by Robyn Repko Waller

AI has a proclivity for exaggeration. This hallucination is integral to its success and its danger.
Much digital ink has been spilled and computational resources consumed as of late in the too rapidly advancing capacities of AI.
Large language models like GPT-4 heralded as a welcome shortcut for email, writing, and coding. Worried discussion for the implications for pedagogical assessment — how to codify and detect AI plagiarism. Open-AI image generation to rival celebrated artists and photographers. And what of the convincing deep fakes?
The convenience of using AI to innovate and make efficient our social world and health, from Tiktok to medical diagnosis and treatment. Continued calls, though, for algorithmic fairness in the use of algorithmic decision-making in finance, government, health, security, and hiring.
Newfound friends, therapists, lovers, and enemies of an artificial nature. Both triumphant and terrified exclamations and warnings of sentient, genuinely intelligent AI. Serious widespread calls for a pause in development of these AI systems. And, in reply, reports that such exclamations and calls are overblown: Doesn’t intelligence require experience? Embodiment?
These are fascinating and important matters. Still, I don’t intend to add to the much-warranted shouting. Instead, I want to draw attention to a curious, yet serious, corollary of the use of such AI systems, the emergence of artificial or machine hallucinations. By such hallucinations, folks mean the phenomenon by which AI systems, especially those driven by machine learning, generate factual inaccuracies or create new misleading or irrelevant content. I will focus on one kind of hallucination, the inherent propensity of AI to exaggerate and skew. Read more »

 ‘Wenn möglich, bitte wenden.’
‘Wenn möglich, bitte wenden.’
 Everyone is talking about artificial intelligence. This is understandable: AI in its current capacity, which we so little understand ourselves, alternately threatens dystopia and promises utopia. We are mostly asking questions. Crucially, we are not asking so much whether the risks outweigh the rewards. That is because the relationship between the first potential and the second is laughably skewed. Most of us are already striving to thrive; whether increasingly superintelligent AI can help us do that is questionable. Whether AI can kill all humans is not.
Everyone is talking about artificial intelligence. This is understandable: AI in its current capacity, which we so little understand ourselves, alternately threatens dystopia and promises utopia. We are mostly asking questions. Crucially, we are not asking so much whether the risks outweigh the rewards. That is because the relationship between the first potential and the second is laughably skewed. Most of us are already striving to thrive; whether increasingly superintelligent AI can help us do that is questionable. Whether AI can kill all humans is not.

 Sughra Raza. NYC, April 2023.
Sughra Raza. NYC, April 2023.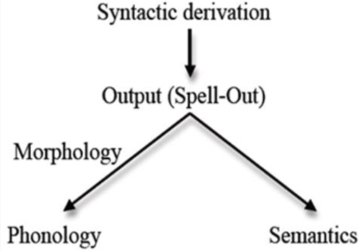
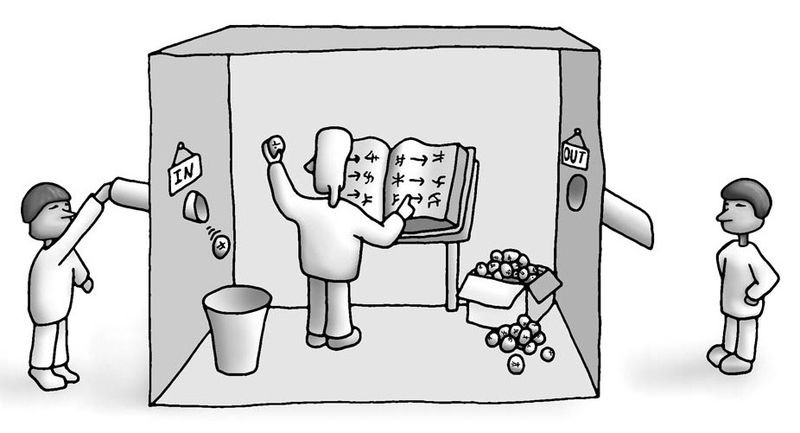 Despite many people’s apocalyptic response to ChatGPT, a great deal of caution and skepticism is in order. Some of it is philosophical, some of it practical and social. Let me begin with the former.
Despite many people’s apocalyptic response to ChatGPT, a great deal of caution and skepticism is in order. Some of it is philosophical, some of it practical and social. Let me begin with the former.



 How intelligent is ChatGPT? That question has loomed large ever since
How intelligent is ChatGPT? That question has loomed large ever since 
 Environmentalists are always complaining that governments are obsessed with GDP and economic growth, and that this is a bad thing because economic growth is bad for the environment. They are partly right but mostly wrong. First, while governments talk about GDP a lot, that does not mean that they actually prioritise economic growth. Second, properly understood economic growth is a great and wonderful thing that we should want more of.
Environmentalists are always complaining that governments are obsessed with GDP and economic growth, and that this is a bad thing because economic growth is bad for the environment. They are partly right but mostly wrong. First, while governments talk about GDP a lot, that does not mean that they actually prioritise economic growth. Second, properly understood economic growth is a great and wonderful thing that we should want more of.