Hephzibah Anderson at The Guardian:
 Where You End and I Begin isn’t in fact that book. Instead, it’s something more amorphous, more exposing. It started as a collaboration between the author and her mother but after Cessie withdrew, it ceased being a journalistic investigation into the Horseman and his crimes (there were other child victims) and became an intimate voyage into the deepest, darkest heart of motherhood and daughterhood, musing too on consent, victim narratives and the ownership of stories. The result is a work of probing insight and undaunted compassion; one that’s fearlessly engrossing, frequently funny and sometimes plain hair-raising.
Where You End and I Begin isn’t in fact that book. Instead, it’s something more amorphous, more exposing. It started as a collaboration between the author and her mother but after Cessie withdrew, it ceased being a journalistic investigation into the Horseman and his crimes (there were other child victims) and became an intimate voyage into the deepest, darkest heart of motherhood and daughterhood, musing too on consent, victim narratives and the ownership of stories. The result is a work of probing insight and undaunted compassion; one that’s fearlessly engrossing, frequently funny and sometimes plain hair-raising.
An account of McLaren’s efforts to win her mother’s blessing for the book over a girls’ weekend in New York frames a narrative composed of chronologically arranged vignettes that capture telling moments from McLaren’s girlhood and early adulthood.
more here.

 During the final months of the Second World War, the publisher Alfred A. Knopf commissioned a reader’s report, consisting of a form on blue paper with a few queries, regarding a translated novel it was considering by an Icelander named Halldór Laxness. Section B of the form instructed the reader, “If you recommend us to publish the book give your chief reason in a single sentence.” The reader replied, “Those who read this book will never forget it.”
During the final months of the Second World War, the publisher Alfred A. Knopf commissioned a reader’s report, consisting of a form on blue paper with a few queries, regarding a translated novel it was considering by an Icelander named Halldór Laxness. Section B of the form instructed the reader, “If you recommend us to publish the book give your chief reason in a single sentence.” The reader replied, “Those who read this book will never forget it.” Why is it that we may agree in advance that a particular result is a fair test of our theory, then see so much more when the result is known? Why can’t we anticipate our response to results that we do not expect to materialize? The psychology of this is straightforward. The normal flow of reasoning is forward from what you believe to a possible consequence. When someone proposes a serious critical test, you cannot get from your theory to the result without adding an extra wrinkle to the theory. The extra wrinkle is hard to find—if it were easy, this would not be a serious critical test. On the other hand, the result probably follows from the adversary’s theory. The lazy solution is to concede provisionally.
Why is it that we may agree in advance that a particular result is a fair test of our theory, then see so much more when the result is known? Why can’t we anticipate our response to results that we do not expect to materialize? The psychology of this is straightforward. The normal flow of reasoning is forward from what you believe to a possible consequence. When someone proposes a serious critical test, you cannot get from your theory to the result without adding an extra wrinkle to the theory. The extra wrinkle is hard to find—if it were easy, this would not be a serious critical test. On the other hand, the result probably follows from the adversary’s theory. The lazy solution is to concede provisionally. Natural immunity induced by infection with SARS-CoV-2 provides a strong shield against reinfection by a pre-Omicron variant for 16 months or longer, according to a study
Natural immunity induced by infection with SARS-CoV-2 provides a strong shield against reinfection by a pre-Omicron variant for 16 months or longer, according to a study IN 2014, the novelist and essayist Cynthia Ozick reviewed the collected fiction of Bernard Malamud for the New York Times. Ozick adores her slightly older contemporary for his bruised moral seriousness. The essay contains just one asterisk: “The reviewer has not read and is not likely ever to read ‘The Natural,’ a baseball novel said to incorporate a mythical theme. Myth may be myth, but baseball is still baseball, so never mind.”
IN 2014, the novelist and essayist Cynthia Ozick reviewed the collected fiction of Bernard Malamud for the New York Times. Ozick adores her slightly older contemporary for his bruised moral seriousness. The essay contains just one asterisk: “The reviewer has not read and is not likely ever to read ‘The Natural,’ a baseball novel said to incorporate a mythical theme. Myth may be myth, but baseball is still baseball, so never mind.” Fallacy though it may be to imagine the narrator of a verse as equivalent with the poet, it’s impossible not to imagine the words of Robert Frost read in that clipped Yankee-via-San-Francisco accent of his, to intuit the blistering cold of a New Hampshire morning or the blinding whiteness of the snow-covered Franconia Range, the damp exertion of sweat under a flannel collar and muddy boots trudging across yellow and brown leaves slick with early morning ice. Frost is forever a poet of loose coffee grounds dumped into boiling water and intricate blue and red quilts, of wooden spoons hanging from hooks next to gas stoves and of curved glass hurricane lamps, of creaking wooden floorboards and doors swollen with summer’s humidity. Visiting his white clapboard, gable-peeked farmstead in Derry, New Hampshire, and perambulating in the golden woods of sugar maple and red oak and it’s hard not to romanticize the old man, eyeing him along the rough granite stone wall that he mended every spring, the famous structure whereby “Good fences make good neighbors,” which he wrote about in his 1914 collection
Fallacy though it may be to imagine the narrator of a verse as equivalent with the poet, it’s impossible not to imagine the words of Robert Frost read in that clipped Yankee-via-San-Francisco accent of his, to intuit the blistering cold of a New Hampshire morning or the blinding whiteness of the snow-covered Franconia Range, the damp exertion of sweat under a flannel collar and muddy boots trudging across yellow and brown leaves slick with early morning ice. Frost is forever a poet of loose coffee grounds dumped into boiling water and intricate blue and red quilts, of wooden spoons hanging from hooks next to gas stoves and of curved glass hurricane lamps, of creaking wooden floorboards and doors swollen with summer’s humidity. Visiting his white clapboard, gable-peeked farmstead in Derry, New Hampshire, and perambulating in the golden woods of sugar maple and red oak and it’s hard not to romanticize the old man, eyeing him along the rough granite stone wall that he mended every spring, the famous structure whereby “Good fences make good neighbors,” which he wrote about in his 1914 collection  This remark, like many of Wittgenstein’s, seems to arise from self-examination. The answer he gives suggests that he is concerned with learning just by thinking, and indeed with the particular kind of learning just by thinking that happens in philosophy (as opposed to, say, mathematics). He seems to be asking how such learning is even possible. What are we to make of his answer?
This remark, like many of Wittgenstein’s, seems to arise from self-examination. The answer he gives suggests that he is concerned with learning just by thinking, and indeed with the particular kind of learning just by thinking that happens in philosophy (as opposed to, say, mathematics). He seems to be asking how such learning is even possible. What are we to make of his answer? At the centre of the Earth, a giant sphere of solid iron is slowly swelling. This is the inner core and scientists have recently uncovered intriguing evidence that suggests its birth half a billion years ago may have played a key role in the evolution of life on Earth.
At the centre of the Earth, a giant sphere of solid iron is slowly swelling. This is the inner core and scientists have recently uncovered intriguing evidence that suggests its birth half a billion years ago may have played a key role in the evolution of life on Earth. I’ve been writing a series of posts about economic development. The last 20 years have seen a marked acceleration in the rate at which poorer countries — not just China, but many countries — are
I’ve been writing a series of posts about economic development. The last 20 years have seen a marked acceleration in the rate at which poorer countries — not just China, but many countries — are  In Laurence Sterne’s 1759 novel
In Laurence Sterne’s 1759 novel  Julia Strand was confident in her scientific findings when they were published in 2018. Strand’s research showed that when a circular beacon of light was present in a noisy setting, people expended less energy listening to their conversation partner and responded quicker than without the light. The feedback was positive and Strand, an associate professor of psychology at Carleton College in Northfield, Minnesota, had received grant funding to continue her research. Some months later, however, Strand was unable to replicate her results. In fact, she found the opposite to be true: The light forced people to think harder. Strand had crossed her t’s, dotted her i’s, and showed her work — and still she was wrong. “The bottom dropped out of my stomach,” Strand says. “It was terrible to realize that I had not just made a mistake, but published a mistake.”
Julia Strand was confident in her scientific findings when they were published in 2018. Strand’s research showed that when a circular beacon of light was present in a noisy setting, people expended less energy listening to their conversation partner and responded quicker than without the light. The feedback was positive and Strand, an associate professor of psychology at Carleton College in Northfield, Minnesota, had received grant funding to continue her research. Some months later, however, Strand was unable to replicate her results. In fact, she found the opposite to be true: The light forced people to think harder. Strand had crossed her t’s, dotted her i’s, and showed her work — and still she was wrong. “The bottom dropped out of my stomach,” Strand says. “It was terrible to realize that I had not just made a mistake, but published a mistake.” ALTHOUGH the more-than-a-half-century career of abstract painter Sam Gilliam was universally recognized and expansive in its reach, his studio and home were in Washington, D.C., which the art world was late to recognize as a place for innovative art and shape-shifting artists. Despite the history surrounding the genesis and development of the Washington Color School—chronicles that include such luminaries as critic Clement Greenberg and painters Morris Louis and Kenneth Noland—the reputation of the nation’s capital for nurturing leading-edge visual artists pales in comparison to cities like New York, Chicago, and Los Angeles. And yet Sam Gilliam’s groundbreaking creations, from his draped canvases to his acrylic-laden structures, cannot be separated from the town that, until recently, was euphemistically referred to as Chocolate City, a setting with an idiosyncratic, generative mixture of bureaucratic precedent, cosmopolitan rapprochement, and African American artistry.
ALTHOUGH the more-than-a-half-century career of abstract painter Sam Gilliam was universally recognized and expansive in its reach, his studio and home were in Washington, D.C., which the art world was late to recognize as a place for innovative art and shape-shifting artists. Despite the history surrounding the genesis and development of the Washington Color School—chronicles that include such luminaries as critic Clement Greenberg and painters Morris Louis and Kenneth Noland—the reputation of the nation’s capital for nurturing leading-edge visual artists pales in comparison to cities like New York, Chicago, and Los Angeles. And yet Sam Gilliam’s groundbreaking creations, from his draped canvases to his acrylic-laden structures, cannot be separated from the town that, until recently, was euphemistically referred to as Chocolate City, a setting with an idiosyncratic, generative mixture of bureaucratic precedent, cosmopolitan rapprochement, and African American artistry. THIS YEAR STANLEY Hauerwas turns 82 years old. To mark the occasion, he has published a book on Karl Barth, who died at the same age in 1968. The timing as well as the pairing is fitting. Barth is the greatest Protestant theologian of the 20th century, and probably the most widely read of any theologian over the last 100 years. As for Hauerwas, since the passing of Reinhold Niebuhr in 1971, he has been the most prolific, influential, and recognizable Christian theological thinker in American public life. Barth somehow graced the cover of Time magazine in 1962, even though he was a Swiss Calvinist whose books on technical theology are so thick they could stop bullets. Hauerwas has never made the cover, but in 2001 Time did call him “America’s best theologian.” That fall, Oprah even invited him onto her show. In short, given Hauerwas’s age and stature, Fully Alive: The Apocalyptic Humanism of Karl Barth has the inevitable feel of a valediction.
THIS YEAR STANLEY Hauerwas turns 82 years old. To mark the occasion, he has published a book on Karl Barth, who died at the same age in 1968. The timing as well as the pairing is fitting. Barth is the greatest Protestant theologian of the 20th century, and probably the most widely read of any theologian over the last 100 years. As for Hauerwas, since the passing of Reinhold Niebuhr in 1971, he has been the most prolific, influential, and recognizable Christian theological thinker in American public life. Barth somehow graced the cover of Time magazine in 1962, even though he was a Swiss Calvinist whose books on technical theology are so thick they could stop bullets. Hauerwas has never made the cover, but in 2001 Time did call him “America’s best theologian.” That fall, Oprah even invited him onto her show. In short, given Hauerwas’s age and stature, Fully Alive: The Apocalyptic Humanism of Karl Barth has the inevitable feel of a valediction. Several days ago, I received from Raymond Geuss a copy of his new book, Not Thinking like a Liberal, which has just been published by Harvard. It is an intense, complex, deeply interior account of his philosophical development first as a boy in a Catholic private school and then as an undergraduate and graduate student at Columbia University. Geuss, as I am sure you all know, is a distinguished philosopher now retired from Cambridge University, the author of a number of books.
Several days ago, I received from Raymond Geuss a copy of his new book, Not Thinking like a Liberal, which has just been published by Harvard. It is an intense, complex, deeply interior account of his philosophical development first as a boy in a Catholic private school and then as an undergraduate and graduate student at Columbia University. Geuss, as I am sure you all know, is a distinguished philosopher now retired from Cambridge University, the author of a number of books.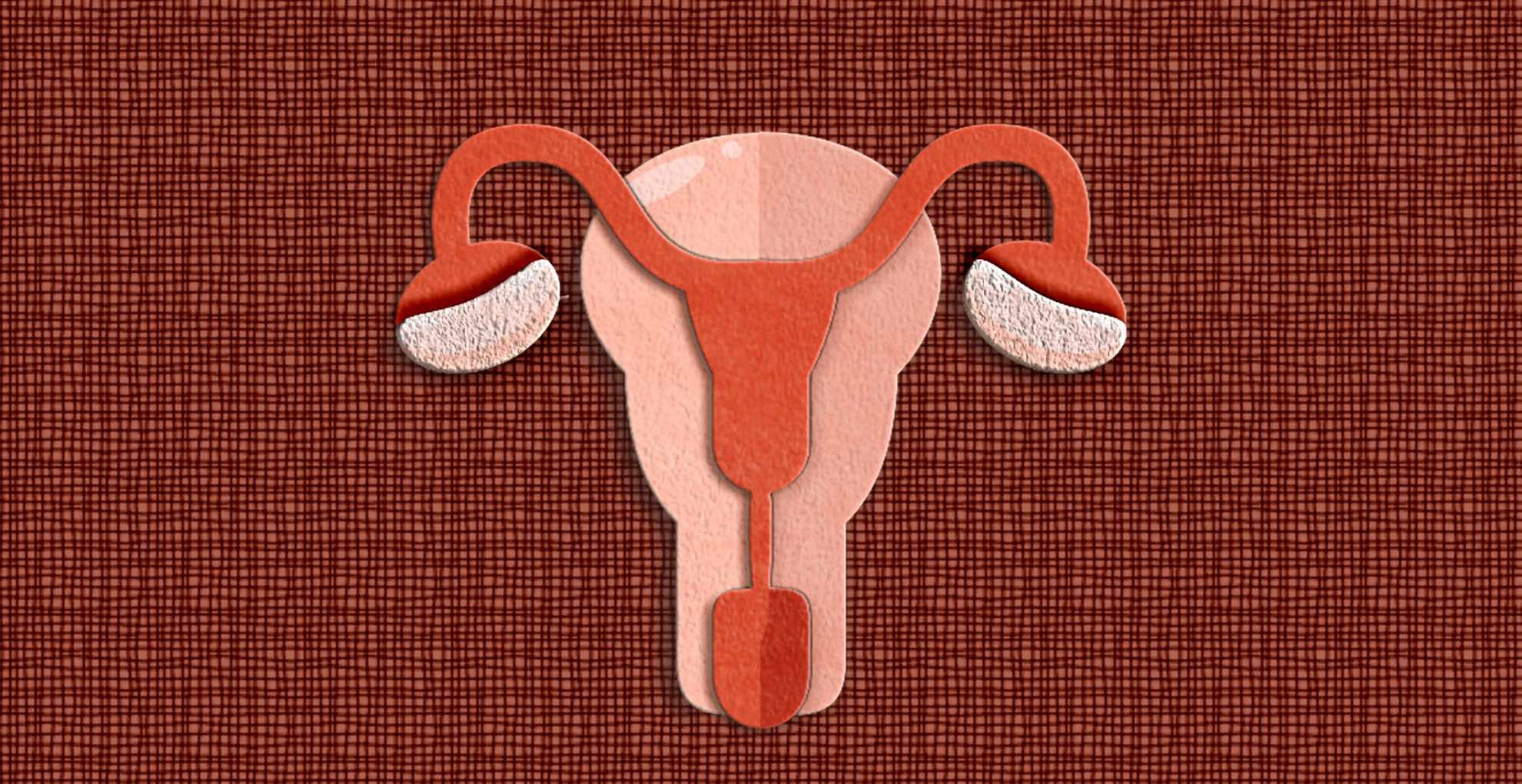 It’s “appalling” that more scientists — whether they’re studying endometriosis or not — aren’t studying menstrual blood, which contains a combination of blood and tissue that lines the uterus, said Metz. Researchers routinely examine
It’s “appalling” that more scientists — whether they’re studying endometriosis or not — aren’t studying menstrual blood, which contains a combination of blood and tissue that lines the uterus, said Metz. Researchers routinely examine  Throughout history, the most effective combatants, revolutionaries and insurgents have been ‘
Throughout history, the most effective combatants, revolutionaries and insurgents have been ‘