Sean Carroll in Preposterous Universe:
 An infinite number of things happen; we bring structure and meaning to the world by making art and telling stories about it. Every work of literature created by human beings comes out of an historical and cultural context, and drawing connections between art and its context can be illuminating for both. Today’s guest, Stephen Greenblatt, is one of the world’s most celebrated literary scholars, famous for helping to establish the New Historicism school of criticism, which he also refers to as “cultural poetics.” We talk about how art becomes entangled with the politics of its day, and how we can learn about ourselves and other cultures by engaging with stories and their milieu.
An infinite number of things happen; we bring structure and meaning to the world by making art and telling stories about it. Every work of literature created by human beings comes out of an historical and cultural context, and drawing connections between art and its context can be illuminating for both. Today’s guest, Stephen Greenblatt, is one of the world’s most celebrated literary scholars, famous for helping to establish the New Historicism school of criticism, which he also refers to as “cultural poetics.” We talk about how art becomes entangled with the politics of its day, and how we can learn about ourselves and other cultures by engaging with stories and their milieu.
More here.

 We are being told of the evils of “cancel culture,” a new scourge that enforces purity, banishes dissent and squelches sober and reasoned debate. But cancel culture is not new. A brief accounting of the illustrious and venerable ranks of blocked and dragged Americans encompasses Sarah Good, Elijah Lovejoy, Ida B. Wells, Dalton Trumbo, Paul Robeson and the Dixie Chicks. What was the Compromise of 1877, which ended Reconstruction, but the cancellation of the black South? What were the detention camps during World War II but the racist muting of Japanese-Americans and their basic rights?
We are being told of the evils of “cancel culture,” a new scourge that enforces purity, banishes dissent and squelches sober and reasoned debate. But cancel culture is not new. A brief accounting of the illustrious and venerable ranks of blocked and dragged Americans encompasses Sarah Good, Elijah Lovejoy, Ida B. Wells, Dalton Trumbo, Paul Robeson and the Dixie Chicks. What was the Compromise of 1877, which ended Reconstruction, but the cancellation of the black South? What were the detention camps during World War II but the racist muting of Japanese-Americans and their basic rights? The male glance is how comedies about women become chick flicks. It’s how discussions of serious movies with female protagonists consign them to the unappealing stable of “strong female characters.” It’s how soap operas and reality television become synonymous with trash. It tricks us into pronouncing mothers intrinsically boring, and it quietly convinces us that female friendships come in two strains: conventional jealousy or the even less appealing non-plot of saccharine love. The third narrative possibility, frenemy-cum-friend, is an only slightly less shallow conversion myth. Who consumes these stories? Who could want to?
The male glance is how comedies about women become chick flicks. It’s how discussions of serious movies with female protagonists consign them to the unappealing stable of “strong female characters.” It’s how soap operas and reality television become synonymous with trash. It tricks us into pronouncing mothers intrinsically boring, and it quietly convinces us that female friendships come in two strains: conventional jealousy or the even less appealing non-plot of saccharine love. The third narrative possibility, frenemy-cum-friend, is an only slightly less shallow conversion myth. Who consumes these stories? Who could want to? A
A Pinckney’s emphasis on the interpolation of class and race can make him appear closer to the leftist Afro-Caribbean tradition of race theorists—exemplified by thinkers such as Paul Gilroy and Stuart Hall—who reject mythical or essentialist theories of racism in favor of a concrete economic analysis, in which racial distinctions have been created and maintained primarily for the sake of capitalist exploitation. For Pinckney, blackness is not an essential quality found in the blood, the spirit, or even the genes (“I’d never liked that way of assigning innate behavioral characteristics to whole nations or groups. The work of every serious social scientist militated against it.”) but a conceptual framework subject to history, like everything else. “The Irish used to be black socially, meaning at the bottom,” he writes in one example. “The gift of being white helped to subdue class antagonism.”
Pinckney’s emphasis on the interpolation of class and race can make him appear closer to the leftist Afro-Caribbean tradition of race theorists—exemplified by thinkers such as Paul Gilroy and Stuart Hall—who reject mythical or essentialist theories of racism in favor of a concrete economic analysis, in which racial distinctions have been created and maintained primarily for the sake of capitalist exploitation. For Pinckney, blackness is not an essential quality found in the blood, the spirit, or even the genes (“I’d never liked that way of assigning innate behavioral characteristics to whole nations or groups. The work of every serious social scientist militated against it.”) but a conceptual framework subject to history, like everything else. “The Irish used to be black socially, meaning at the bottom,” he writes in one example. “The gift of being white helped to subdue class antagonism.” As Thanksgiving approaches, would-be chefs and hosts, including apparently my editors, are perfecting their techniques for making the all-important gravy for the turkey and potatoes. I have my moments as a cook — come over for my stardust waffles some Sunday morning — but I have never had the patience or skill to master gravy, so it usually comes out lumpy. This is a problem at the dinner table. On the grandest possible scale, however, lumps are a good thing. During the Big Bang 14 billion years ago, a fizzy stew of energy and gas emerged that became, and still suffuses, the universe. Astronomers initially thought this cosmic gravy was perfectly uniform, like something Julia Child might have whipped up. But not even Einstein’s “Old One” can make a perfect gravy, apparently, and in 1992 astronomers discovered that the cosmic gravy is, like mine, lumpy. And that’s a reason to be thankful this year, or any year, because without those lumps there would be no us. “If you’re religious, it’s like seeing God,” George Smoot, an astronomer at the University of California’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory who won a Nobel Prize for the 1992 discovery, said at the time.
As Thanksgiving approaches, would-be chefs and hosts, including apparently my editors, are perfecting their techniques for making the all-important gravy for the turkey and potatoes. I have my moments as a cook — come over for my stardust waffles some Sunday morning — but I have never had the patience or skill to master gravy, so it usually comes out lumpy. This is a problem at the dinner table. On the grandest possible scale, however, lumps are a good thing. During the Big Bang 14 billion years ago, a fizzy stew of energy and gas emerged that became, and still suffuses, the universe. Astronomers initially thought this cosmic gravy was perfectly uniform, like something Julia Child might have whipped up. But not even Einstein’s “Old One” can make a perfect gravy, apparently, and in 1992 astronomers discovered that the cosmic gravy is, like mine, lumpy. And that’s a reason to be thankful this year, or any year, because without those lumps there would be no us. “If you’re religious, it’s like seeing God,” George Smoot, an astronomer at the University of California’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory who won a Nobel Prize for the 1992 discovery, said at the time. Rates of squamous cell carcinoma of the anus and related mortality have risen sharply over the past 15 years, according to results of a retrospective study published in Journal of the National Cancer Institute. The findings reflect an urgent need for improved anal cancer awareness and prevention strategies, according to researchers. “Given the historical perception that anal cancer is rare, it is often neglected,” Ashish A. Deshmukh, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine at UTHealth School of Public Health in Houston, said in a press release. “Our findings of the dramatic rise in incidence among black millennials and white women, rising rates of distant-stage disease, and increases in anal cancer mortality rates are very concerning.” More than 90% of cases of squamous cell carcinoma of the anus are
Rates of squamous cell carcinoma of the anus and related mortality have risen sharply over the past 15 years, according to results of a retrospective study published in Journal of the National Cancer Institute. The findings reflect an urgent need for improved anal cancer awareness and prevention strategies, according to researchers. “Given the historical perception that anal cancer is rare, it is often neglected,” Ashish A. Deshmukh, PhD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine at UTHealth School of Public Health in Houston, said in a press release. “Our findings of the dramatic rise in incidence among black millennials and white women, rising rates of distant-stage disease, and increases in anal cancer mortality rates are very concerning.” More than 90% of cases of squamous cell carcinoma of the anus are 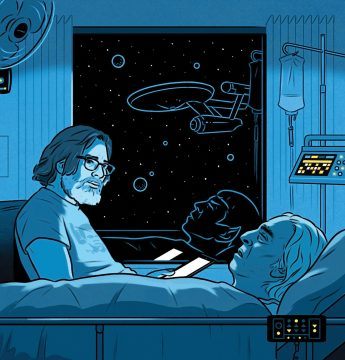 Ensign Spock, a young half-Vulcan science officer fresh out of Starfleet Academy and newly posted to the Enterprise, found himself alone in a turbolift with the ship’s formidable first officer, a human woman known as Number One. They were waiting for me to rescue them from the silence that reigns in all elevators, as universal as the vacuum of space.
Ensign Spock, a young half-Vulcan science officer fresh out of Starfleet Academy and newly posted to the Enterprise, found himself alone in a turbolift with the ship’s formidable first officer, a human woman known as Number One. They were waiting for me to rescue them from the silence that reigns in all elevators, as universal as the vacuum of space. Azra Raza is an oncologist
Azra Raza is an oncologist After the 2008 financial mess, austerity was touted as an economic cure-all. Deep budget cuts were forced upon nations and their citizens as a prerequisite for bailout loans. Now, we’re seeing the fallout. Anti-austerity protests have gripped countries around the world,
After the 2008 financial mess, austerity was touted as an economic cure-all. Deep budget cuts were forced upon nations and their citizens as a prerequisite for bailout loans. Now, we’re seeing the fallout. Anti-austerity protests have gripped countries around the world,  Scientists have confirmed every society on the planet makes music and it is used in “strikingly similar ways,” from lullabies to love songs.
Scientists have confirmed every society on the planet makes music and it is used in “strikingly similar ways,” from lullabies to love songs. Like many students of the Middle East, I am still haunted by Edward Said 41 years after he wrote “Orientalism”. The seminal book argued that Western academics, writers, artists and journalists had been agents of European soft power for over two centuries, constructing an image of the East that was exotic and therefore in need of taming. Orientalists’ art, literature, maps and artefacts reinforced the superior mindset of colonialists and whetted the appetite of Western governments to invade and possess Eastern nations, according to Said. His ideas shook up coverage of the Middle East years before I began working as a journalist in the region, but I wrote racked with guilt. On one of my first assignments in Egypt, the British embassy in Cairo flew me with the then British prime minister, John Major, to visit the war cemeteries that Britain tends for soldiers killed fighting in the deserts of El Alamein during the second world war. It was a privilege rarely afforded to a young reporter and they expected a puff piece. I returned with a report about irate locals demanding Britain give up control of a site commemorating battles between two invading European armies on Egyptian soil. I titled it “Egypt for the Egyptians”.
Like many students of the Middle East, I am still haunted by Edward Said 41 years after he wrote “Orientalism”. The seminal book argued that Western academics, writers, artists and journalists had been agents of European soft power for over two centuries, constructing an image of the East that was exotic and therefore in need of taming. Orientalists’ art, literature, maps and artefacts reinforced the superior mindset of colonialists and whetted the appetite of Western governments to invade and possess Eastern nations, according to Said. His ideas shook up coverage of the Middle East years before I began working as a journalist in the region, but I wrote racked with guilt. On one of my first assignments in Egypt, the British embassy in Cairo flew me with the then British prime minister, John Major, to visit the war cemeteries that Britain tends for soldiers killed fighting in the deserts of El Alamein during the second world war. It was a privilege rarely afforded to a young reporter and they expected a puff piece. I returned with a report about irate locals demanding Britain give up control of a site commemorating battles between two invading European armies on Egyptian soil. I titled it “Egypt for the Egyptians”. Dozens nationwide have shuttered in the past decade, and a quarter of the estimated 1,100 that remain are projected to follow by 2022, opening large swaths of empty space. “We built too many malls, and we built them too cheaply,” said Amanda Nicholson, a professor of retail practice at Syracuse University. “Only the strong will survive, while the weaker ones idle and fold.” The die-off has created challenges for the municipalities and developers tasked with repurposing millions of square feet of vacant retail space and parking lots. But the successes have taken multiple forms: community colleges, public preschools, churches and libraries. Some old malls have turned into micro-apartments or microbreweries, and at least one abandoned shopping mall is now an Amazon fulfillment center, offering a glimpse into consumers’ shifting habits and priorities.
Dozens nationwide have shuttered in the past decade, and a quarter of the estimated 1,100 that remain are projected to follow by 2022, opening large swaths of empty space. “We built too many malls, and we built them too cheaply,” said Amanda Nicholson, a professor of retail practice at Syracuse University. “Only the strong will survive, while the weaker ones idle and fold.” The die-off has created challenges for the municipalities and developers tasked with repurposing millions of square feet of vacant retail space and parking lots. But the successes have taken multiple forms: community colleges, public preschools, churches and libraries. Some old malls have turned into micro-apartments or microbreweries, and at least one abandoned shopping mall is now an Amazon fulfillment center, offering a glimpse into consumers’ shifting habits and priorities. Adam Shatz in The New Yorker:
Adam Shatz in The New Yorker: