Robin Wright in The New Yorker:
 The girls and women of Iran are just bitchin’ brave, flipping the bird at its Supreme Leader in a challenge to one of the most significant revolutions in modern history. Day after dangerous day, on open streets and in gated schools, in a flood of tweets and brazen videos, they have ridiculed a theocracy that deems itself the government of God. The average age of the protesters who have been arrested is just fifteen, the Revolutionary Guard’s deputy commander claimed last week. In the process, they have captured the world’s imagination; sympathy rallies have been held from London to Los Angeles, Sydney to Seoul, and Tokyo to Tunis.
The girls and women of Iran are just bitchin’ brave, flipping the bird at its Supreme Leader in a challenge to one of the most significant revolutions in modern history. Day after dangerous day, on open streets and in gated schools, in a flood of tweets and brazen videos, they have ridiculed a theocracy that deems itself the government of God. The average age of the protesters who have been arrested is just fifteen, the Revolutionary Guard’s deputy commander claimed last week. In the process, they have captured the world’s imagination; sympathy rallies have been held from London to Los Angeles, Sydney to Seoul, and Tokyo to Tunis.
Iran’s protests may well be the first time in history that women have been both the spark and engine for an attempted counter-revolution. “The role played by Iranian women right now seems very unprecedented,” Daniel Edelstein, a political scientist at Stanford and an expert on revolutions, told me. One of the few possible parallels was the role of Parisian female poissonières, or market workers, who stormed Versailles to prevent the king from turning against the National Assembly and crushing the nascent French Revolution, he said. In that case, however, “the women were seeking to prevent counter-revolution, not contributing to it.” During the Russian Revolution, bread riots led by women in Petrograd played a pivotal role in the tsarist empire’s collapse, Anne O’Donnell, a Russia historian at New York University, told me. But Iran’s protests have been unique because, she said, “this is not just an upheaval involving women, it is an upheaval about women and women’s freedom, and that makes it very special.”
More here.

 Fredric Jameson in Sidecar:
Fredric Jameson in Sidecar: Alden Young in Phenomenal World:
Alden Young in Phenomenal World: Blake Smith in American Affairs:
Blake Smith in American Affairs: I
I One of the funny things about adolescence is that the world can seem enormous, brimming with possibility, while at the same time the urgency to define oneself — fastidiously curating likes and dislikes, ruthlessly sorting people according to their musical tastes — can make the world feel extremely small.
One of the funny things about adolescence is that the world can seem enormous, brimming with possibility, while at the same time the urgency to define oneself — fastidiously curating likes and dislikes, ruthlessly sorting people according to their musical tastes — can make the world feel extremely small.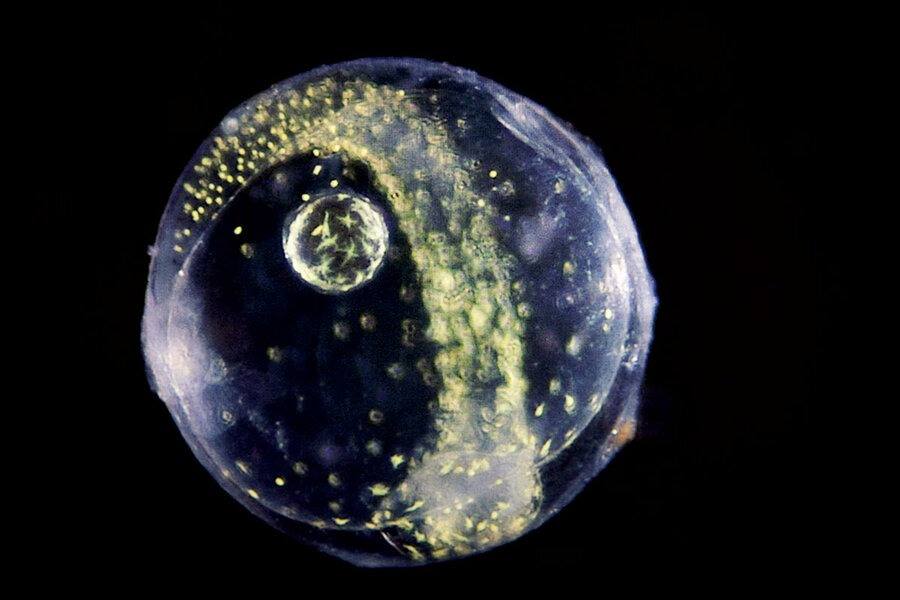
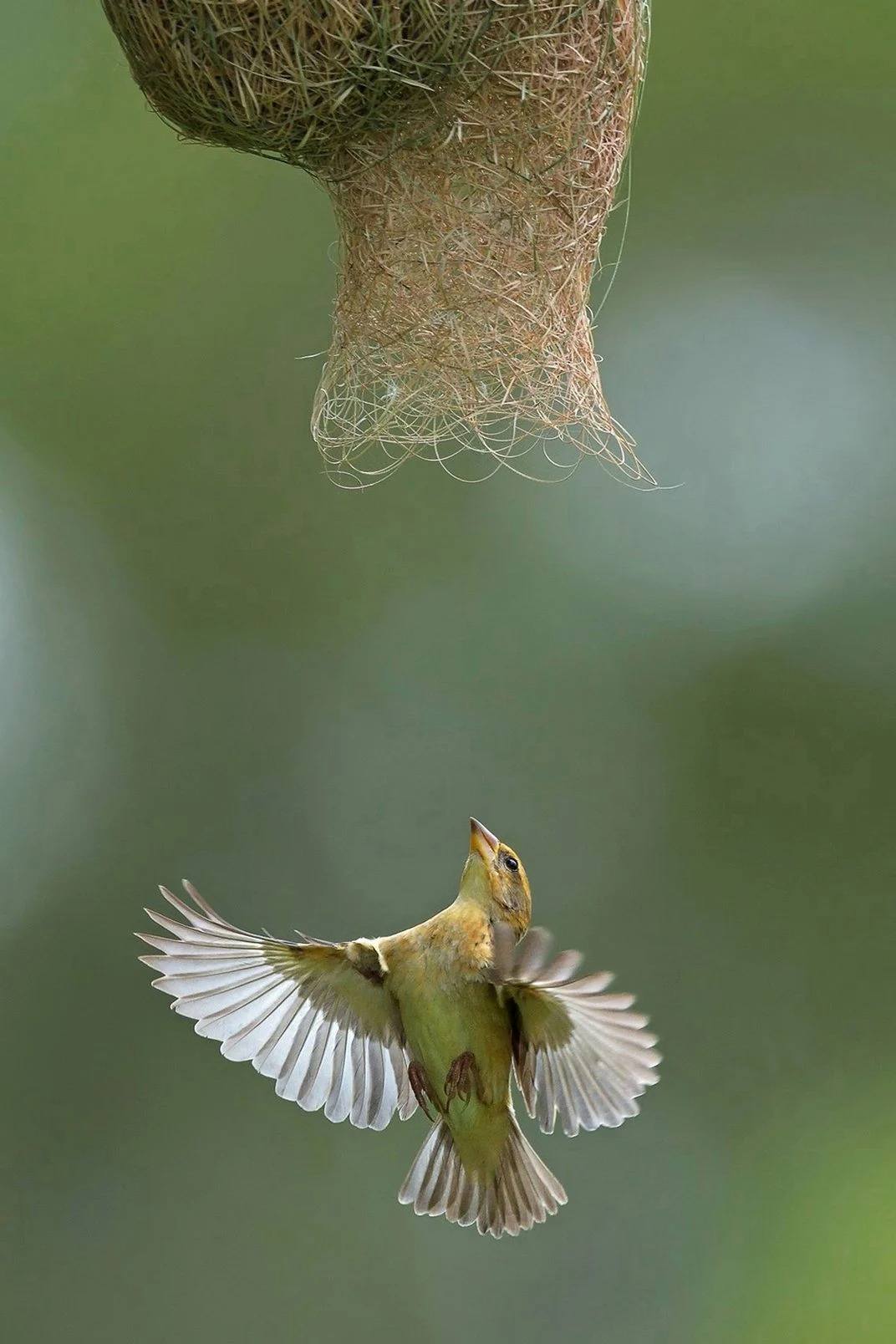


 Three chemists who pioneered a useful technique called click chemistry to join molecules together efficiently have won this year’s Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
Three chemists who pioneered a useful technique called click chemistry to join molecules together efficiently have won this year’s Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Love hungers for knowledge. For someone newly in love, nothing is better than learning about the beloved, nothing better than revealing yourself to them in turn. “The talk of lovers who have just declared their love,” writes Iris Murdoch in The Bell (1958), “is one of life’s most sweet delights. . . . Each one in haste to declare all that he is, so that no part of his being escapes the hallowing touch.”
Love hungers for knowledge. For someone newly in love, nothing is better than learning about the beloved, nothing better than revealing yourself to them in turn. “The talk of lovers who have just declared their love,” writes Iris Murdoch in The Bell (1958), “is one of life’s most sweet delights. . . . Each one in haste to declare all that he is, so that no part of his being escapes the hallowing touch.” “I have always wanted to write the sort of book that I find it impossible to talk about afterward, the sort of book that makes it impossible for me to withstand the gaze of others,” writes Annie Ernaux’s narrator near the end of her 1998 autofiction, Shame. Ernaux takes the sentiment further in the opening lines of her 2008 book, The Possession: “I have always wanted to write as if I would be gone when the book was published. To write as if I were about to die—no more judges.”
“I have always wanted to write the sort of book that I find it impossible to talk about afterward, the sort of book that makes it impossible for me to withstand the gaze of others,” writes Annie Ernaux’s narrator near the end of her 1998 autofiction, Shame. Ernaux takes the sentiment further in the opening lines of her 2008 book, The Possession: “I have always wanted to write as if I would be gone when the book was published. To write as if I were about to die—no more judges.” The Swiss composer Othmar Schoeck, who lived from 1886 to 1957, is little known outside his native land, but his moments of fame have been as striking as they are strange. For one thing, Schoeck gained the admiration of several leading writers of the twentieth century. Hermann Hesse ranked Schoeck’s songs alongside those of Schubert and Schumann; James Joyce considered him a rival to Stravinsky; Thomas Mann also thought highly of him. A further quiver of notoriety followed in the nineteen-seventies, when, as Calvin Trillin
The Swiss composer Othmar Schoeck, who lived from 1886 to 1957, is little known outside his native land, but his moments of fame have been as striking as they are strange. For one thing, Schoeck gained the admiration of several leading writers of the twentieth century. Hermann Hesse ranked Schoeck’s songs alongside those of Schubert and Schumann; James Joyce considered him a rival to Stravinsky; Thomas Mann also thought highly of him. A further quiver of notoriety followed in the nineteen-seventies, when, as Calvin Trillin  O
O F
F