Yanis Varoufakis in Project Syndicate:

Back in the 1830s, Thomas Peel decided to migrate from England to Swan River in Western Australia. A man of means, Peel took along, besides his family, “300 persons of the working class, men, women, and children,” as well as “means of subsistence and production to the amount of £50,000.” But soon after arrival, Peel’s plans were in ruins.
The cause was not disease, disaster, or bad soil. Peel’s labor force abandoned him, got themselves plots of land in the surrounding wilderness, and went into “business” for themselves. Although Peel had brought labor, money, and physical capital with him, the workers’ access to alternatives meant that he could not bring capitalism.
Karl Marx recounted Peel’s story in Capital, Volume I to make the point that “capital is not a thing, but a social relation between persons.” The parable remains useful today in illuminating not only the difference between money and capital, but also why austerity, despite its illogicality, keeps coming back.
More here.

 For decades, the Democratic Party has stood by Israel in times of war and peace.
For decades, the Democratic Party has stood by Israel in times of war and peace. I believe that the books and stories we fall in love with make us who we are, or, not to claim too much, the beloved tale becomes a part of the way in which we understand things and make judgments and choices in our daily lives. A book may cease to speak to us as we grow older, and our feeling for it will fade. Or we may suddenly, as our lives shape and hopefully increase our understanding, be able to appreciate a book we dismissed earlier; we may suddenly be able to hear its music, to be enraptured by its song.
I believe that the books and stories we fall in love with make us who we are, or, not to claim too much, the beloved tale becomes a part of the way in which we understand things and make judgments and choices in our daily lives. A book may cease to speak to us as we grow older, and our feeling for it will fade. Or we may suddenly, as our lives shape and hopefully increase our understanding, be able to appreciate a book we dismissed earlier; we may suddenly be able to hear its music, to be enraptured by its song. Democracy posits the radical idea that political power and legitimacy should ultimately be found in all of the people, rather than a small group of experts or for that matter arbitrarily-chosen hereditary dynasties. Nevertheless, a good case can be made that the bottom-up and experimental nature of democracy actually makes for better problem-solving in the political arena than other systems. Political theorist Henry Farrell (in collaboration with statistician
Democracy posits the radical idea that political power and legitimacy should ultimately be found in all of the people, rather than a small group of experts or for that matter arbitrarily-chosen hereditary dynasties. Nevertheless, a good case can be made that the bottom-up and experimental nature of democracy actually makes for better problem-solving in the political arena than other systems. Political theorist Henry Farrell (in collaboration with statistician  When we first traveled to
When we first traveled to  Along with fish, aluminium and Björk, Eve Online is one of Iceland’s biggest exports. Launched in 2003, it is a science-fiction project of unprecedented scale and ambition. It presents a cosmos of 7,500 interconnected star systems, known as New Eden, which can be travelled in spaceships built and flown by any individual. In-game professions vary. There are miners, traders, pirates, journalists and educators. You are free to work alone or in loose-knit corporations and alliances, the largest of which are comprised of tens of thousands of members.
Along with fish, aluminium and Björk, Eve Online is one of Iceland’s biggest exports. Launched in 2003, it is a science-fiction project of unprecedented scale and ambition. It presents a cosmos of 7,500 interconnected star systems, known as New Eden, which can be travelled in spaceships built and flown by any individual. In-game professions vary. There are miners, traders, pirates, journalists and educators. You are free to work alone or in loose-knit corporations and alliances, the largest of which are comprised of tens of thousands of members. The American Land Museum is a network of landscape exhibition sites being developed across the United States by the Center for Land Use Interpretation and other agencies. The purpose of the museum is to create a dynamic contemporary portrait of the nation, a portrait composed of the national landscape itself. Selected exhibition locations represent regional land use patterns, themes, and development issues. Within each exhibit location are a number of specified experiential zones with collections of material artifacts in the landscape, landmarks selected from among the field of existing structures.
The American Land Museum is a network of landscape exhibition sites being developed across the United States by the Center for Land Use Interpretation and other agencies. The purpose of the museum is to create a dynamic contemporary portrait of the nation, a portrait composed of the national landscape itself. Selected exhibition locations represent regional land use patterns, themes, and development issues. Within each exhibit location are a number of specified experiential zones with collections of material artifacts in the landscape, landmarks selected from among the field of existing structures. Reading Battles in the Desert, one will note the special magic of Pacheco’s writing — that simplicity, so deceptive and so masterful. The narrative voice is a well-calibrated device gliding through the reality of things, stories, and emotions, always giving the impression that memory never betrays. “Pacheco’s craft and mastery make writing look easy,” writes Luis Jorge Boone in “José Emilio Pacheco: Un lector fuera del tiempo” (“José Emilio Pacheco: a reader outside of time”), an essay on the author’s work. “Achieving that almost magical ease took Pacheco years of rewrites, edits, cuts. The layers upon layers of work the author put into his books over the years is legendary.”
Reading Battles in the Desert, one will note the special magic of Pacheco’s writing — that simplicity, so deceptive and so masterful. The narrative voice is a well-calibrated device gliding through the reality of things, stories, and emotions, always giving the impression that memory never betrays. “Pacheco’s craft and mastery make writing look easy,” writes Luis Jorge Boone in “José Emilio Pacheco: Un lector fuera del tiempo” (“José Emilio Pacheco: a reader outside of time”), an essay on the author’s work. “Achieving that almost magical ease took Pacheco years of rewrites, edits, cuts. The layers upon layers of work the author put into his books over the years is legendary.” During the final weeks of the Trump Administration, a senior official on the National Security Council sat at his desk in the Eisenhower Executive Office Building, across from the West Wing, on the White House grounds. It was mid-November, and he had recently returned from a work trip abroad. At the end of the day, he left the building and headed toward his car, which was parked a few hundred yards away, along the Ellipse, between the White House and the Washington Monument. As he walked, he began to hear a ringing in his ears. His body went numb, and he had trouble controlling the movement of his legs and his fingers. Trying to speak to a passerby, he had difficulty forming words. “It came on very suddenly,” the official recalled later, while describing the experience to a colleague. “In a matter of about seven minutes, I went from feeling completely fine to thinking, Oh, something’s not right, to being very, very worried and actually thinking I was going to die.”
During the final weeks of the Trump Administration, a senior official on the National Security Council sat at his desk in the Eisenhower Executive Office Building, across from the West Wing, on the White House grounds. It was mid-November, and he had recently returned from a work trip abroad. At the end of the day, he left the building and headed toward his car, which was parked a few hundred yards away, along the Ellipse, between the White House and the Washington Monument. As he walked, he began to hear a ringing in his ears. His body went numb, and he had trouble controlling the movement of his legs and his fingers. Trying to speak to a passerby, he had difficulty forming words. “It came on very suddenly,” the official recalled later, while describing the experience to a colleague. “In a matter of about seven minutes, I went from feeling completely fine to thinking, Oh, something’s not right, to being very, very worried and actually thinking I was going to die.” I
I Many philosophers, at least in the West, have sought to identify the invariable or essential conditions of being a self. A widely taken approach is what’s known as a psychological continuity view of the self, where the self is a consciousness with self-awareness and personal memories. Sometimes these approaches frame the self as a combination of mind and body, as René Descartes did, or as primarily or solely consciousness. John Locke’s prince/pauper thought experiment, wherein a prince’s consciousness and all his memories are transferred into the body of a cobbler, is an illustration of the idea that personhood goes with consciousness. Philosophers have devised numerous subsequent thought experiments – involving personality transfers, split brains and teleporters – to explore the psychological approach. Contemporary philosophers in the ‘animalist’ camp are critical of the psychological approach, and argue that selves are essentially human biological organisms. (Aristotle might also be closer to this approach than to the purely psychological.) Both psychological and animalist approaches are ‘container’ frameworks, positing the body as a container of psychological functions or the bounded location of bodily functions.
Many philosophers, at least in the West, have sought to identify the invariable or essential conditions of being a self. A widely taken approach is what’s known as a psychological continuity view of the self, where the self is a consciousness with self-awareness and personal memories. Sometimes these approaches frame the self as a combination of mind and body, as René Descartes did, or as primarily or solely consciousness. John Locke’s prince/pauper thought experiment, wherein a prince’s consciousness and all his memories are transferred into the body of a cobbler, is an illustration of the idea that personhood goes with consciousness. Philosophers have devised numerous subsequent thought experiments – involving personality transfers, split brains and teleporters – to explore the psychological approach. Contemporary philosophers in the ‘animalist’ camp are critical of the psychological approach, and argue that selves are essentially human biological organisms. (Aristotle might also be closer to this approach than to the purely psychological.) Both psychological and animalist approaches are ‘container’ frameworks, positing the body as a container of psychological functions or the bounded location of bodily functions. From his magnum opus, How to Cook Everything, and its many cookbook companions, to his recipes for The New York Times, to his essays on food policy, Bittman has developed a breeziness that masks the weight of the politics and economics that surround the making and consuming of food. In Animal, Vegetable, Junk, his latest book, he offers us his most thoroughgoing attack on the corporate forces that govern our food, tracking the evolution of cultivation and consumption from primordial to modern times and developing what is arguably his most radical and forthright argument yet about how to address our contemporary food cultures’ many ills. But it still goes down easy; the broccoli tastes good enough that you’ll happily go for seconds.
From his magnum opus, How to Cook Everything, and its many cookbook companions, to his recipes for The New York Times, to his essays on food policy, Bittman has developed a breeziness that masks the weight of the politics and economics that surround the making and consuming of food. In Animal, Vegetable, Junk, his latest book, he offers us his most thoroughgoing attack on the corporate forces that govern our food, tracking the evolution of cultivation and consumption from primordial to modern times and developing what is arguably his most radical and forthright argument yet about how to address our contemporary food cultures’ many ills. But it still goes down easy; the broccoli tastes good enough that you’ll happily go for seconds. When Shashank Yadav took to Twitter to plead for oxygen to save his dying grandfather
When Shashank Yadav took to Twitter to plead for oxygen to save his dying grandfather 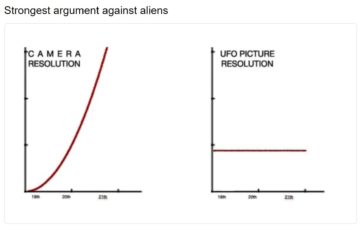 The idea of UFOs has gone mainstream. The dam broke with a New York Times story about a year ago on
The idea of UFOs has gone mainstream. The dam broke with a New York Times story about a year ago on