by Scott F. Aikin and Robert B. Talisse

One way to think about argument is to think of it as a fight. In fact, it’s the default interpretation of how things went if someone reports that they’d had an argument with a neighbor or a colleague. If it’s an argument, that means things got sideways.
In logic, though, arguments are distinguished from fights and quarrels. Arguments, as collections of claims, have a functional feature of being divisible into premises and conclusions (with the former supporting the latter), and they have consequent functional features of being exchanges of reasons for the sake of identifying outcomes acceptable to all. So arguments play both pragmatic and epistemic roles – they aim to resolve disagreements and identify what’s true. The hope is that with good argument, we get both.
If argument has that resolution-aspiring and truth-seeking core, is there any room for adversariality in it? There are two reasons to think it has to. One has to do with the pragmatic background for argument – if it’s going to be in the service of establishing a resolution, then the resolved sides must have had fair and complete representation in the process. Otherwise, it’s resolution in name only. That seems clear.
The second reason has to do with how reasons work in general. Read more »

 The United States continues to be virtually the
The United States continues to be virtually the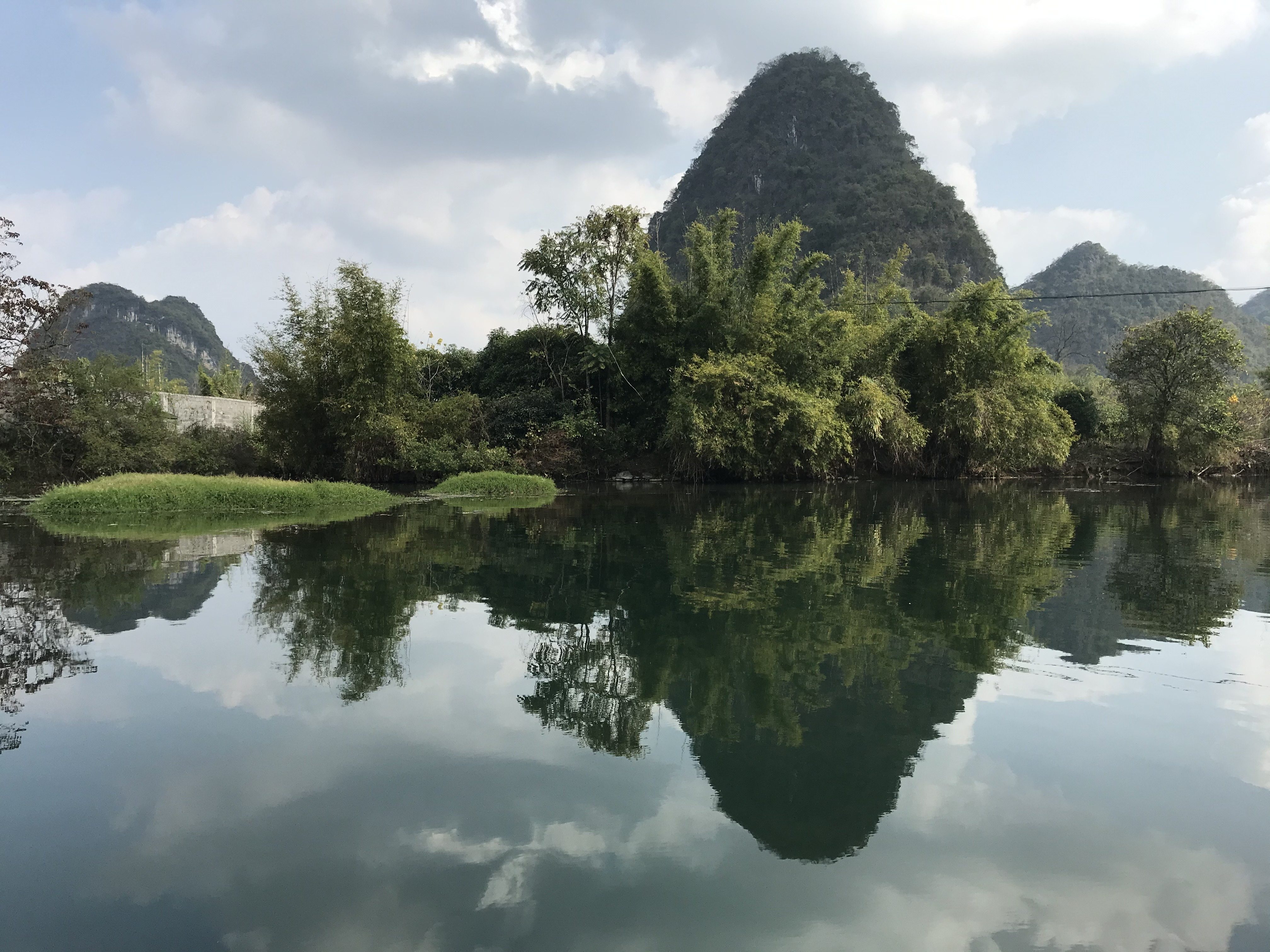  Sughra Raza. Rorschach on the River Li. Yangshuo, China, January, 2020.
Sughra Raza. Rorschach on the River Li. Yangshuo, China, January, 2020. While you might not break into a neighbor’s house to log onto your Facebook account if your internet were down, a case can be made that many of us are victims of at least a moderate behavioral addiction when it comes to our smartphones. At the playground with our kids, we’re on our phones. At dinner with friends, we’re on our phones. In the middle of the night. At the movies. At a concert. At a funeral. (I was recently at a memorial service for my friend’s mother, and someone’s cell phone rang during my friend’s reminiscence.)
While you might not break into a neighbor’s house to log onto your Facebook account if your internet were down, a case can be made that many of us are victims of at least a moderate behavioral addiction when it comes to our smartphones. At the playground with our kids, we’re on our phones. At dinner with friends, we’re on our phones. In the middle of the night. At the movies. At a concert. At a funeral. (I was recently at a memorial service for my friend’s mother, and someone’s cell phone rang during my friend’s reminiscence.)

 When Vienna‘s Albertina Museum exhibition of works by Albrecht Dürer ended in January 2020, it seemed quite possible that several of the masterpieces on display might never again be seen by the public, among them The Great Piece of Turf. This may sound like a dire prediction for a fragile work that is routinely exhibited every decade or so, but as the UN announced recently, we may already have passed the tipping point in the race to save our world and ourselves. A decade from now we may be too engaged in the struggle to survive to focus our attention on a small, exquisite watercolor created 500 years ago.
When Vienna‘s Albertina Museum exhibition of works by Albrecht Dürer ended in January 2020, it seemed quite possible that several of the masterpieces on display might never again be seen by the public, among them The Great Piece of Turf. This may sound like a dire prediction for a fragile work that is routinely exhibited every decade or so, but as the UN announced recently, we may already have passed the tipping point in the race to save our world and ourselves. A decade from now we may be too engaged in the struggle to survive to focus our attention on a small, exquisite watercolor created 500 years ago.
 During my late 1970s New York City childhood, repeats of Star Trek aired every weeknight on channel 11, WPIX. The original 79 episodes ran about three times per year, which means that, allowing for the occasional miss, I’d seen each episode about 10 – 12 times before reaching high school.
During my late 1970s New York City childhood, repeats of Star Trek aired every weeknight on channel 11, WPIX. The original 79 episodes ran about three times per year, which means that, allowing for the occasional miss, I’d seen each episode about 10 – 12 times before reaching high school. For the last three years, I have struggled with a dilemma: As a reasonable, quite liberal person, what should I think of my 60 million fellow Americans who voted for Donald Trump in 2016, and the vast majority of whom continue to support him today? Normally, a personal dilemma is a private thing, not a topic for public airing, but I feel that this particular problem is one the vexes many others – perhaps even a majority of Americans, as more of us voted for Hillary Clinton and many did not vote at all. Since that bleak day in November 2016, an unspoken – and sometimes loudly spoken – question hangs in the air: What kind of “
For the last three years, I have struggled with a dilemma: As a reasonable, quite liberal person, what should I think of my 60 million fellow Americans who voted for Donald Trump in 2016, and the vast majority of whom continue to support him today? Normally, a personal dilemma is a private thing, not a topic for public airing, but I feel that this particular problem is one the vexes many others – perhaps even a majority of Americans, as more of us voted for Hillary Clinton and many did not vote at all. Since that bleak day in November 2016, an unspoken – and sometimes loudly spoken – question hangs in the air: What kind of “ In November 1918, a 17-year-student from Rome sat for the entrance examination of the Scuola Normale Superiore in Pisa, Italy’s most prestigious science institution. Students applying to the institute had to write an essay on a topic that the examiners picked. The topics were usually quite general, so the students had considerable leeway. Most students wrote about well-known subjects that they had already learnt about in high school. But this student was different. The title of the topic he had been given was “Characteristics of Sound”, and instead of stating basic facts about sound, he “set forth the partial differential equation of a vibrating rod and solved it using Fourier analysis, finding the eigenvalues and eigenfrequencies. The entire essay continued on this level which would have been creditable for a doctoral examination.” The man writing these words was the 17-year-old’s future student, friend and Nobel laureate, Emilio Segre. The student was Enrico Fermi. The examiner was so startled by the originality and sophistication of Fermi’s analysis that he broke precedent and invited the boy to meet him in his office, partly to make sure that the essay had not been plagiarized. After convincing himself that Enrico had done the work himself, the examiner congratulated him and predicted that he would become an important scientist.
In November 1918, a 17-year-student from Rome sat for the entrance examination of the Scuola Normale Superiore in Pisa, Italy’s most prestigious science institution. Students applying to the institute had to write an essay on a topic that the examiners picked. The topics were usually quite general, so the students had considerable leeway. Most students wrote about well-known subjects that they had already learnt about in high school. But this student was different. The title of the topic he had been given was “Characteristics of Sound”, and instead of stating basic facts about sound, he “set forth the partial differential equation of a vibrating rod and solved it using Fourier analysis, finding the eigenvalues and eigenfrequencies. The entire essay continued on this level which would have been creditable for a doctoral examination.” The man writing these words was the 17-year-old’s future student, friend and Nobel laureate, Emilio Segre. The student was Enrico Fermi. The examiner was so startled by the originality and sophistication of Fermi’s analysis that he broke precedent and invited the boy to meet him in his office, partly to make sure that the essay had not been plagiarized. After convincing himself that Enrico had done the work himself, the examiner congratulated him and predicted that he would become an important scientist.

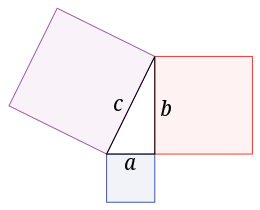 I have some very simple New Year’s resolutions, and some that require an entire column to spell out. One example of the latter is that I want to make a subtle but meaningful change in how I talk to my (middle and high school) math students about proofs.
I have some very simple New Year’s resolutions, and some that require an entire column to spell out. One example of the latter is that I want to make a subtle but meaningful change in how I talk to my (middle and high school) math students about proofs.