by Chris Horner

In May 1919 the remains of a woman were fished from the Landwehr canal in Berlin. The three doctors available must have suspected the identity of the corpse, as they refused to perform a post mortem on it. Identification was in any case made by examination of the clothes on the body. This had been Rosa Luxemburg. She had perished essentially because the leftist uprising in Berlin, initiated by her fellow Sparticist leader Karl Liebknecht without her agreement, had failed. Luxemburg, who had fiercely criticised the Bolshevik approach to revolution as dangerously authoritarian was clubbed and then shot to death by members of the Freikorps, whose repressive violence makes them fitting antecedents to the Nazis.
The great revolutions in ‘The West’ are often seen as turning points, thresholds, new stages in history, and their very dates have a kind of resonance: 1776, 1789 (or 1794), 1917, and so on. History, of course, may make us change our minds about the degree of success, the meaning, the import of those events, but they remain potent as symbols, whatever posterity’s judgment may be. And there is a second sequence, of course, that of the failed revolutions: 1796, 1821, 1848, 1871, 1905, 1918, and 1956. These are the abortive revolutions and uprisings. This second list is the longer one, but like the successful ones, judgment about ultimate meaning, including the meaning of ‘success’ and ‘failure’, remain open to revision and reconsideration.
Of the revolutions that never were, it is the one that began in Germany in 1918 that is most relevant to Hannah Arendt. Arendt, born in 1906, married to Heinrich Blucher (an ex Sparticist) has a biography and a set of concerns defined by the fate of Germany after 1918. Rosa Luxemburg’s life and death – including the nature of the regime that connived in her murder – was the subject of an eloquent and moving essay by Arendt and published in Men in Dark Times in 1966. For all her criticism of Rosa Luxemburg’s mistakes, it is clear that she stands as a kind of exemplar for Arendt. If it had succeeded, if some kind of ‘Red’ government has seized and kept hold of power in the 1918-9 period, the effect on Germany, the nascent Soviet State in Russia, and the rest of the world would have been, one assumes, huge. But it failed, and Hitler and Stalin were the successors to that non-event. Read more »

 During my late 1970s New York City childhood, repeats of Star Trek aired every weeknight on channel 11, WPIX. The original 79 episodes ran about three times per year, which means that, allowing for the occasional miss, I’d seen each episode about 10 – 12 times before reaching high school.
During my late 1970s New York City childhood, repeats of Star Trek aired every weeknight on channel 11, WPIX. The original 79 episodes ran about three times per year, which means that, allowing for the occasional miss, I’d seen each episode about 10 – 12 times before reaching high school. For the last three years, I have struggled with a dilemma: As a reasonable, quite liberal person, what should I think of my 60 million fellow Americans who voted for Donald Trump in 2016, and the vast majority of whom continue to support him today? Normally, a personal dilemma is a private thing, not a topic for public airing, but I feel that this particular problem is one the vexes many others – perhaps even a majority of Americans, as more of us voted for Hillary Clinton and many did not vote at all. Since that bleak day in November 2016, an unspoken – and sometimes loudly spoken – question hangs in the air: What kind of “
For the last three years, I have struggled with a dilemma: As a reasonable, quite liberal person, what should I think of my 60 million fellow Americans who voted for Donald Trump in 2016, and the vast majority of whom continue to support him today? Normally, a personal dilemma is a private thing, not a topic for public airing, but I feel that this particular problem is one the vexes many others – perhaps even a majority of Americans, as more of us voted for Hillary Clinton and many did not vote at all. Since that bleak day in November 2016, an unspoken – and sometimes loudly spoken – question hangs in the air: What kind of “ In November 1918, a 17-year-student from Rome sat for the entrance examination of the Scuola Normale Superiore in Pisa, Italy’s most prestigious science institution. Students applying to the institute had to write an essay on a topic that the examiners picked. The topics were usually quite general, so the students had considerable leeway. Most students wrote about well-known subjects that they had already learnt about in high school. But this student was different. The title of the topic he had been given was “Characteristics of Sound”, and instead of stating basic facts about sound, he “set forth the partial differential equation of a vibrating rod and solved it using Fourier analysis, finding the eigenvalues and eigenfrequencies. The entire essay continued on this level which would have been creditable for a doctoral examination.” The man writing these words was the 17-year-old’s future student, friend and Nobel laureate, Emilio Segre. The student was Enrico Fermi. The examiner was so startled by the originality and sophistication of Fermi’s analysis that he broke precedent and invited the boy to meet him in his office, partly to make sure that the essay had not been plagiarized. After convincing himself that Enrico had done the work himself, the examiner congratulated him and predicted that he would become an important scientist.
In November 1918, a 17-year-student from Rome sat for the entrance examination of the Scuola Normale Superiore in Pisa, Italy’s most prestigious science institution. Students applying to the institute had to write an essay on a topic that the examiners picked. The topics were usually quite general, so the students had considerable leeway. Most students wrote about well-known subjects that they had already learnt about in high school. But this student was different. The title of the topic he had been given was “Characteristics of Sound”, and instead of stating basic facts about sound, he “set forth the partial differential equation of a vibrating rod and solved it using Fourier analysis, finding the eigenvalues and eigenfrequencies. The entire essay continued on this level which would have been creditable for a doctoral examination.” The man writing these words was the 17-year-old’s future student, friend and Nobel laureate, Emilio Segre. The student was Enrico Fermi. The examiner was so startled by the originality and sophistication of Fermi’s analysis that he broke precedent and invited the boy to meet him in his office, partly to make sure that the essay had not been plagiarized. After convincing himself that Enrico had done the work himself, the examiner congratulated him and predicted that he would become an important scientist.

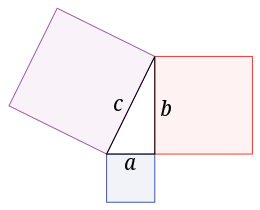 I have some very simple New Year’s resolutions, and some that require an entire column to spell out. One example of the latter is that I want to make a subtle but meaningful change in how I talk to my (middle and high school) math students about proofs.
I have some very simple New Year’s resolutions, and some that require an entire column to spell out. One example of the latter is that I want to make a subtle but meaningful change in how I talk to my (middle and high school) math students about proofs.

 We find ourselves always in the middle of an experience. But it’s what we do next – how we characterize the experience – that lays down a host of important and almost subterranean conditions. Am I sitting in a chair, gazing out the dusty window into a world of sunlight, trees, and snow? Am I meditating on the nature of experience? Am I praying? Am I simply spacing out? Depending on which way I parse whatever the hell I’m up to, my experience shifts from something ineffable (or at any rate, not currently effed) to something meaningful and determinate, festooned with many other conversational hooks and openings: “enjoying nature”, “introspecting”, “conversing with God”, “resting”, “procrastinating”, and so on. Putting the experience into words tells me what to do with it next.
We find ourselves always in the middle of an experience. But it’s what we do next – how we characterize the experience – that lays down a host of important and almost subterranean conditions. Am I sitting in a chair, gazing out the dusty window into a world of sunlight, trees, and snow? Am I meditating on the nature of experience? Am I praying? Am I simply spacing out? Depending on which way I parse whatever the hell I’m up to, my experience shifts from something ineffable (or at any rate, not currently effed) to something meaningful and determinate, festooned with many other conversational hooks and openings: “enjoying nature”, “introspecting”, “conversing with God”, “resting”, “procrastinating”, and so on. Putting the experience into words tells me what to do with it next.
 Forever is a long time.
Forever is a long time.

 Lili Marleen is one of the best known songs of the twentieth century. A plaintive expression of a soldier’s desire to be with his girlfriend, it is indelibly associated with World War II, in part because it was popular with soldiers on both sides. It was
Lili Marleen is one of the best known songs of the twentieth century. A plaintive expression of a soldier’s desire to be with his girlfriend, it is indelibly associated with World War II, in part because it was popular with soldiers on both sides. It was  Marlene Dietrich, who worked tirelessly during world war two entertaining allied troops, also recorded both a
Marlene Dietrich, who worked tirelessly during world war two entertaining allied troops, also recorded both a 
 While waiting, shivering and jetlagged, for a train home from the Paris airport this week, I alternately stared into space and checked the train timetables. My train was an hour late. I later learned, thanks to the friendliness of a fellow traingoer, that the train had hit a deer.
While waiting, shivering and jetlagged, for a train home from the Paris airport this week, I alternately stared into space and checked the train timetables. My train was an hour late. I later learned, thanks to the friendliness of a fellow traingoer, that the train had hit a deer.