by Joseph Shieber

Within the last few weeks, a high ranking official within the municipal government in Philadelphia resigned for making anti-Semitic remarks. Among those remarks, apparently, was the claim that the Holocaust film Schindler’s List was “Jewish propaganda.”
It’s probably a sign that I’ve been thinking about these issues for too long, but my first thought was, Why is it an insult to call something propaganda? What’s wrong with propaganda?
The term “propaganda” itself stems only from the 17th century, when the Catholic Church formed the Congregatio de Propaganda Fide, a committee of cardinals responsible for the Church’s efforts to proselytize non-believers. The use of the term as a denotation for a strategy for influencing public opinion, however, only really exploded at the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century, as journalism became professionalized. It was then that practitioners, theorists and politicians began to reflect on the ways in which governments and other organizations could use media outlets to shape public opinion.
Here, for example, is the Google Ngram viewer of “propaganda” from 1600 to 2016:
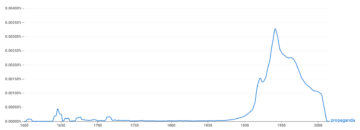
Although the term is less than 400 years old, the phenomenon of propaganda is far older. The pyramids of Egypt, to take one example, are propagandistic, attesting to the power of the Pharaohs who could enslave thousands of people to erect them. (But see this.) So are the coins stamped with the likenesses of the Roman emperors and circulated throughout the Mediterranean.

Given its ubiquity as a phenomenon, it is surprising how meager the theoretical discussion of propaganda actually is. Although there was a surge in works attempting to treat propaganda as a subject of academic inquiry in the first half of the 20th century, since then there have been comparatively few studies of propaganda, apart from largely historical assessments. Read more »

 Beauford Delaney. James Baldwin (Circa 1945-50).
Beauford Delaney. James Baldwin (Circa 1945-50). A couple of weeks ago, on the pages of this website,
A couple of weeks ago, on the pages of this website, 
 One of those mysterious concepts that we use as a criterion for judging a novel or film is a “sense of place.” I call it mysterious because it’s so often poorly defined—we recognize it because we can feel it, but what goes into creating it? How can one go about transporting a reader, for example, into a time and place via text? I’m under the impression that if asked this question, most people would mention things like using the five senses to describe a character’s impressions of his or her surroundings, or providing detail via adjectives and adverbs. This may be a gross generalization, but it’s what I’ve gathered from my experience in creative writing courses. It’s also the sense I get from reading short stories in literary journals, which seem to be where aspiring writers publish their attempts at fiction. I often find this writing technically good, but lifeless; it has all the components of effective writing but doesn’t add up to anything compelling. I don’t mean to suggest that I could do better, but I do know what I enjoy reading and what I don’t.
One of those mysterious concepts that we use as a criterion for judging a novel or film is a “sense of place.” I call it mysterious because it’s so often poorly defined—we recognize it because we can feel it, but what goes into creating it? How can one go about transporting a reader, for example, into a time and place via text? I’m under the impression that if asked this question, most people would mention things like using the five senses to describe a character’s impressions of his or her surroundings, or providing detail via adjectives and adverbs. This may be a gross generalization, but it’s what I’ve gathered from my experience in creative writing courses. It’s also the sense I get from reading short stories in literary journals, which seem to be where aspiring writers publish their attempts at fiction. I often find this writing technically good, but lifeless; it has all the components of effective writing but doesn’t add up to anything compelling. I don’t mean to suggest that I could do better, but I do know what I enjoy reading and what I don’t.
 Though I decided to go back to India, which institution I’d join there took some more time to determine. I had a standing invitation from K.N. Raj at the Delhi School of Economics. Even before I left MIT he asked me to teach a course in MIT’s summer-vacation period. I went and taught part of a course, which had good students (including Amitava Bose, who in his later professional life became close to me, served as a Director of the Indian Institute of Management in Kolkata, and finally lost his long battle against cancer). But I soon found out that the only job Raj could offer me was that of a Readership (Associate Professorship), as a full Professorship was not yet vacant. Amartya-da advised me against accepting a Readership, since in Indian universities there could be ‘many a slip’ even when a Professorship became vacant. I went back to MIT after the vacation, and soon after I got a message from T.N. Srinivasan of the Indian Statistical Institute (ISI) in Delhi, offering a full Professorship there, which I accepted.
Though I decided to go back to India, which institution I’d join there took some more time to determine. I had a standing invitation from K.N. Raj at the Delhi School of Economics. Even before I left MIT he asked me to teach a course in MIT’s summer-vacation period. I went and taught part of a course, which had good students (including Amitava Bose, who in his later professional life became close to me, served as a Director of the Indian Institute of Management in Kolkata, and finally lost his long battle against cancer). But I soon found out that the only job Raj could offer me was that of a Readership (Associate Professorship), as a full Professorship was not yet vacant. Amartya-da advised me against accepting a Readership, since in Indian universities there could be ‘many a slip’ even when a Professorship became vacant. I went back to MIT after the vacation, and soon after I got a message from T.N. Srinivasan of the Indian Statistical Institute (ISI) in Delhi, offering a full Professorship there, which I accepted.
 I began writing this series eighteen months ago to explore the human experience and human potential in the face of climate change, through the stories we tell. It’s been a remarkable journey for me as I followed trails of questions through new fields of ideas along entirely unexpected paths of enquiry. New vistas revealed themselves, sometimes perilous, always compelling. And so I went. The more I’ve learned, the more I’ve come to realize that our present environmental predicament is actually far worse off—that is to say, more threatening to near-term human wellbeing and civilizational integrity—than most of us recognize. This journey is changing me. So when I now look at contemporary works of fiction about climate change—so-called cli-fi, which I’d hoped might provide fresh insights—so much of it strikes me as somewhat underwhelming before the task: narrow, shallow, tepid, unimaginative, or even dishonest.
I began writing this series eighteen months ago to explore the human experience and human potential in the face of climate change, through the stories we tell. It’s been a remarkable journey for me as I followed trails of questions through new fields of ideas along entirely unexpected paths of enquiry. New vistas revealed themselves, sometimes perilous, always compelling. And so I went. The more I’ve learned, the more I’ve come to realize that our present environmental predicament is actually far worse off—that is to say, more threatening to near-term human wellbeing and civilizational integrity—than most of us recognize. This journey is changing me. So when I now look at contemporary works of fiction about climate change—so-called cli-fi, which I’d hoped might provide fresh insights—so much of it strikes me as somewhat underwhelming before the task: narrow, shallow, tepid, unimaginative, or even dishonest. When I was growing up during the 1970s, America still had a vibrant and thriving newspaper culture. My hometown New York City boasted a half-dozen dailies to choose from, plus countless neighborhood newspapers. Me and other kids started reading newspapers in about the 5th grade. Sports sections, comics, and movie listings mostly, but still. By middle school, newspapers were all over the place, and not because teachers foisted them upon us, but because kids picked them up on the way to school and read them.
When I was growing up during the 1970s, America still had a vibrant and thriving newspaper culture. My hometown New York City boasted a half-dozen dailies to choose from, plus countless neighborhood newspapers. Me and other kids started reading newspapers in about the 5th grade. Sports sections, comics, and movie listings mostly, but still. By middle school, newspapers were all over the place, and not because teachers foisted them upon us, but because kids picked them up on the way to school and read them.


 Although there might be nothing wrong with our hearing, we are quickly losing our ability to practice three formative modalities of democratic listening: Mindful, Aesthetic and Critical. These three modalities support our active participation in sustained, intimate conversations where we learn with and from each other. Millennials in particular struggle to listen to their friends, parents, and teachers for more than a few seconds without their brains becoming distracted by the ubiquitous hand of technology.
Although there might be nothing wrong with our hearing, we are quickly losing our ability to practice three formative modalities of democratic listening: Mindful, Aesthetic and Critical. These three modalities support our active participation in sustained, intimate conversations where we learn with and from each other. Millennials in particular struggle to listen to their friends, parents, and teachers for more than a few seconds without their brains becoming distracted by the ubiquitous hand of technology. Many years ago, I returned to my old high school for a visit with friends who were classmates back in the ’80s. Exploring the school and marveling over what had changed and what remained exactly the same, we ventured into the language lab. The room smelled exactly the same as it had in 1983, and it took me right back to those days of incredibly boring language lessons and sitting in that room with headphones on repeating monotonous phrases.
Many years ago, I returned to my old high school for a visit with friends who were classmates back in the ’80s. Exploring the school and marveling over what had changed and what remained exactly the same, we ventured into the language lab. The room smelled exactly the same as it had in 1983, and it took me right back to those days of incredibly boring language lessons and sitting in that room with headphones on repeating monotonous phrases.