by Adele A Wilby
 In today’s political world where liberal democracy is purported to have triumphed and ‘the end of history’ is supposed to be with us, many people might be content to rest on their laurels that fascism has been confined to the dustbin of political history, and at most its supporters on the fringe of contemporary politics. Not so however, for Paul Mason. For him ‘fascism is back’ and poses a real threat to democracies. Indeed, so convinced is he of his argument that fascism is emerging as a force to be reckoned with, his recent book How to Stop Fascism: History, Ideology, Resistance is a call to arms for greater understanding of its modern manifestations, and to resist its influence in politics.
In today’s political world where liberal democracy is purported to have triumphed and ‘the end of history’ is supposed to be with us, many people might be content to rest on their laurels that fascism has been confined to the dustbin of political history, and at most its supporters on the fringe of contemporary politics. Not so however, for Paul Mason. For him ‘fascism is back’ and poses a real threat to democracies. Indeed, so convinced is he of his argument that fascism is emerging as a force to be reckoned with, his recent book How to Stop Fascism: History, Ideology, Resistance is a call to arms for greater understanding of its modern manifestations, and to resist its influence in politics.
An award-winning writer, Mason has many books to his credit. He is also a broadcaster and filmmaker and his reporting on events during the Greek debt crisis in 2015 while working as the Economics Editor for Channel 4 for several years, are memorable. But Mason is also one of those human beings who matches his intellectual work with political activism. He has been a relentless political activist with decades of resistance to fascism behind him that gives him the edge over the topic he takes on in the book: he has been exposed to the phenomenon and is familiar with fascism in political activist terms. Read more »

 In
In 
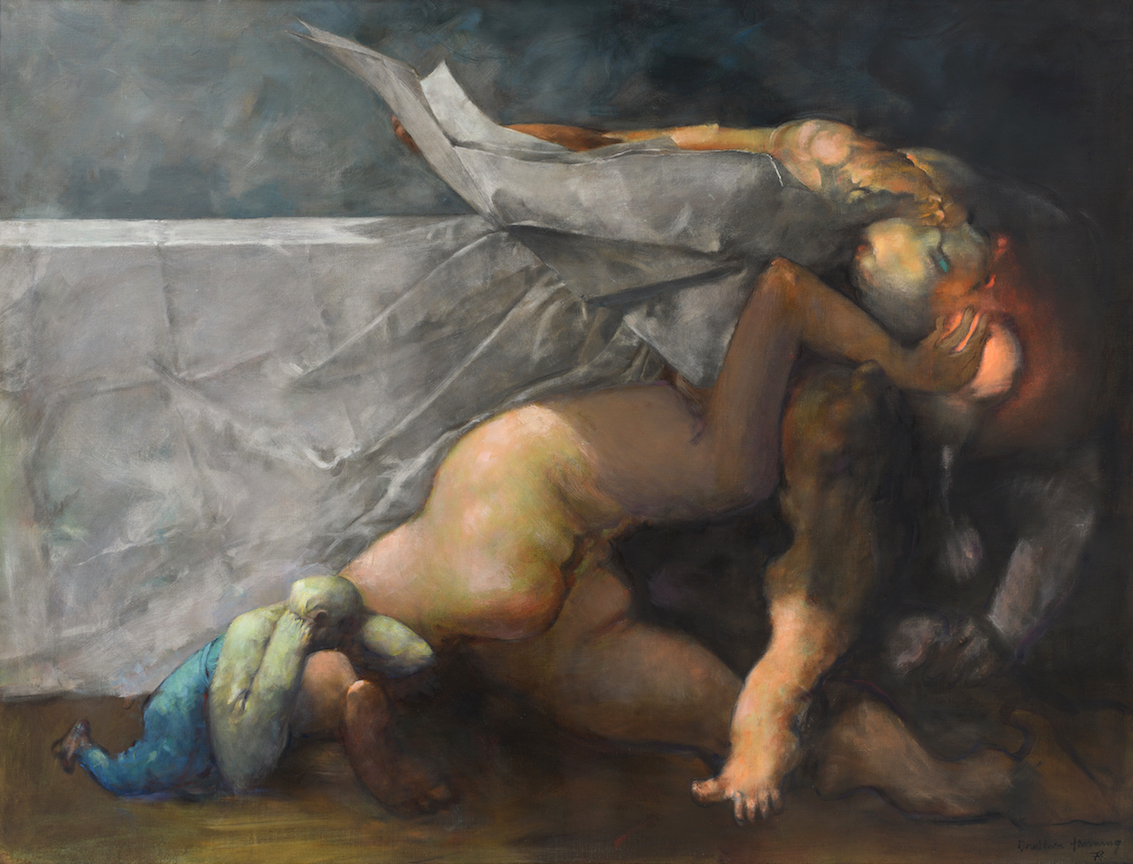 Dorothea Tanning. Notes for An Apocalypse, 1978.
Dorothea Tanning. Notes for An Apocalypse, 1978.




 Covid has given rise to a variety of counterintuitive mathematical outcomes. A good example is this recent headline (link below): One third of those hospitalized in Massachusetts are vaccinated. Anti-vaxxers have seized on this and similar such factually accurate headlines to bolster their positions. They, and others as well, interpret them as evidence that the vaccine isn’t that effective or perhaps hardly works at all since even states with very high vaccination rates seem to have many breakthrough infections that lead to hospitalization. Contrary to intuition, however, such truthful headlines actually indicate that the vaccine is very effective. I could cite common cognitive biases, Bayes’ theorem, graphs, tables, and formulas to explain this, but a metaphor involving fruit may be more convincing and more palatable.
Covid has given rise to a variety of counterintuitive mathematical outcomes. A good example is this recent headline (link below): One third of those hospitalized in Massachusetts are vaccinated. Anti-vaxxers have seized on this and similar such factually accurate headlines to bolster their positions. They, and others as well, interpret them as evidence that the vaccine isn’t that effective or perhaps hardly works at all since even states with very high vaccination rates seem to have many breakthrough infections that lead to hospitalization. Contrary to intuition, however, such truthful headlines actually indicate that the vaccine is very effective. I could cite common cognitive biases, Bayes’ theorem, graphs, tables, and formulas to explain this, but a metaphor involving fruit may be more convincing and more palatable. Growing up in India I knew how hierarchical and status-oriented Indian society was, but the city of New Delhi took it to a bureaucratic extreme. I was told that in those days, if you gave out your Government quarters address, people would immediately know your approximate salary scale. The city’s residential pattern, inherited from the colonial rulers, was highly structured. If you are a top Secretary in a Ministry, your assigned quarters will be a large bungalow with acres of gardens in prize real estate in the city center, often a short distance from your office which you traverse in a chauffeur-driven official car. But if you are a lowly clerk or an orderly/peon in the same office building, you’ll come in a crowded bus from many miles away often outside the city.
Growing up in India I knew how hierarchical and status-oriented Indian society was, but the city of New Delhi took it to a bureaucratic extreme. I was told that in those days, if you gave out your Government quarters address, people would immediately know your approximate salary scale. The city’s residential pattern, inherited from the colonial rulers, was highly structured. If you are a top Secretary in a Ministry, your assigned quarters will be a large bungalow with acres of gardens in prize real estate in the city center, often a short distance from your office which you traverse in a chauffeur-driven official car. But if you are a lowly clerk or an orderly/peon in the same office building, you’ll come in a crowded bus from many miles away often outside the city.







