Marian L. Tupy in Human Progress:

On Monday, William Nordhaus and Paul Romer were awarded the Nobel Prize in Economics. Nordhaus, the Sterling Professor of Economics at Yale University, is best known for his work in economic modelling and climate change. Romer, who teaches at New York University, is a pioneer of endogenous growth theory, which holds that investment in human capital, innovation, and knowledge are significant contributors to economic growth.
The two American economists’ research is vital in showing the way people underestimate the progress humanity has already made and the likelihood that it will continue well into the future.
In his 1996 paper, Do Real-Output and Real-Wage Measures Capture Reality? The History of Lighting Suggests Not, Nordhaus looked at the economics of light. Open fire, he noted, produced a mere 0.00235 lumens per watt (a lumen is a measure of how much visible light is emitted by a source.) Lumens per watt refers to the energy efficiency of lighting. A traditional 60 watt incandescent bulb, for example, produces 860 lumens.
A sesame lamp could produce 0.0597 lumens per watt; a sperm tallow candle 0.1009 lumens; whale oil 0.1346 lumens and an early town gaslamp 0.2464 lumens. An electric filament lamp, which was launched in 1883, achieved an unbelievable 2.6 lumens per watt and, due to subsequent technological improvements, managed to deliver an astonishing 14.1667 lumens by 1990. Yet that’s small beer compared to the compact fluorescent lightbulb, which delivered 68.2778 lumens per watt when it was launched in 1992.
More here.

 In 2014, two archaeologists,
In 2014, two archaeologists,  It’s no secret that computers are insecure. Stories like the
It’s no secret that computers are insecure. Stories like the 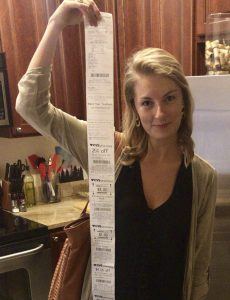 CVS is a drugstore much like other drugstores, with one important difference: The receipts are very long.
CVS is a drugstore much like other drugstores, with one important difference: The receipts are very long. A picture is worth a thousand words. In the case of Indian filmmaker (not to be confused with the Pakistani actor) Rahat Kazmi’s 2018 film Lihaaf: The Quilt, based on Ismat Chughtai’s controversial short story of the same name, the production’s publicity poster says perhaps more than a thousand words.
A picture is worth a thousand words. In the case of Indian filmmaker (not to be confused with the Pakistani actor) Rahat Kazmi’s 2018 film Lihaaf: The Quilt, based on Ismat Chughtai’s controversial short story of the same name, the production’s publicity poster says perhaps more than a thousand words. Somewhere in my parents’ photo albums there is a picture of me, aged seven or eight, lying in my bed, reading. On the wall, there are postcards from holidays, a poster of space pirate
Somewhere in my parents’ photo albums there is a picture of me, aged seven or eight, lying in my bed, reading. On the wall, there are postcards from holidays, a poster of space pirate  Last week Donna Strickland, an associate professor at the University of Waterloo, won the Nobel Prize in Physics. She is the third woman to be awarded the prize in its history—Marie Curie received it in 1903 and Maria Goeppert Mayer in 1963—but as recently as last May, Wikipedia rejected a draft page about Strickland on the grounds that she did not meet “notability guidelines.” The work for which she received the Nobel—generating the “shortest and most intense laser pulses ever created by mankind,” according to the prize committee—is over 30 years old. She published the groundbreaking paper, with co-authors and now co–Nobel winners Gerard Mourou and Arthur Ashkin, in 1985. Between then and now she has won many prizes, but it took a Nobel for her to become Wikipedia-worthy.
Last week Donna Strickland, an associate professor at the University of Waterloo, won the Nobel Prize in Physics. She is the third woman to be awarded the prize in its history—Marie Curie received it in 1903 and Maria Goeppert Mayer in 1963—but as recently as last May, Wikipedia rejected a draft page about Strickland on the grounds that she did not meet “notability guidelines.” The work for which she received the Nobel—generating the “shortest and most intense laser pulses ever created by mankind,” according to the prize committee—is over 30 years old. She published the groundbreaking paper, with co-authors and now co–Nobel winners Gerard Mourou and Arthur Ashkin, in 1985. Between then and now she has won many prizes, but it took a Nobel for her to become Wikipedia-worthy. A year ago, on a late afternoon in November, I decided to walk the seven miles from my hotel in Manhattan to Brooklyn’s Community Bookstore. It was a cool day, on the cusp of evening, at a moment when things, even grimy New York-type of things, seem to glow, and I was so busy looking around that I almost didn’t notice the small white sign that someone had placed at the bottom of Brooklyn Bridge. The green lettering was newly painted and read: ‘LIFE IS WORTH LIVING.’
A year ago, on a late afternoon in November, I decided to walk the seven miles from my hotel in Manhattan to Brooklyn’s Community Bookstore. It was a cool day, on the cusp of evening, at a moment when things, even grimy New York-type of things, seem to glow, and I was so busy looking around that I almost didn’t notice the small white sign that someone had placed at the bottom of Brooklyn Bridge. The green lettering was newly painted and read: ‘LIFE IS WORTH LIVING.’

 Last month, Apple unveiled the latest version of its watch, featuring new health-monitoring features such as alerts for unusually low or high heart rates, and a way to sense when the wearer has fallen over and, if so, call the emergency services. In itself, that sounds pretty cool, and might even help save lives. But it’s also another nail in the coffin of social solidarity.
Last month, Apple unveiled the latest version of its watch, featuring new health-monitoring features such as alerts for unusually low or high heart rates, and a way to sense when the wearer has fallen over and, if so, call the emergency services. In itself, that sounds pretty cool, and might even help save lives. But it’s also another nail in the coffin of social solidarity.

 IF THERE WERE
IF THERE WERE In the rendering, the structure looks like an enormous golden wave, spilling from the Upper Esplanade of Melbourne’s St Kilda Beach, crossing a busy road and crashing onto the sand. In reality, it would be a canopy of nearly 9,000 flexible photovoltaic panels designed to connect a shopping and entertainment district with the beach while generating renewable energy. Called “Light Up,” the proposal is the winner of a contest sponsored by the Land Art Generator Initiative (LAGI), an
In the rendering, the structure looks like an enormous golden wave, spilling from the Upper Esplanade of Melbourne’s St Kilda Beach, crossing a busy road and crashing onto the sand. In reality, it would be a canopy of nearly 9,000 flexible photovoltaic panels designed to connect a shopping and entertainment district with the beach while generating renewable energy. Called “Light Up,” the proposal is the winner of a contest sponsored by the Land Art Generator Initiative (LAGI), an  May 1968 marked the political awakening of my generation. I was a junior at the American College for Girls in Istanbul at the time, feeling the revolutionary winds as a young Jewish woman in a predominantly Muslim society and because of the anti-Americanism precipitated by the Vietnam War. Pictures of napalm attacks on Vietnamese children and adults circulated among us during lunch hours. And when the U.S. Navy’s Sixth Fleet scheduled a visit to Istanbul, and many boyfriends, relatives, and others were clubbed by the police, our sense of political disappointment with and opposition to U.S. policies increased.
May 1968 marked the political awakening of my generation. I was a junior at the American College for Girls in Istanbul at the time, feeling the revolutionary winds as a young Jewish woman in a predominantly Muslim society and because of the anti-Americanism precipitated by the Vietnam War. Pictures of napalm attacks on Vietnamese children and adults circulated among us during lunch hours. And when the U.S. Navy’s Sixth Fleet scheduled a visit to Istanbul, and many boyfriends, relatives, and others were clubbed by the police, our sense of political disappointment with and opposition to U.S. policies increased. A landmark report from the United Nations’ scientific panel on climate change paints a far more dire picture of the immediate consequences of climate change than previously thought and says that avoiding the damage requires transforming the world economy at a speed and scale that has “no documented historic precedent.”
A landmark report from the United Nations’ scientific panel on climate change paints a far more dire picture of the immediate consequences of climate change than previously thought and says that avoiding the damage requires transforming the world economy at a speed and scale that has “no documented historic precedent.”