by Thomas Larson

One late spring day in my twelfth-grade English class, my teacher carried a box up and down the aisles, handing each of the thirty students a new Signet Classic paperback. Mr. Demorest, who had a waddle under his chin and a doo-wop singer’s curve in his hairdo, said this novel might be tough reading and pledged plenty of mimeos. He said the school district had prepared us by reading, in previous grades, Silas Marner, Lord of the Flies, A Separate Peace, and The Scarlet Letter, whose baroque language (“Fruits, milk, freshest butter, will make thy fleshy tabernacle youthful”) brought a cascade of snickers from the back of the room. Demorest said that he’d taught this novel before, but he’d be reading it with us again, since with literature there was always more to glean. That word glean fell inside me like a coin tossed in a fountain. The novel was Thomas Hardy’s Tess of the D’Urbervilles.
Demorest said to get through the first 50 pages until Tess meets Alec. What’s the story? It’s about a girl becoming a woman. As we’ll see, she has a child by one man, Alec, runs from him and marries another, name of Angel. Angel is her true love but, fearful he’ll discover her dark secret on his own, confesses the child’s fate to him. Mortified, Angel abandons her, and she ends up with the first man again, with whom she is forced, for the sake of her family and her reputation (what’s left of it) to—well, you’ll see, he said. Don’t get hung up on the names of English villages. You might look up any Biblical allusions. Pay close attention to how the book makes you feel. Does it make you feel? Where in the story are you moved? Make a mark. Do you care what happens to Tess? Why? Think about it—what does Alec and Angel want from Tess and what does she want from these two men, opposites though they may be? Read more »


 Abstract: This article, written by the Digital Philosophy Group of TU Delft is inspired by the Netflix documentary The Social Dilemma. It is not a review of the show, but rather uses it as a lead to a wide-ranging philosophical piece on the ethics of digital technologies. The underlying idea is that the documentary fails to give an impression of how deep the ethical and social problems of our digital societies in the 21st century actually are; and it does not do sufficient justice to the existing approaches to rethinking digital technologies. The article is written, we hope, in an accessible and captivating style. In the first part (“the problems”), we explain some major issues with digital technologies: why massive data collection is not only a problem for privacy but also for democracy (“nothing to hide, a lot to lose”); what kind of knowledge AI produces (“what does the Big Brother really know”) and is it okay to use this knowledge in sensitive social domains (“the risks of artificial judgement”), why we cannot cultivate digital well-being individually (“with a little help from my friends”), and how digital tech may make persons less responsible and create a “digital Nuremberg”. In the second part (“The way forward”) we outline some of the existing philosophical approaches to rethinking digital technologies: design for values, comprehensive engineering, meaningful human control, new engineering education, and a global digital culture.
Abstract: This article, written by the Digital Philosophy Group of TU Delft is inspired by the Netflix documentary The Social Dilemma. It is not a review of the show, but rather uses it as a lead to a wide-ranging philosophical piece on the ethics of digital technologies. The underlying idea is that the documentary fails to give an impression of how deep the ethical and social problems of our digital societies in the 21st century actually are; and it does not do sufficient justice to the existing approaches to rethinking digital technologies. The article is written, we hope, in an accessible and captivating style. In the first part (“the problems”), we explain some major issues with digital technologies: why massive data collection is not only a problem for privacy but also for democracy (“nothing to hide, a lot to lose”); what kind of knowledge AI produces (“what does the Big Brother really know”) and is it okay to use this knowledge in sensitive social domains (“the risks of artificial judgement”), why we cannot cultivate digital well-being individually (“with a little help from my friends”), and how digital tech may make persons less responsible and create a “digital Nuremberg”. In the second part (“The way forward”) we outline some of the existing philosophical approaches to rethinking digital technologies: design for values, comprehensive engineering, meaningful human control, new engineering education, and a global digital culture. 
 Religion has always had an uneasy relationship with money-making. A lot of religions, at least in principle, are about charity and self-improvement. Money does not directly figure in seeking either of these goals. Yet one has to contend with the stark fact that over the last 500 years or so, Europe and the United States in particular acquired wealth and enabled a rise in people’s standard of living to an extent that was unprecedented in human history. And during the same period, while religiosity in these countries varied there is no doubt, especially in Europe, that religion played a role in people’s everyday lives whose centrality would be hard to imagine today. Could the rise of religion in first Europe and then the United States somehow be connected with the rise of money and especially the free-market system that has brought not just prosperity but freedom to so many of these nations’ citizens? Benjamin Friedman who is a professor of political economy at Harvard explores this fascinating connection in his book “Religion and the Rise of Capitalism”. The book is a masterclass on understanding the improbable links between the most secular country in the world and the most economically developed one.
Religion has always had an uneasy relationship with money-making. A lot of religions, at least in principle, are about charity and self-improvement. Money does not directly figure in seeking either of these goals. Yet one has to contend with the stark fact that over the last 500 years or so, Europe and the United States in particular acquired wealth and enabled a rise in people’s standard of living to an extent that was unprecedented in human history. And during the same period, while religiosity in these countries varied there is no doubt, especially in Europe, that religion played a role in people’s everyday lives whose centrality would be hard to imagine today. Could the rise of religion in first Europe and then the United States somehow be connected with the rise of money and especially the free-market system that has brought not just prosperity but freedom to so many of these nations’ citizens? Benjamin Friedman who is a professor of political economy at Harvard explores this fascinating connection in his book “Religion and the Rise of Capitalism”. The book is a masterclass on understanding the improbable links between the most secular country in the world and the most economically developed one.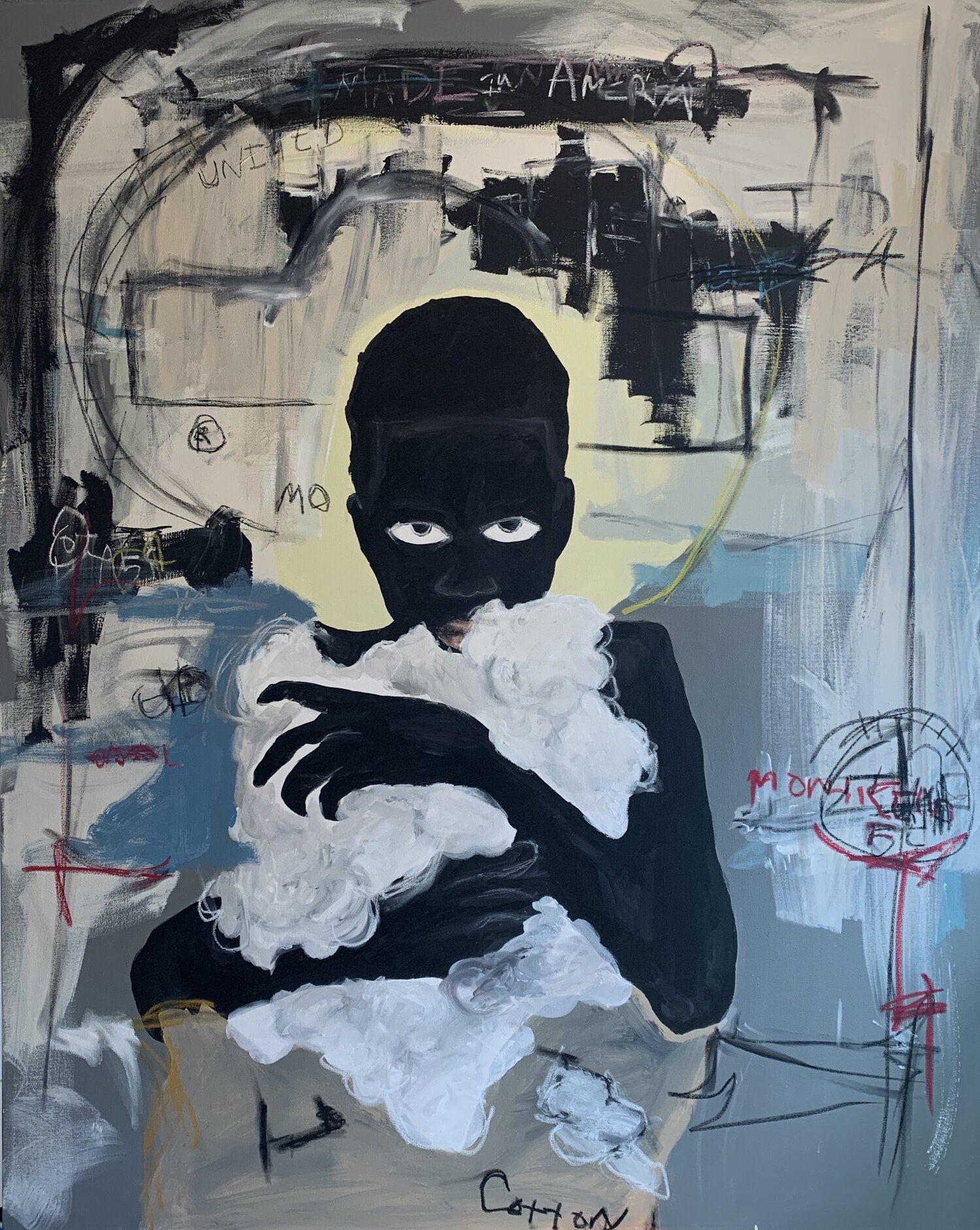
 Tragically, President Biden’s 21-page “
Tragically, President Biden’s 21-page “







 Jesus is reported to have critiqued the seventh commandment as follows:
Jesus is reported to have critiqued the seventh commandment as follows:  by Thomas R. Wells
by Thomas R. Wells