Daniela Gabor in Phenomenal World:
From the turbulent perch of the present, 2015 seems like a lifetime ago. That year, a trifecta of UN agreements announced transformative global ambitions on climate and development. In July 2015, 193 UN Member States agreed to the Addis Ababa Action Plan of the Third International Conference on Financing for Development (FfD3). Solving the financing question, the UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon stressed, provided “the foundation of a revitalized global partnership for sustainable development that will leave no one behind.” In September of that year, UN members signed the Agenda 2030 for Sustainable Development, a “broad and universal policy agenda” aiming to “transform our world” through a new set of Sustainable Development Goals. Then, the Paris Agreement in December marked a new direction in climate politics. Climate action was no longer synonymous with carbon pricing, but instead a long-term project of economic transformation.
The FfD3, the World Bank reported, was marked by “one stark difference from previous gatherings in Doha and Monterrey: unequivocal acceptance that the financing will have to come from private as well as public resources.” The change was inaugurated in part by the sheer force of a new Bank-created motto for financing development: “From Billions to Trillions.” Public, concessional funding in the billions could unlock trillions in private investment. To meet the aims of the social development goals, the Bank claimed, required trillions in financing, which could only materialize through “a paradigm shift… a financing framework capable of channelling resources and investments of all kinds—public and private, national, and global.” It was music to many ears, eager to hear that trillions of investment only required small amounts of public expenditure.
More here.
Enjoying the content on 3QD? Help keep us going by donating now.

 I skirted an abandoned development of some kind, half-built, its windows smashed, wild dogs on its concrete foundation barking at me not to come any closer…
I skirted an abandoned development of some kind, half-built, its windows smashed, wild dogs on its concrete foundation barking at me not to come any closer… OpenAI had stunned the world by releasing ChatGPT in November 2022, but it turns out that the researchers working on the technology were even more stunned at what they’d developed.
OpenAI had stunned the world by releasing ChatGPT in November 2022, but it turns out that the researchers working on the technology were even more stunned at what they’d developed. There is clearly a groundswell of anti-MAGA political energy across the country, and yet the most recent Quinnipiac University
There is clearly a groundswell of anti-MAGA political energy across the country, and yet the most recent Quinnipiac University  This Buddha — its head and shoulders the color of translucent flames, its torso pockmarked by wounds, its robes a rich burgundy — is the manifestation of an idea of art that’s both dazzlingly new and profoundly ancient. If you’ve not seen anything quite like it — well, neither have I. (It’s on show at the
This Buddha — its head and shoulders the color of translucent flames, its torso pockmarked by wounds, its robes a rich burgundy — is the manifestation of an idea of art that’s both dazzlingly new and profoundly ancient. If you’ve not seen anything quite like it — well, neither have I. (It’s on show at the  Ryan Reynolds is trying to focus on our conversation. But all he can think about is the script pulled up on his laptop. The screenwriting software Final Draft has frozen so he can’t plug in his latest ideas for a project that he has asked me not to share. He reluctantly abandons his computer but can’t help but fidget. Reynolds knows he’ll only have a few hours later to return to the story before he’s on dad duty. “I’m obsessive,” he says. “Even right now I’m thinking what I have after you, and if I can get back to it again.” His schedule after our interview is packed: a business meeting; someone is coming to fix Final Draft; then a walk-and-talk with Deadpool & Wolverine director Shawn Levy to discuss Levy’s upcoming Star Wars movie starring the other Ryan—Gosling.
Ryan Reynolds is trying to focus on our conversation. But all he can think about is the script pulled up on his laptop. The screenwriting software Final Draft has frozen so he can’t plug in his latest ideas for a project that he has asked me not to share. He reluctantly abandons his computer but can’t help but fidget. Reynolds knows he’ll only have a few hours later to return to the story before he’s on dad duty. “I’m obsessive,” he says. “Even right now I’m thinking what I have after you, and if I can get back to it again.” His schedule after our interview is packed: a business meeting; someone is coming to fix Final Draft; then a walk-and-talk with Deadpool & Wolverine director Shawn Levy to discuss Levy’s upcoming Star Wars movie starring the other Ryan—Gosling. According to the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, phenomenology is defined as the study of “the structure of various types of experience ranging from perception, thought, memory, imagination, emotion, desire, and volition to bodily awareness, embodied action, and social activity, including linguistic activity. The structure of these forms of experience typically involves what Husserl called ‘intentionality,’ that is, the directedness of experience toward things in the world, the property of consciousness that it is a consciousness of or about something.” That’s quite a load for a kiddie ride but let’s turn Porky loose and see what he can do.
According to the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, phenomenology is defined as the study of “the structure of various types of experience ranging from perception, thought, memory, imagination, emotion, desire, and volition to bodily awareness, embodied action, and social activity, including linguistic activity. The structure of these forms of experience typically involves what Husserl called ‘intentionality,’ that is, the directedness of experience toward things in the world, the property of consciousness that it is a consciousness of or about something.” That’s quite a load for a kiddie ride but let’s turn Porky loose and see what he can do. The virgin allegations emerged about a decade ago. Young people “are so sexually inactive that it practically boggles the mind,” a writer for Bustle
The virgin allegations emerged about a decade ago. Young people “are so sexually inactive that it practically boggles the mind,” a writer for Bustle  I don’t tell this story often, and have never told it in such detail publicly before. However, given our current moment of crisis in the United States, only a few months into the second Trump administration, it seems an important story to tell. It is a set of experiences that were horrible to live through, and yet, I would not be the person I am today had they not happened. Ultimately, the story is about power, leverage, and fear, and also about the potential for solidarity and love.
I don’t tell this story often, and have never told it in such detail publicly before. However, given our current moment of crisis in the United States, only a few months into the second Trump administration, it seems an important story to tell. It is a set of experiences that were horrible to live through, and yet, I would not be the person I am today had they not happened. Ultimately, the story is about power, leverage, and fear, and also about the potential for solidarity and love. We may still wonder why Balzac occupied so much space in James’s writing career and particularly in The Prefaces. In temperament and method the two were poles apart. But Balzac had come to represent for James something primal, fundamentally generative—more a natural phenomenon than an individual. The sculptor Gloriani, who appears in James’s first novel, Roderick Hudson, reappears in The Ambassadors, at the center of his garden in Paris, a man in touch with “the great world,” Strether thinks, a figure who has “something covertly tigerish” about him, compelling a stab of envy and admiration for “the glossy male tiger, magnificently marked.” This is the moment when Strether realizes, and tells little Bilham, “Live now! Live all you can; it’s a mistake not to . . . Live!” It’s difficult here to ignore Balzac as Gloriani’s progenitor, the figure that kept telling James to embrace life with more vital courage—and greater response to its magnificence. Gloriani appears again in “The Velvet Glove,” a short story of 1909, but he’s also present in metaphors like the beast in “The Beast in the Jungle,” in which John Marcher waits passively for Life’s big revelation to seize him—that was Strether’s mistake, too. Think of Balzac again when you read about James visiting Edith Wharton at The Mount in 1904 and reading aloud together Walt Whitman’s celebrations of “The Body Electric” with unselfconscious joy.
We may still wonder why Balzac occupied so much space in James’s writing career and particularly in The Prefaces. In temperament and method the two were poles apart. But Balzac had come to represent for James something primal, fundamentally generative—more a natural phenomenon than an individual. The sculptor Gloriani, who appears in James’s first novel, Roderick Hudson, reappears in The Ambassadors, at the center of his garden in Paris, a man in touch with “the great world,” Strether thinks, a figure who has “something covertly tigerish” about him, compelling a stab of envy and admiration for “the glossy male tiger, magnificently marked.” This is the moment when Strether realizes, and tells little Bilham, “Live now! Live all you can; it’s a mistake not to . . . Live!” It’s difficult here to ignore Balzac as Gloriani’s progenitor, the figure that kept telling James to embrace life with more vital courage—and greater response to its magnificence. Gloriani appears again in “The Velvet Glove,” a short story of 1909, but he’s also present in metaphors like the beast in “The Beast in the Jungle,” in which John Marcher waits passively for Life’s big revelation to seize him—that was Strether’s mistake, too. Think of Balzac again when you read about James visiting Edith Wharton at The Mount in 1904 and reading aloud together Walt Whitman’s celebrations of “The Body Electric” with unselfconscious joy. In the novels of André Aciman
In the novels of André Aciman The most significant developments in society and technology have all occurred over the past 10,000 years or so. That includes the agricultural, scientific, industrial, and digital revolutions, not to mention the dawn of religion, money, and any of the other symbolic concepts that separate Homo sapiens from other species.
The most significant developments in society and technology have all occurred over the past 10,000 years or so. That includes the agricultural, scientific, industrial, and digital revolutions, not to mention the dawn of religion, money, and any of the other symbolic concepts that separate Homo sapiens from other species. In 2019, the Business Roundtable, an association of the United States’ most powerful CEOs, won widespread praise by
In 2019, the Business Roundtable, an association of the United States’ most powerful CEOs, won widespread praise by 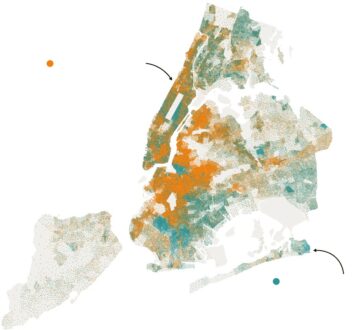 Five years ago, at the height of the Covid-19 pandemic, Andrew Cuomo was at the apex of his political power, watched by millions as he delivered daily televised briefings as the governor of New York. Zohran Mamdani, a then-unknown 28-year-old, was running for State Assembly as a democratic socialist in the gentrifying Western Queens neighborhood of Astoria. He would prevail by fewer than 500 votes.
Five years ago, at the height of the Covid-19 pandemic, Andrew Cuomo was at the apex of his political power, watched by millions as he delivered daily televised briefings as the governor of New York. Zohran Mamdani, a then-unknown 28-year-old, was running for State Assembly as a democratic socialist in the gentrifying Western Queens neighborhood of Astoria. He would prevail by fewer than 500 votes.