Ellin Berman is a board-certified medical oncologist and hematologist with a clinical and research focus on new drug development in acute and chronic leukemias, including acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) and chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). As a member of the multidisciplinary Leukemia Disease Management Team at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC), she works closely with the many individuals who make up the clinical and research programs there. Along with other members of the Leukemia Service, she is involved in clinical trials of new drugs that hopefully will lead to new treatment approaches for these diseases. She has also worked closely with the Food and Drug Administration in this regard, and for the last 20 years have helped review new drug applications for the treatment of leukemia. She is a member of KSKCC’s Institutional Review Board (IRB), the committee that approves, monitors, and reviews research studies at the Center. She is an Associate Editor for the journal Leukemia Research, and reviews articles for a number of other journals including Blood, the Journal of Clinical Oncology, Cancer Research, The Lancet, and the New England Journal of Medicine.
Azra Raza, author of the forthcoming book The First Cell: And the Human Costs of Pursuing Cancer to the Last, oncologist and professor of medicine at Columbia University, and 3QD editor, decided to speak to more than 20 leading cancer investigators and ask each of them the same five questions listed below. She videotaped the interviews and over the next months we will be posting them here one at a time each Monday. Please keep in mind that Azra and the rest of us at 3QD neither endorse nor oppose any of the answers given by the researchers as part of this project. Their views are their own. One can browse all previous interviews here.
1. We were treating acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with 7+3 (7 days of the drug cytosine arabinoside and 3 days of daunomycin) in 1977. We are still doing the same in 2019. What is the best way forward to change it by 2028?
2. There are 3.5 million papers on cancer, 135,000 in 2017 alone. There is a staggering disconnect between great scientific insights and translation to improved therapy. What are we doing wrong?
3. The fact that children respond to the same treatment better than adults seems to suggest that the cancer biology is different and also that the host is different. Since most cancers increase with age, even having good therapy may not matter as the host is decrepit. Solution?
4. You have great knowledge and experience in the field. If you were given limitless resources to plan a cure for cancer, what will you do?
5. Offering patients with advanced stage non-curable cancer, palliative but toxic treatments is a service or disservice in the current therapeutic landscape?

 Sometimes, history moves faster than thought. Something like that is happening in the United States in these early days of fall. Though the season is taking longer than normal to turn, the political season has changed more quickly than anyone expected. The opinions of last week – such as the long article I had written for 3QD on the prospects of Donald Trump and the Democrats in 2020 – have suddenly become irrelevant, and I find myself writing this wholly surprising piece on the possible impeachment of Donald Trump. As these lines are being written, 223 Democrats and one Independent in the US House of Representatives – a clear majority –
Sometimes, history moves faster than thought. Something like that is happening in the United States in these early days of fall. Though the season is taking longer than normal to turn, the political season has changed more quickly than anyone expected. The opinions of last week – such as the long article I had written for 3QD on the prospects of Donald Trump and the Democrats in 2020 – have suddenly become irrelevant, and I find myself writing this wholly surprising piece on the possible impeachment of Donald Trump. As these lines are being written, 223 Democrats and one Independent in the US House of Representatives – a clear majority – 
 I remember the first time I thought I might be able to get on board with Stoicism. I read a
I remember the first time I thought I might be able to get on board with Stoicism. I read a 

 Do you remember when the Irish playwright and critic George Bernard Shaw suggested significant changes to English spelling so that it would make more sense? Probably not, because it was more than 70 years ago. According to him
Do you remember when the Irish playwright and critic George Bernard Shaw suggested significant changes to English spelling so that it would make more sense? Probably not, because it was more than 70 years ago. According to him 
 Things are changing. Always, everywhere, immensely and minutely, the history of mankind unfolds as we rotate around a grand burning star (also, everything everywhere else changes; the history of mankind may be of the least consequence on a cosmic scale, but I digress). I digress too early; I include parentheticals too soon; I stall with flowery descriptions of the sun. Because – ugh – I’m going to talk about “how divided we are as a nation.” It’s such a tired phrase; I don’t want to write about it. It’s stale because it’s static, and anyway, the declaration is often accompanied by divisive rhetoric. Wherever one may fall on the political spectrum (and here I’m being gracious; how often do we now identify with a “side”), they likely have established opinions of those who lie elsewhere. It does seem increasingly difficult to imagine a sweeping reconciliation when we continue to pour our definitions in concrete and defend our positions by reason of consistency. Inflexibility begets inability to listen, and thus to understand, which is why we find our differences so baffling and allow our prejudices to influence our opinions. So, finally, here it is: my own personal take on how we can get people to stop saying how divided we are. Bear with me, because I’m going to try and sell contradictions as potential energy for unity.
Things are changing. Always, everywhere, immensely and minutely, the history of mankind unfolds as we rotate around a grand burning star (also, everything everywhere else changes; the history of mankind may be of the least consequence on a cosmic scale, but I digress). I digress too early; I include parentheticals too soon; I stall with flowery descriptions of the sun. Because – ugh – I’m going to talk about “how divided we are as a nation.” It’s such a tired phrase; I don’t want to write about it. It’s stale because it’s static, and anyway, the declaration is often accompanied by divisive rhetoric. Wherever one may fall on the political spectrum (and here I’m being gracious; how often do we now identify with a “side”), they likely have established opinions of those who lie elsewhere. It does seem increasingly difficult to imagine a sweeping reconciliation when we continue to pour our definitions in concrete and defend our positions by reason of consistency. Inflexibility begets inability to listen, and thus to understand, which is why we find our differences so baffling and allow our prejudices to influence our opinions. So, finally, here it is: my own personal take on how we can get people to stop saying how divided we are. Bear with me, because I’m going to try and sell contradictions as potential energy for unity.
 Firstly, of course we should rescue the art first. Secondly, of course we should not.
Firstly, of course we should rescue the art first. Secondly, of course we should not.

 Following in the footsteps of the brilliant and exhaustive account of the British opium wars in his hefty Ibis Trilogy, Amitav Ghosh’s latest book Gun Island at just over 300 pages, is a relatively slim volume in which he returns to the Sundarbans to pick up from where his 2004 novel The Hungry Tide left off, with a dire warning about the ravaged ecological plight of the region. Only this time, Ghosh’s novel takes us out of the Sundarbans to Venice via Brooklyn, Kolkata and Los Angeles.
Following in the footsteps of the brilliant and exhaustive account of the British opium wars in his hefty Ibis Trilogy, Amitav Ghosh’s latest book Gun Island at just over 300 pages, is a relatively slim volume in which he returns to the Sundarbans to pick up from where his 2004 novel The Hungry Tide left off, with a dire warning about the ravaged ecological plight of the region. Only this time, Ghosh’s novel takes us out of the Sundarbans to Venice via Brooklyn, Kolkata and Los Angeles. A degree in engineering from India, grad school at an American university, and a job at an American corporation: call it the Indian-engineer version of the American dream. Like hundreds of thousands of Indian immigrants, Ved, the 36-year old protagonist of
A degree in engineering from India, grad school at an American university, and a job at an American corporation: call it the Indian-engineer version of the American dream. Like hundreds of thousands of Indian immigrants, Ved, the 36-year old protagonist of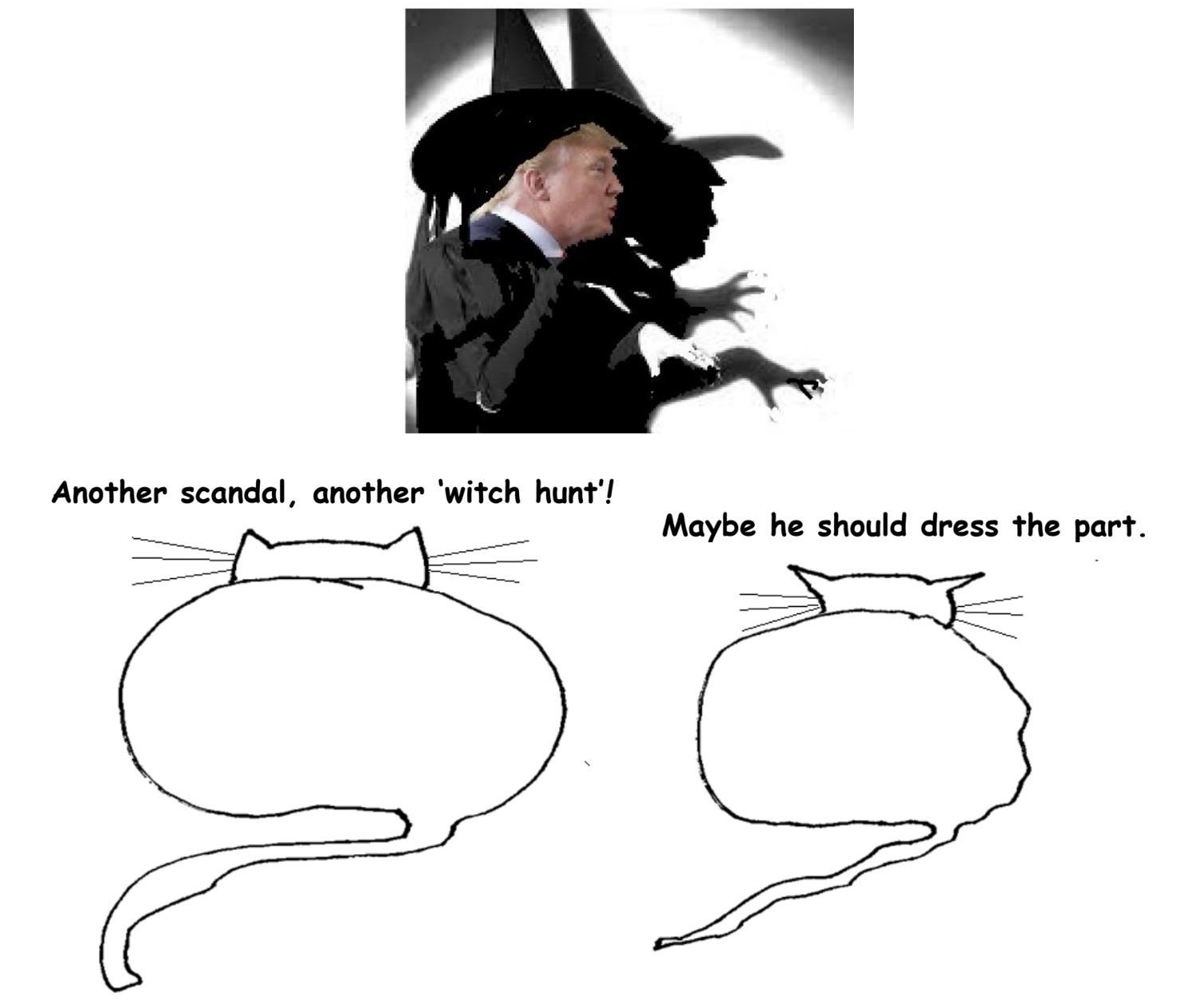 
 Academic dishonesty is a widespread problem in colleges in many countries, and it is getting worse. One particular form of cheating has become especially common in the age of the internet: students buying custom-written essays–a.k.a. “contract cheating.” A recent study estimated that over 15% of college students had paid someone else to do their work for them;
Academic dishonesty is a widespread problem in colleges in many countries, and it is getting worse. One particular form of cheating has become especially common in the age of the internet: students buying custom-written essays–a.k.a. “contract cheating.” A recent study estimated that over 15% of college students had paid someone else to do their work for them;