the left parties may inflict. Among all the fascinating mythical creatures that populate the folklore of various cultures, one that stands out is
Among all the fascinating mythical creatures that populate the folklore of various cultures, one that stands out is  Sughra Raza. Beech Bark Landscape. June, 2021.
Sughra Raza. Beech Bark Landscape. June, 2021. Suppose you are Father God, or Mother Nature, or Mother God, or Father Nature — doesn’t matter — and you want to raise up a crop of mammals who can reason well about what’s true. At first you think, “No problem! I’ll just ex nihilo some up in a jiffy!” but then you remember that you have resolved to build everything through the painstaking process of evolution by natural selection, which requires small random shifts over time, with every step toward your target resulting in some sort of reproductive advantage for the mammal in question. Okay; this is going to be hard.
Suppose you are Father God, or Mother Nature, or Mother God, or Father Nature — doesn’t matter — and you want to raise up a crop of mammals who can reason well about what’s true. At first you think, “No problem! I’ll just ex nihilo some up in a jiffy!” but then you remember that you have resolved to build everything through the painstaking process of evolution by natural selection, which requires small random shifts over time, with every step toward your target resulting in some sort of reproductive advantage for the mammal in question. Okay; this is going to be hard. I’ve always loved the name Sinus Iridum (Bay of Rainbows), which describes a beautiful semicircular dark feature on the face of the Moon. Browsing a lunar map reveals other names equally beautiful or evocative: Sinus Concordiae (Bay of Harmony) and Sinus Aestuum (Seething Bay), for example. Other lunar plains with watery names include Mare Anguis (Serpent Sea), Palus Somni (Marsh of Sleep), and Mare Imbrium (Sea of Showers). Montes Harbinger is a group of mountains in Mare Imbrium; when they’re lit by the rising sun, they herald the approach of sunrise to Aristarchus crater.
I’ve always loved the name Sinus Iridum (Bay of Rainbows), which describes a beautiful semicircular dark feature on the face of the Moon. Browsing a lunar map reveals other names equally beautiful or evocative: Sinus Concordiae (Bay of Harmony) and Sinus Aestuum (Seething Bay), for example. Other lunar plains with watery names include Mare Anguis (Serpent Sea), Palus Somni (Marsh of Sleep), and Mare Imbrium (Sea of Showers). Montes Harbinger is a group of mountains in Mare Imbrium; when they’re lit by the rising sun, they herald the approach of sunrise to Aristarchus crater.



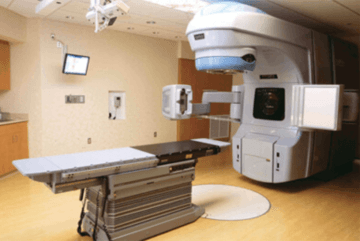 It’s the middle of July, 2020, the middle of a heat wave in the middle of the pandemic, and my first day in the radiation room. I stand in socks and starchy hospital gown before the Star Trek-ish linear accelerator, waiting for the technicians to fit me on the machine’s bed-like tray for best positioning. But in my mind I’m standing four years ago in the kitchen of my new home in Rhode Island, where beside me a cable company worker tapped in a phone number for advice about how to maneuver spotty Internet service into a happy ending. While he waited for his boss to call back, he mentioned, with a hint of wonder in his voice, “Y’know, this is my first day on the job after four months.”
It’s the middle of July, 2020, the middle of a heat wave in the middle of the pandemic, and my first day in the radiation room. I stand in socks and starchy hospital gown before the Star Trek-ish linear accelerator, waiting for the technicians to fit me on the machine’s bed-like tray for best positioning. But in my mind I’m standing four years ago in the kitchen of my new home in Rhode Island, where beside me a cable company worker tapped in a phone number for advice about how to maneuver spotty Internet service into a happy ending. While he waited for his boss to call back, he mentioned, with a hint of wonder in his voice, “Y’know, this is my first day on the job after four months.”


 Climate change is such a terrifying large problem that it is hard to think sensibly about. On the one hand this makes many people prefer denial. On the other hand it can exert a warping effect on the reasoning of even those who do take it seriously. In particular, many confuse the power we have over what the lives of future generations will be like – and the moral responsibility that follows from that – with the idea that we are better off than them. These people seem to have taken the idea of the world as finite and combined it with the idea that this generation is behaving selfishly to produce a picture of us as gluttons whose overconsumption will reduce future generations to penury. But this completely misrepresents the challenge of climate change.
Climate change is such a terrifying large problem that it is hard to think sensibly about. On the one hand this makes many people prefer denial. On the other hand it can exert a warping effect on the reasoning of even those who do take it seriously. In particular, many confuse the power we have over what the lives of future generations will be like – and the moral responsibility that follows from that – with the idea that we are better off than them. These people seem to have taken the idea of the world as finite and combined it with the idea that this generation is behaving selfishly to produce a picture of us as gluttons whose overconsumption will reduce future generations to penury. But this completely misrepresents the challenge of climate change.
 Adam Smith’s The Wealth of Nations begins with this claim:
Adam Smith’s The Wealth of Nations begins with this claim: