by Michael Klenk
Manipulation often seems to involve a hidden influence. Manipulators are pushing the emotional buttons of their unsuspecting victims, exploiting their subconscious habits and leading them astray. That view of manipulation explains a lot of the current moral outrage about digital technology and the companies behind it. Digital technologies provide the unprecedented potential for hidden influence, and, therefore, pose a manipulation threat, or so the argument goes.

But the hidden influence view of manipulation is false. Manipulation neither requires hidden influence, nor is hidden influence sufficient for manipulation. For example, guilt-tripping is manipulative and also often clear as the day. When your partner who wants to go hiking, knowing that you don’t, has already packed the car with the beaming kids, it becomes hard to say no. You are being manipulated, but it is obvious to everyone what is going on. Conversely, hidden influence does not automatically make an interaction manipulative. For example, you may simply fail to attend to the actions of a nurse assisting in operation on you. So the nurse’s influence on you remains hidden, but that does not make it manipulative. Thus, the hidden influence view is inadequate to characterise and understand interpersonal manipulation. Manipulation may sometimes be hidden, but often it is not.
Therefore, we need a better understanding of manipulation. We cannot just rely on the fact that some interpersonal influence is hidden to determine whether we have a case of manipulation. Why care? Because understanding manipulation is crucial in the current critical debate about digital technologies in moral philosophy and related disciplines. Read more »

 1. As the coronavirus continues to disrupt human life in many corners of the globe, a phrase from George Frideric Handel’s Messiah has wormed its way through the background noise of my attention span. It occurs in a Part III
1. As the coronavirus continues to disrupt human life in many corners of the globe, a phrase from George Frideric Handel’s Messiah has wormed its way through the background noise of my attention span. It occurs in a Part III  We get half a sunny day every other day since Corona has coaxed us to quit public spaces. In the past fortnight or so, sunlight has been in short supply just as masks, disinfectant spray and toilet paper. When the sun is out, it’s no ordinary gift; it brings a rush of joy that wipes out not only the free-floating, dystopic COVID -19 anxiety, but also the other recent traumas we’ve faced as a family. Indoors, socially-distant by three feet, hunched over our phones for news of loved ones, we forget it is spring, but mornings the sunlight hits the windows feel as if God has turned on the power-wash setting: one is shocked into vigor, tricked into optimism. On such a day, I step down the patio threshold as if pulled by a magnet; just out of the shower and still combing my wet hair, I’m suddenly aware of another gift— soap.
We get half a sunny day every other day since Corona has coaxed us to quit public spaces. In the past fortnight or so, sunlight has been in short supply just as masks, disinfectant spray and toilet paper. When the sun is out, it’s no ordinary gift; it brings a rush of joy that wipes out not only the free-floating, dystopic COVID -19 anxiety, but also the other recent traumas we’ve faced as a family. Indoors, socially-distant by three feet, hunched over our phones for news of loved ones, we forget it is spring, but mornings the sunlight hits the windows feel as if God has turned on the power-wash setting: one is shocked into vigor, tricked into optimism. On such a day, I step down the patio threshold as if pulled by a magnet; just out of the shower and still combing my wet hair, I’m suddenly aware of another gift— soap.


 I was a minor mess in high school. Had no idea what to do with my curly hair. Unduly influenced by a childhood spent watching late ‘70s television, I stubbornly brushed it to the side in a vain attempt to straighten and shape it into a helmet à la The Six Million Dollar Man or countless B-actors on The Love Boat and Fantasy Island. I couldn’t muster any fashion beyond jeans, t-shirts, and Pumas. In the winter I wore a green army coat. In the summer it was shorts and knee high tube socks.
I was a minor mess in high school. Had no idea what to do with my curly hair. Unduly influenced by a childhood spent watching late ‘70s television, I stubbornly brushed it to the side in a vain attempt to straighten and shape it into a helmet à la The Six Million Dollar Man or countless B-actors on The Love Boat and Fantasy Island. I couldn’t muster any fashion beyond jeans, t-shirts, and Pumas. In the winter I wore a green army coat. In the summer it was shorts and knee high tube socks.
 I must admit that when I first flipped through Capitalism on Edge: How Fighting Precarity Can Achieve Radical Change Without Crisis or Utopia by Albena Azmanova, it did not look too inviting. The blurbs on the jacket did nothing to reassure me, suggesting that this was yet another post-Marxist critique of greedy capitalists and their enablers. As it turns out, it is, but in a way that is more interesting than I had assumed. As soon as I started reading the Introduction, I was gripped by the lucidity of ideas and clarity of the prose. For an academic text written from the perspective of Critical Theory, this is a wonderfully direct, incisive and insightful book. One does not need to agree with all the details of the analysis to find reading it a rewarding experience.
I must admit that when I first flipped through Capitalism on Edge: How Fighting Precarity Can Achieve Radical Change Without Crisis or Utopia by Albena Azmanova, it did not look too inviting. The blurbs on the jacket did nothing to reassure me, suggesting that this was yet another post-Marxist critique of greedy capitalists and their enablers. As it turns out, it is, but in a way that is more interesting than I had assumed. As soon as I started reading the Introduction, I was gripped by the lucidity of ideas and clarity of the prose. For an academic text written from the perspective of Critical Theory, this is a wonderfully direct, incisive and insightful book. One does not need to agree with all the details of the analysis to find reading it a rewarding experience.
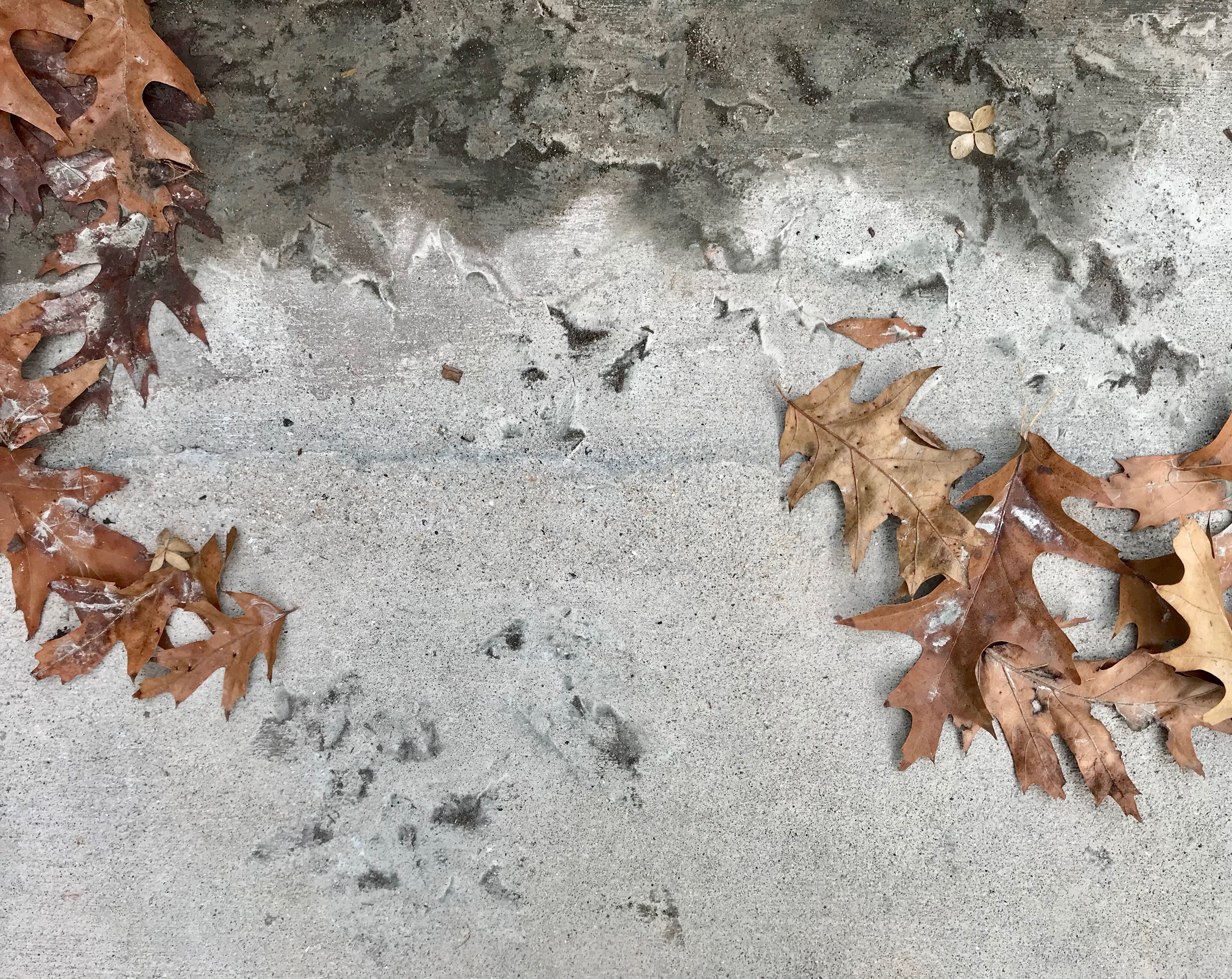 Sughra Raza. Mid-winter Fall. February 2020.
Sughra Raza. Mid-winter Fall. February 2020.

 If you, like me, have read premodern philosophers not just for antiquarian interest but also as possible sources of wisdom, you will probably have felt a certain awkwardness. Looking for guidance or assistance in ordering our own beliefs, attitudes and actions, we inevitably run into the problem that the great thinkers of the past knew nothing about what our world would look like.
If you, like me, have read premodern philosophers not just for antiquarian interest but also as possible sources of wisdom, you will probably have felt a certain awkwardness. Looking for guidance or assistance in ordering our own beliefs, attitudes and actions, we inevitably run into the problem that the great thinkers of the past knew nothing about what our world would look like.