by Eric J. Weiner
 What is commonsense to most people who received a K-12 public education in the United States is that every formal system of state schooling throughout the modern world is designed to educate its students to develop, what Charles Lemert calls “sociologically competencies” within whatever ideological system is dominating at the time of their schooling. People correctly assume that children going to school during the Weimar Republic, for example, were educated to function competently within that ideological system. Children who were in school during the reign of Chairman Mao in the People’s Republic of China were educated to function competently within that system. Children in China today are educated to be sociologically competent in China’s current government and economic system. Children in France, Spain, Portugal, Israel, Mexico, Argentina, Brazil, and Iran likewise are educated to function competently in those systems. In the Soviet Union, children were educated to function within its version of communism. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, children were required to learn different civic knowledge and skills in order to be competent within the newly emerging political ideologies of reformed nation states.
What is commonsense to most people who received a K-12 public education in the United States is that every formal system of state schooling throughout the modern world is designed to educate its students to develop, what Charles Lemert calls “sociologically competencies” within whatever ideological system is dominating at the time of their schooling. People correctly assume that children going to school during the Weimar Republic, for example, were educated to function competently within that ideological system. Children who were in school during the reign of Chairman Mao in the People’s Republic of China were educated to function competently within that system. Children in China today are educated to be sociologically competent in China’s current government and economic system. Children in France, Spain, Portugal, Israel, Mexico, Argentina, Brazil, and Iran likewise are educated to function competently in those systems. In the Soviet Union, children were educated to function within its version of communism. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, children were required to learn different civic knowledge and skills in order to be competent within the newly emerging political ideologies of reformed nation states.
For people educated in the United States, the connection to ideology and schooling is obvious except when it comes to their own perception of the kind of public schooling they and/or their children received. At most, people might blame the educational system for being too liberal or too conservative, but to recognize the constitutive connection between schooling and ideology goes too far. Ideology is something that defines other governmental and educational systems, not their own. Ironically, this points to the deep level of ideological indoctrination that state schools have helped to achieve over several generations in the United States. Fueled by the complimentary discourses of choice, individualism, and Judeo-Christian morality, the connection between ideology and schooling is hidden in plain sight behind a translucent veil of American exceptionalism. What we are left with is an education system that teaches students to believe in an illusion of freedom, while disciplining what Michel Foucault famously called docile bodies and obedient minds. Read more »


 Notwithstanding the spread of English as a global lingua franca, translation continues to be a vital component of international relations, whether political, commercial, or cultural. In certain cases, translation is also necessary nationally, for instance in countries comprising more than one significant linguistic group. This is so in Switzerland, which voted by an overwhelming majority in 1938 to add a fourth national tongue to thwart the irredentist aspirations of its Italian neighbor, and which in certain contexts is obliged to use a Latin version of its own name (Confoederatio Helvetica) to avoid favoring one language group over another.
Notwithstanding the spread of English as a global lingua franca, translation continues to be a vital component of international relations, whether political, commercial, or cultural. In certain cases, translation is also necessary nationally, for instance in countries comprising more than one significant linguistic group. This is so in Switzerland, which voted by an overwhelming majority in 1938 to add a fourth national tongue to thwart the irredentist aspirations of its Italian neighbor, and which in certain contexts is obliged to use a Latin version of its own name (Confoederatio Helvetica) to avoid favoring one language group over another. If you listen to that track as featured in the mix, my judgment may seem a little harsh. The track is on the static side, but that’s hardly a fault in the context: the textures are lovely, and there’s plenty of movement; and at under four minutes it can’t really be said to overstay its welcome. A minor work, perhaps, but as a brief linking interlude it works perfectly well. So what’s the problem?
If you listen to that track as featured in the mix, my judgment may seem a little harsh. The track is on the static side, but that’s hardly a fault in the context: the textures are lovely, and there’s plenty of movement; and at under four minutes it can’t really be said to overstay its welcome. A minor work, perhaps, but as a brief linking interlude it works perfectly well. So what’s the problem?
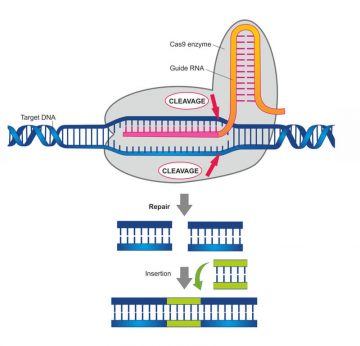 front of some her UC Berkeley colleagues, Doudna shared, “a story … about some research … that led in an unexpected direction … ” producing “ … some science that has profound implications going forward…but also makes us really think about what it means to be human and what it means to have the power to manipulate the very code of life …”
front of some her UC Berkeley colleagues, Doudna shared, “a story … about some research … that led in an unexpected direction … ” producing “ … some science that has profound implications going forward…but also makes us really think about what it means to be human and what it means to have the power to manipulate the very code of life …” He is an enigma. He sits up there in his marble chair, set in a Greek temple, literally larger than life, and he defies us to understand him.
He is an enigma. He sits up there in his marble chair, set in a Greek temple, literally larger than life, and he defies us to understand him.

 There should be more.
There should be more. So, here’s a game. Try to imagine: “What unbelievable moral achievements might humanity witness a century from now?” Now, discuss.
So, here’s a game. Try to imagine: “What unbelievable moral achievements might humanity witness a century from now?” Now, discuss. The translated versions from Tamil into English of Perumal Murugan’s two books, One Part Woman and the The Story of A Goat, weave stories of the complex life of the rural people of South India in an engaging and highly readable form.
The translated versions from Tamil into English of Perumal Murugan’s two books, One Part Woman and the The Story of A Goat, weave stories of the complex life of the rural people of South India in an engaging and highly readable form. Jack Youngerman. Long March II, 1965.
Jack Youngerman. Long March II, 1965. The political philosophy, and more importantly, political practice that took root in the wake of the ‘Age of Revolutions’ (say 1775-1848) was liberalism of various kinds: a commitment to certain principles and practices that eventually came to seem, like any successful ideology, a kind of common sense. With this, however, came a growing sense of dissatisfaction with what it seemed to represent: ‘bourgeois society’. Here is a paradox: at the very point at which the Enlightenment promise of the free society seemed to be coming true, discontent with that promise, or with the way it was being fulfilled, took hold. This was a sense that the modern citizen and subject was somehow still unfree. If this seems at least an aspect of how things stand with us in 2020 it might be worth looking back, for doubts about the liberal project have accompanied it since its inception.
The political philosophy, and more importantly, political practice that took root in the wake of the ‘Age of Revolutions’ (say 1775-1848) was liberalism of various kinds: a commitment to certain principles and practices that eventually came to seem, like any successful ideology, a kind of common sense. With this, however, came a growing sense of dissatisfaction with what it seemed to represent: ‘bourgeois society’. Here is a paradox: at the very point at which the Enlightenment promise of the free society seemed to be coming true, discontent with that promise, or with the way it was being fulfilled, took hold. This was a sense that the modern citizen and subject was somehow still unfree. If this seems at least an aspect of how things stand with us in 2020 it might be worth looking back, for doubts about the liberal project have accompanied it since its inception.

 As she returned to her country after eight years of self-imposed exile in Dubai, Benazir reflected in her posthumously-published memoir
As she returned to her country after eight years of self-imposed exile in Dubai, Benazir reflected in her posthumously-published memoir  Gibraltar in the background, I pose sideways, wearing a Spanish Chrysanthemum claw in my hair, gitana style, taking a dare from my husband. The photo is from an August afternoon, captured in the sun’s manic glare. My shadow in profile, with the oversized flower behind my ear, mirrors the shape of Gibraltar, Jabl ut Tariq or “Tariq’s rock.” An actual visit to Gibraltar is more than a decade ahead in the future. I would spend years researching the civilization of al Andalus (Muslim Spain, 711-1492) and publish a book about the convivencia of the Abrahamic people before finally setting foot on Gibraltar. “In Cordoba,” I write, “I’m inside the tremor of exile— the primeval, paramount home of poetry” and that “I am drawn to the world of al Andalus because it is a gift of exiles, a celebration of the cusp and of plural identities, the meeting point of three continents and three faiths, where the drama of boundaries and their blurring took place.” At the heart of this pursuit is my own story, one that is illuminated only recently when I see in Gibraltar more facets of my own exile and encounter with borders.
Gibraltar in the background, I pose sideways, wearing a Spanish Chrysanthemum claw in my hair, gitana style, taking a dare from my husband. The photo is from an August afternoon, captured in the sun’s manic glare. My shadow in profile, with the oversized flower behind my ear, mirrors the shape of Gibraltar, Jabl ut Tariq or “Tariq’s rock.” An actual visit to Gibraltar is more than a decade ahead in the future. I would spend years researching the civilization of al Andalus (Muslim Spain, 711-1492) and publish a book about the convivencia of the Abrahamic people before finally setting foot on Gibraltar. “In Cordoba,” I write, “I’m inside the tremor of exile— the primeval, paramount home of poetry” and that “I am drawn to the world of al Andalus because it is a gift of exiles, a celebration of the cusp and of plural identities, the meeting point of three continents and three faiths, where the drama of boundaries and their blurring took place.” At the heart of this pursuit is my own story, one that is illuminated only recently when I see in Gibraltar more facets of my own exile and encounter with borders.