by Omar Baig

Dave Chappelle grapples with the intractability of gender norms in The Closer: his most recent and final stand-up special for Netflix. Early into the set, Chappelle recounts the one-sided fight he had at a nightclub with a lesbian woman. When she interrupts his conversation with a female fan, Dave assumes they’re a jealous boyfriend. He deescalates the situation, however, once he realizes they are actually a jealous girlfriend; yet his unintentional misgendering only antagonizes her more. She reacts by squaring up in “a perfect southpaw stance” and throws the first punch. Chappelle reflexively dodges, then reacts in kind, by knocking “the toxic masculinity” out of her.
This, ladies and gentle-folx, is Edgelord comedy at its spiciest. Now, was it okay for Dave to misgender this woman, even unintentionally? No. Did Chappelle have to respond by, “softly and sweetly,” telling her: “Bitch, I’m about to slap the shit out of you!” Also, no. Yet was he justified in “tenderizing those titties like chicken cutlets,” in self-defense, once she threw that first punch? In my opinion, yes. This anecdote illustrates that toxic masculinity, like public acts of jealousy or public aggression, is not only limited to men. It also features two of The Closer’s recurring motifs: (1) Dave’s respect of others as reciprocal to their respect for his personal boundaries (i.e., irrespective of sexual or gender identity); or (2) by all the ways that performing informs his personal, social, and creative interactions. Read more »



 Everyone knows—or should know—how burdensome a pregnancy is on a woman. It’s especially hard now if you live in Texas where a fetal heartbeat detected at six weeks means by law the woman cannot terminate her pregnancy; she must carry it to term. The burden of having a child, whether planned for or forced, is made worse by the financial responsibility of raising that offspring, for parents and families, through childhood and adolescence, the next eighteen years. Would any man argue that such a load, for poor women in particular, is among the toughest things she’ll ever face?
Everyone knows—or should know—how burdensome a pregnancy is on a woman. It’s especially hard now if you live in Texas where a fetal heartbeat detected at six weeks means by law the woman cannot terminate her pregnancy; she must carry it to term. The burden of having a child, whether planned for or forced, is made worse by the financial responsibility of raising that offspring, for parents and families, through childhood and adolescence, the next eighteen years. Would any man argue that such a load, for poor women in particular, is among the toughest things she’ll ever face? When Robert Solow asked me in Cambridge if I’d like to join the faculty at MIT in the other Cambridge, I was taken aback, and asked for some time to think about it. Until then I never imagined living in the US, a country I had never visited before, and what I saw in Hollywood films was not always attractive. I was planning to go back to India where my aging parents, younger siblings, and the majority of my friends were.
When Robert Solow asked me in Cambridge if I’d like to join the faculty at MIT in the other Cambridge, I was taken aback, and asked for some time to think about it. Until then I never imagined living in the US, a country I had never visited before, and what I saw in Hollywood films was not always attractive. I was planning to go back to India where my aging parents, younger siblings, and the majority of my friends were.

 Someone described the US Federal Government as a huge insurance company that has its own army. There’s real truth to that description. The vast majority of the federal budget goes to Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid. Those entitlement programs take up about 65% of the federal budget, while the military takes up about 11% of the federal budget. The interest on the federal debt takes up another 8%, leaving only about 15% for “discretionary” spending. The money spent on the military is also considered discretionary but given our vast reach with hundreds of military bases in dozens of countries, voting to reduce the military budget much would be political suicide.
Someone described the US Federal Government as a huge insurance company that has its own army. There’s real truth to that description. The vast majority of the federal budget goes to Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid. Those entitlement programs take up about 65% of the federal budget, while the military takes up about 11% of the federal budget. The interest on the federal debt takes up another 8%, leaving only about 15% for “discretionary” spending. The money spent on the military is also considered discretionary but given our vast reach with hundreds of military bases in dozens of countries, voting to reduce the military budget much would be political suicide.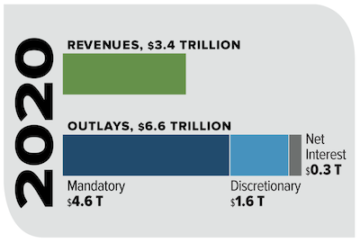 Last year the federal government took in $3.4 trillion of taxes and spent $6.6 trillion, nearly twice its revenues. A trillion dollars is a vast, almost inconceivable amount of money. And yet our government spends money in such cosmic sums that congresspeople and senators toss around the word trillion as if it’s the cost of a night’s stay in a Motel 8. Perhaps the two best quotes about casually spending and losing vast sums of money come from the late Texas oilman Nelson Bunker Hunt. When asked about his $1.7 billion losses after he tried to corner the silver market, he replied, “A billion dollars isn’t what it used to be.” Then at a congressional hearing when asked about his net worth, Hunt replied, “I don’t have the figures in my head. People who know how much they’re worth aren’t usually worth that much.”
Last year the federal government took in $3.4 trillion of taxes and spent $6.6 trillion, nearly twice its revenues. A trillion dollars is a vast, almost inconceivable amount of money. And yet our government spends money in such cosmic sums that congresspeople and senators toss around the word trillion as if it’s the cost of a night’s stay in a Motel 8. Perhaps the two best quotes about casually spending and losing vast sums of money come from the late Texas oilman Nelson Bunker Hunt. When asked about his $1.7 billion losses after he tried to corner the silver market, he replied, “A billion dollars isn’t what it used to be.” Then at a congressional hearing when asked about his net worth, Hunt replied, “I don’t have the figures in my head. People who know how much they’re worth aren’t usually worth that much.”  Tanya Goel. Mechanisms 3, 2019.
Tanya Goel. Mechanisms 3, 2019.


 Clairvoyant of the Small, Susan Bernofsky’s long-awaited biography of the Swiss modernist writer Robert Walser, is erudite, painstakingly thorough, and sensitively written. Readers of Walser finally have a volume that connects the development of the writer’s work and its publishing history to the various episodes of his peripatetic adult life in the cities of Biel, Bern, Zurich, Berlin, and finally the sanatoriums in Waldau and later Herisau, where Walser—revered by Franz Kafka and Max Brod, Walter Benjamin, W. G. Sebald, and many others—presumably ceased writing altogether.
Clairvoyant of the Small, Susan Bernofsky’s long-awaited biography of the Swiss modernist writer Robert Walser, is erudite, painstakingly thorough, and sensitively written. Readers of Walser finally have a volume that connects the development of the writer’s work and its publishing history to the various episodes of his peripatetic adult life in the cities of Biel, Bern, Zurich, Berlin, and finally the sanatoriums in Waldau and later Herisau, where Walser—revered by Franz Kafka and Max Brod, Walter Benjamin, W. G. Sebald, and many others—presumably ceased writing altogether.

 Men have always wanted to fly to the moon and stars. We wanted to find out what was up there on the moon and planets? Was it heaven? Were there angels? Or were these worlds inhabited by strange creatures who built canals? We looked up, we used telescopes. We watched the stars and charted their movements. But we wanted to do more than look and imagine; we wanted to go up there and see for ourselves? The birds could fly, why couldn’t we?
Men have always wanted to fly to the moon and stars. We wanted to find out what was up there on the moon and planets? Was it heaven? Were there angels? Or were these worlds inhabited by strange creatures who built canals? We looked up, we used telescopes. We watched the stars and charted their movements. But we wanted to do more than look and imagine; we wanted to go up there and see for ourselves? The birds could fly, why couldn’t we?

 Imagine a world where the prison population was a rough mirror of wider society. In such a world there is a similar spread of rich and poor, highly educated and less educated, as well as a roughly equal proportion of men and women and those from deprived areas and well-off areas. The proportions of different ethnic groups reflect those in the surrounding society, as does the age profile, and having a mental health problem bears no relation to the likelihood of being in prison, neither does being in care in any systematic way increase the chances of ending up as a young offender. In addition, there seems to be no pattern from year to year. Some years there are low levels of crime and in other years the crime rate jumps for no discernible reason. The random nature of the prison population is recognised as providing good evidence for the belief that criminality is simply a result of individuals using their free will to make bad decisions, since we are all equally capable of this. After all, it could be argued, everyone is equal in possessing free will, and crime is a conscious and fully autonomous act in which social and psychological conditions play little part. Anyone, the argument goes, can be selfish or greedy and so succumb to criminality. In such a world, the general view is that prison exists to teach these individuals the error of their ways by providing them with extra motivation to retain their self-control next time temptation beckons.
Imagine a world where the prison population was a rough mirror of wider society. In such a world there is a similar spread of rich and poor, highly educated and less educated, as well as a roughly equal proportion of men and women and those from deprived areas and well-off areas. The proportions of different ethnic groups reflect those in the surrounding society, as does the age profile, and having a mental health problem bears no relation to the likelihood of being in prison, neither does being in care in any systematic way increase the chances of ending up as a young offender. In addition, there seems to be no pattern from year to year. Some years there are low levels of crime and in other years the crime rate jumps for no discernible reason. The random nature of the prison population is recognised as providing good evidence for the belief that criminality is simply a result of individuals using their free will to make bad decisions, since we are all equally capable of this. After all, it could be argued, everyone is equal in possessing free will, and crime is a conscious and fully autonomous act in which social and psychological conditions play little part. Anyone, the argument goes, can be selfish or greedy and so succumb to criminality. In such a world, the general view is that prison exists to teach these individuals the error of their ways by providing them with extra motivation to retain their self-control next time temptation beckons.