Shelly Fan in Singularity Hub:
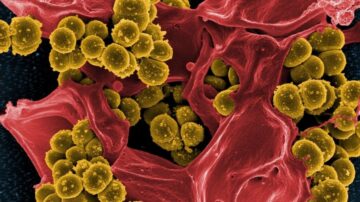 Humans and bacteria are in a perpetual war.
Humans and bacteria are in a perpetual war.
For most of history, bacteria won. Before 1928, a simple scrape on the knee, a cut when cooking dinner, or giving birth could lead to death from infection. The discovery of penicillin, a molecule secreted from mold, changed the balance. For the first time, humans had a way to fight back. Since then, generations of antibiotics have targeted different phases of bacterial growth and spread inside the body, efficiently eliminating them before they can infect other people. But bacteria have an evolutionary upper hand. Their DNA readily adapts to evolutionary pressures—including from antibiotics—so they can mutate over generations to escape the drugs. They also have a “phone line” of sorts that transmits adapted DNA to other nearby bacteria, giving them the power to resist an antibiotic too. Rinse and repeat: Soon an entire population of bacteria gains the ability to fight back.
We might be slowly losing the war. Antibiotic resistance is now a public health threat that caused roughly 1.27 million deaths around the globe in 2019. The World Health Organization (WHO) and others say that without newer generations of antibiotics, surgery, cancer chemotherapy, and other life-saving treatments face increasing risk of death due to infection. Traditionally, a new antibiotic takes roughly a decade to develop, test, and finally reach patients. “There is an urgent need for new methods for antibiotic discovery,” Dr. Luis Pedro Coelho, a computational biologist and author of a new study on the topic, said in a press release. Coelho and team tapped into AI to speed up the whole process. Analyzing huge databases of genetic material from the environment, they uncovered nearly one million potential antibiotics.
More here.

 M
M Dear Reader,
Dear Reader, George Salis: Your latest book is
George Salis: Your latest book is  A small, unassuming fern-like plant has something massive lurking within: the largest genome ever discovered, outstripping the
A small, unassuming fern-like plant has something massive lurking within: the largest genome ever discovered, outstripping the  It is a matter of being able to identify the true conspiracies, recognise genuine injustices and abuses of power, distinguish between credible and dubious information, plausible and implausible explanations. Klein makes a point of acknowledging that the irrational theories she examines in Doppelganger often arise from a justified sense that something is wrong – large pharmaceutical companies, for example, have real histories of unethical conduct and they really did make out like bandits during the pandemic. The question she confronts is how, and why, the valid instinct to distrust the powerful ends up being rerouted into bizarre fantasies.
It is a matter of being able to identify the true conspiracies, recognise genuine injustices and abuses of power, distinguish between credible and dubious information, plausible and implausible explanations. Klein makes a point of acknowledging that the irrational theories she examines in Doppelganger often arise from a justified sense that something is wrong – large pharmaceutical companies, for example, have real histories of unethical conduct and they really did make out like bandits during the pandemic. The question she confronts is how, and why, the valid instinct to distrust the powerful ends up being rerouted into bizarre fantasies. For the most part, Bowlero doesn’t build its own centers. Instead, it purchases existing ones and makes them over in the Bowlero style: dim lights, loud music, expensive cocktails. At Bowleros, bowling isn’t bowling. It’s “
For the most part, Bowlero doesn’t build its own centers. Instead, it purchases existing ones and makes them over in the Bowlero style: dim lights, loud music, expensive cocktails. At Bowleros, bowling isn’t bowling. It’s “ A new documentary portrait series, From the Streets to the Heart, focuses on homeless LGBTQIA+ youth and young adults in New York City. The project was initiated and created by Dutch photographer Ernst Coppejans, who also interviewed each of the 30 subjects to get their background stories and current situations. The combination of dignified portraits and the often harrowing stories (including audio clips allowing us to hear each person’s own voice) creates a palpable and empathetic understanding of how these people came to be who and where they are in the present moment. The project is a testament to the courage and resilience of people who are compelled to take very difficult steps in their lives to be true to themselves — despite tremendous emotional and financial challenges, physical danger and everyday prejudice.
A new documentary portrait series, From the Streets to the Heart, focuses on homeless LGBTQIA+ youth and young adults in New York City. The project was initiated and created by Dutch photographer Ernst Coppejans, who also interviewed each of the 30 subjects to get their background stories and current situations. The combination of dignified portraits and the often harrowing stories (including audio clips allowing us to hear each person’s own voice) creates a palpable and empathetic understanding of how these people came to be who and where they are in the present moment. The project is a testament to the courage and resilience of people who are compelled to take very difficult steps in their lives to be true to themselves — despite tremendous emotional and financial challenges, physical danger and everyday prejudice. Dakwar explores the myths and misconceptions of addiction, as well as the science, and shows how the patient’s experience is at least as important as what the latest research tells us. He describes in detail the use of ketamine given in combination with psychotherapy, and of the difficulties he has faced acquiring permission and funding to pursue his research into a treatment that itself suffers from being labelled a dangerous “street” drug.
Dakwar explores the myths and misconceptions of addiction, as well as the science, and shows how the patient’s experience is at least as important as what the latest research tells us. He describes in detail the use of ketamine given in combination with psychotherapy, and of the difficulties he has faced acquiring permission and funding to pursue his research into a treatment that itself suffers from being labelled a dangerous “street” drug.