Alan Burdick in The New Yorker:
 In 2005, Barry Marshall, an Australian gastroenterologist and researcher, shared the Nobel Prize in Medicine for the discovery that peptic ulcers are caused not by stress, as was commonly thought, but by a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori. (Marshall, the director of the Marshall Centre for Infectious Diseases Research and Training, at the University of Western Australia, proved this in part by ingesting H. pylori himself and becoming ill.) The finding meant that ulcers could be treated with antibiotics, and it has made stomach cancer, often associated with ulcers, a rarity in developed countries.
In 2005, Barry Marshall, an Australian gastroenterologist and researcher, shared the Nobel Prize in Medicine for the discovery that peptic ulcers are caused not by stress, as was commonly thought, but by a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori. (Marshall, the director of the Marshall Centre for Infectious Diseases Research and Training, at the University of Western Australia, proved this in part by ingesting H. pylori himself and becoming ill.) The finding meant that ulcers could be treated with antibiotics, and it has made stomach cancer, often associated with ulcers, a rarity in developed countries.
Marshall has also spent considerable time confronting another common gut ailment, irritable-bowel syndrome, or I.B.S. “It occupies about thirty per cent of my practice,” he told me recently. I.B.S. is a complex of conditions that is defined mainly by its broad array of symptoms, which can include stomach pain, bloating, cramps, diarrhea, constipation, or any combination thereof; eleven per cent of Americans suffer from it. “It’s a diagnosis of exclusion,” Marshall said, meaning that it’s the vague category of what’s left over when more serious possibilities are ruled out. As a result, patients often must endure a steeplechase of uncomfortable tests—colonoscopies, biopsies, stool samples—only to learn, months later, that they have I.B.S., which can be treated with medicine, changes in diet, or both.
Marshall now thinks he’s found a way to diagnose I.B.S. quickly and directly: by listening to it. Earlier this week, at the annual Digestive Disease Week conference, in Washington, D.C., Marshall described a device that he and colleagues are developing: a wide belt, to be worn by the patient, that records the creaks and undulations of the gut, analyzes them with software, and recognizes the distinct sonic signature of I.B.S. For centuries, physicians have used their ears to pick up hints of trouble in the heart and lungs. In theory, I.B.S. should succumb to a similar approach. Marshall described the ailment as “a motility problem”—an abnormal movement of matter and gases through the intestines, producing a wild range of sounds as the bowel squeezes harder or softly at different times in different places. But the gut, unlike the heart or lungs, is more than twenty feet long, and, although physicians can listen to it, “they don’t listen long enough, and it’s hard to know what to listen for,” Marshall said. He began to imagine a high-tech gadget that could listen for a couple of hours, parse the many frequency patterns, and analyze the results. “That was just a concept,” Marshall said. “When we started, it wasn’t obvious that this would work.”
Marshall drew his inspiration, in part, from his son, who helps analyze seismic data from the seabed for hints of undiscovered reserves of petroleum.
More here.


 The second-worst thing about cancer chairs is that they are attached to televisions. Someone somewhere is always at war with silence. It’s impossible to read, so I answer email, or watch some cop drama on my computer, or, if it seems unavoidable, explore the lives of my nurses. A trip to Cozumel with old girlfriends, a costume party with political overtones, an advanced degree on the internet: they’re all the same, these lives, which is to say that the nurses tell me nothing, perhaps because amid the din and pain it’s impossible to say anything of substance, or perhaps because they know that nothing is precisely what we both expect. It’s the very currency of the place. Perhaps they are being excruciatingly candid.
The second-worst thing about cancer chairs is that they are attached to televisions. Someone somewhere is always at war with silence. It’s impossible to read, so I answer email, or watch some cop drama on my computer, or, if it seems unavoidable, explore the lives of my nurses. A trip to Cozumel with old girlfriends, a costume party with political overtones, an advanced degree on the internet: they’re all the same, these lives, which is to say that the nurses tell me nothing, perhaps because amid the din and pain it’s impossible to say anything of substance, or perhaps because they know that nothing is precisely what we both expect. It’s the very currency of the place. Perhaps they are being excruciatingly candid. In 2005, Barry Marshall, an Australian gastroenterologist and researcher, shared the Nobel Prize in Medicine for the discovery that peptic ulcers are caused not by stress, as was commonly thought, but by a bacterium called
In 2005, Barry Marshall, an Australian gastroenterologist and researcher, shared the Nobel Prize in Medicine for the discovery that peptic ulcers are caused not by stress, as was commonly thought, but by a bacterium called  In his new book, The Drunken Silenus,
In his new book, The Drunken Silenus,  A pair of studies published this week is shedding light on the duration of immunity following COVID-19, showing patients lose their IgG antibodies—the virus-specific, slower-forming antibodies associated with long-term immunity—within weeks or months after recovery. With COVID-19, most people who become infected do
A pair of studies published this week is shedding light on the duration of immunity following COVID-19, showing patients lose their IgG antibodies—the virus-specific, slower-forming antibodies associated with long-term immunity—within weeks or months after recovery. With COVID-19, most people who become infected do  On Saturday, the
On Saturday, the In one of the twentieth century’s most memorable scenes from literature, a man is standing on a beach, pulling on a long rope that stretches out to sea. The rope is covered in thick seaweed. He yanks and tugs, and out of the foaming waves comes a horse’s head. It’s black and shiny and lies there at the water’s edge, its dead eyes staring while greenish eels slither from every orifice. The eels crawl out, shiny and entrails-like, more than two dozen of them; when the man has shoved them all into a potato sack, he pries open the horse’s grinning mouth, sticks his hands into its throat, and pulls out two more eels, as thick as his own arms.
In one of the twentieth century’s most memorable scenes from literature, a man is standing on a beach, pulling on a long rope that stretches out to sea. The rope is covered in thick seaweed. He yanks and tugs, and out of the foaming waves comes a horse’s head. It’s black and shiny and lies there at the water’s edge, its dead eyes staring while greenish eels slither from every orifice. The eels crawl out, shiny and entrails-like, more than two dozen of them; when the man has shoved them all into a potato sack, he pries open the horse’s grinning mouth, sticks his hands into its throat, and pulls out two more eels, as thick as his own arms. Until I read Howard Means’s Splash! and Bonnie Tsui’s Why We Swim, my main encounter with the history of the sport had been a Victorian-inspired swimming gala organised by members of my local team at north London’s Parliament Hill Lido. We competed in novelty races that predated the streamlining of swimming into a competitive sport, swimming upright holding umbrellas in one race, wearing blindfolds in another. We jumped into the pool in vintage dresses to see what it was like to swim hampered by heavy fabrics.
Until I read Howard Means’s Splash! and Bonnie Tsui’s Why We Swim, my main encounter with the history of the sport had been a Victorian-inspired swimming gala organised by members of my local team at north London’s Parliament Hill Lido. We competed in novelty races that predated the streamlining of swimming into a competitive sport, swimming upright holding umbrellas in one race, wearing blindfolds in another. We jumped into the pool in vintage dresses to see what it was like to swim hampered by heavy fabrics. Nothing—not even the Plague—has posed a more persistent threat to humanity than viral diseases: yellow fever, measles, and smallpox have been causing epidemics for thousands of years. At the end of the First World War, fifty million people died of the Spanish flu; smallpox may have killed half a billion during the twentieth century alone. Those viruses were highly infectious, yet their impact was limited by their ferocity: a virus may destroy an entire culture, but if we die it dies, too. As a result, not even smallpox possessed the evolutionary power to influence humans as a species—to alter our genetic structure. That would require an organism to insinuate itself into the critical cells we need in order to reproduce: our germ cells. Only retroviruses, which reverse the usual flow of genetic code from DNA to RNA, are capable of that. A retrovirus stores its genetic information in a single-stranded molecule of RNA, instead of the more common double-stranded DNA. When it infects a cell, the virus deploys a special enzyme, called reverse transcriptase, that enables it to copy itself and then paste its own genes into the new cell’s DNA. It then becomes part of that cell forever; when the cell divides, the virus goes with it. Scientists have long suspected that if a retrovirus happens to infect a human sperm cell or egg, which is rare, and if that embryo survives—which is rarer still—the retrovirus could take its place in the blueprint of our species, passed from mother to child, and from one generation to the next, much like a gene for eye color or asthma.
Nothing—not even the Plague—has posed a more persistent threat to humanity than viral diseases: yellow fever, measles, and smallpox have been causing epidemics for thousands of years. At the end of the First World War, fifty million people died of the Spanish flu; smallpox may have killed half a billion during the twentieth century alone. Those viruses were highly infectious, yet their impact was limited by their ferocity: a virus may destroy an entire culture, but if we die it dies, too. As a result, not even smallpox possessed the evolutionary power to influence humans as a species—to alter our genetic structure. That would require an organism to insinuate itself into the critical cells we need in order to reproduce: our germ cells. Only retroviruses, which reverse the usual flow of genetic code from DNA to RNA, are capable of that. A retrovirus stores its genetic information in a single-stranded molecule of RNA, instead of the more common double-stranded DNA. When it infects a cell, the virus deploys a special enzyme, called reverse transcriptase, that enables it to copy itself and then paste its own genes into the new cell’s DNA. It then becomes part of that cell forever; when the cell divides, the virus goes with it. Scientists have long suspected that if a retrovirus happens to infect a human sperm cell or egg, which is rare, and if that embryo survives—which is rarer still—the retrovirus could take its place in the blueprint of our species, passed from mother to child, and from one generation to the next, much like a gene for eye color or asthma.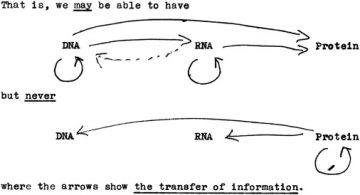 On May 13, 1961, two articles appeared in Nature, authored by a total of nine people, including Sydney Brenner, François Jacob and Jim Watson, announcing the isolation of messenger RNA (mRNA)
On May 13, 1961, two articles appeared in Nature, authored by a total of nine people, including Sydney Brenner, François Jacob and Jim Watson, announcing the isolation of messenger RNA (mRNA)  In Theory of the Gimmick (Harvard University Press, 2020), Ngai tracks the gimmick through a number of guises: stage props, wigs, stainless-steel banana slicers, temp agencies, fraudulent photographs, subprime loans, technological doodads, the novel of ideas. Across its many forms, the gimmick arouses our suspicion. When we say something is a gimmick, we mean it is overrated and deceptive, that you would have to be a sucker to fall for it. Yet gimmicks exert a strange hold on us. As with a magic show, we can enjoy the gimmick even while we know we are being tricked.
In Theory of the Gimmick (Harvard University Press, 2020), Ngai tracks the gimmick through a number of guises: stage props, wigs, stainless-steel banana slicers, temp agencies, fraudulent photographs, subprime loans, technological doodads, the novel of ideas. Across its many forms, the gimmick arouses our suspicion. When we say something is a gimmick, we mean it is overrated and deceptive, that you would have to be a sucker to fall for it. Yet gimmicks exert a strange hold on us. As with a magic show, we can enjoy the gimmick even while we know we are being tricked. Rome’s
Rome’s  A core principle of the academic movement that shot through elite schools in America since the early nineties was the view that individual rights, humanism, and the democratic process are all just stalking-horses for white supremacy. The concept, as articulated in books like former corporate consultant Robin DiAngelo’s White Fragility (Amazon’s
A core principle of the academic movement that shot through elite schools in America since the early nineties was the view that individual rights, humanism, and the democratic process are all just stalking-horses for white supremacy. The concept, as articulated in books like former corporate consultant Robin DiAngelo’s White Fragility (Amazon’s  O
O William James in turn experienced a vastation of his own. In Varieties of Religious Experience he provides a report by a ‘French correspondent’ – in reality, himself – that describes how on an ordinary evening, at twilight, ‘suddenly there fell upon me without warning, just as if it came out of darkness, a horrible fear of my own existence’. His terror became embodied in the image of an epileptic patient he had seen in an asylum, ‘like a sculptured Egyptian cat or Peruvian mummy, moving nothing but his black eyes … That shape am I.’
William James in turn experienced a vastation of his own. In Varieties of Religious Experience he provides a report by a ‘French correspondent’ – in reality, himself – that describes how on an ordinary evening, at twilight, ‘suddenly there fell upon me without warning, just as if it came out of darkness, a horrible fear of my own existence’. His terror became embodied in the image of an epileptic patient he had seen in an asylum, ‘like a sculptured Egyptian cat or Peruvian mummy, moving nothing but his black eyes … That shape am I.’