
Charlie Wood in Quanta:
On December 11, 2021, a beam of gamma rays — the most energetic form of light — slammed into NASA’s Swift satellite. Within 120 seconds, the satellite had swiveled toward the blast and spotted the glowing embers of a cosmic catastrophe. Ten minutes later, alerts went out to astronomers around the world.
Among them was Jillian Rastinejad, a graduate student at Northwestern University. To Rastinejad and her collaborators, this gamma-ray burst looked oddly similar to an unusual burst from 2006. Rastinejad called up the Gemini Observatory in Hawai‘i and enlisted researchers there to stare deeply at the patch of sky where the burst had come from. A few days later, when clouds rolled in, a researcher at the MMT Observatory in Arizona took over, doing her best to keep the telescope trained on the fading spot of light a billion light-years away.
It was no small feat given that the weather was turning there too, Rastinejad said. “She found a hole in the clouds for us around 4 a.m. every day.”
By the time the chain of observations had wrapped up a week or so later, Rastinejad and her colleagues had a pretty good idea of what had fired those gamma rays across the universe. As they’d watched, the burst’s aftermath had turned redder and redder — an unmistakable sign that in the debris, heavy atoms like gold and platinum were being forged. The main source of such cosmic alchemy is collisions involving neutron stars, the unimaginably dense cores of dead suns.
The only problem was that such a conclusion seemed impossible. When neutron stars merge, astrophysicists suspect, it’s all over in a fraction of a second. But Swift had recorded a gamma-ray bombardment lasting a relatively interminable 51 seconds — normally the signature of a very different type of cosmic drama.
More here.


 Ignacio Silva Neira in Phenomenal World:
Ignacio Silva Neira in Phenomenal World: T
T The Latin American Boom of the 1960s and ‘70s is associated with some of contemporary Spanish-language literature’s most towering figures, among them Julio Cortázar, Carlos Fuentes, Mario Vargas Llosa, and Gabriel García Márquez. But of all the
The Latin American Boom of the 1960s and ‘70s is associated with some of contemporary Spanish-language literature’s most towering figures, among them Julio Cortázar, Carlos Fuentes, Mario Vargas Llosa, and Gabriel García Márquez. But of all the 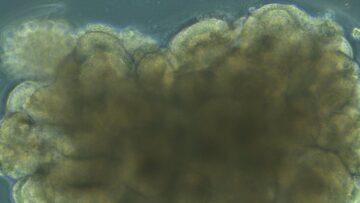 A tiny ball of brain cells hums with activity as it sits atop an array of electrodes. For two days, it receives a pattern of electrical zaps, each stimulation encoding the speech peculiarities of eight people. By day three, it can discriminate between speakers. Dubbed Brainoware, the system raises the bar for biocomputing by tapping into 3D brain organoids, or “mini-brains.” These models, usually grown from human stem cells, rapidly expand into a variety of neurons knitted into neural networks.
A tiny ball of brain cells hums with activity as it sits atop an array of electrodes. For two days, it receives a pattern of electrical zaps, each stimulation encoding the speech peculiarities of eight people. By day three, it can discriminate between speakers. Dubbed Brainoware, the system raises the bar for biocomputing by tapping into 3D brain organoids, or “mini-brains.” These models, usually grown from human stem cells, rapidly expand into a variety of neurons knitted into neural networks. “Class consciousness takes a vacation while we’re in the thrall of this book,” Barbara Grizzuti Harrison
“Class consciousness takes a vacation while we’re in the thrall of this book,” Barbara Grizzuti Harrison  Sometimes when I’m looking out across the northern meadow of Brooklyn’s Prospect Park, or even the concrete parking lot outside my office window, I wonder if someone like Shakespeare or Emily Dickinson could have taken in the same view and seen more. I don’t mean making out blurry details or more objects in the scene. But through the lens of their minds, could they encounter the exact same world as me and yet have a richer experience? One way to answer that question, at least as a thought experiment, could be to compare the electrical activity inside our brains while gazing out upon the same scene, and running some statistical analysis designed to actually tell us whose brain activity indicates more richness. But that’s just a loopy thought experiment, right?
Sometimes when I’m looking out across the northern meadow of Brooklyn’s Prospect Park, or even the concrete parking lot outside my office window, I wonder if someone like Shakespeare or Emily Dickinson could have taken in the same view and seen more. I don’t mean making out blurry details or more objects in the scene. But through the lens of their minds, could they encounter the exact same world as me and yet have a richer experience? One way to answer that question, at least as a thought experiment, could be to compare the electrical activity inside our brains while gazing out upon the same scene, and running some statistical analysis designed to actually tell us whose brain activity indicates more richness. But that’s just a loopy thought experiment, right? “Earthrise, that iconic photograph
“Earthrise, that iconic photograph  Art is useless, said Wilde. Art is for art’s sake—that is, for beauty’s sake. But why do we possess a sense of beauty to begin with? A question we will never answer. Perhaps it’s just a kind of superfluity of sexual attraction. Nature needs us to feel drawn to other human bodies, but evolution is imprecise. In order to go far enough, to make that feeling strong enough, it went too far. Others are powerfully lovely to us, but so, in a strangely different, strangely similar way, are flowers and sunsets. Art, in turn, this line of thought might go, is a response to natural beauty. Stunned by it, we seek to rival it, to reproduce it, to prolong it. Flowers fade, sunsets melt from moment to moment; the love of bodies brings us grief. Art abides. “When old age shall this generational waste, / Thou shalt remain.”
Art is useless, said Wilde. Art is for art’s sake—that is, for beauty’s sake. But why do we possess a sense of beauty to begin with? A question we will never answer. Perhaps it’s just a kind of superfluity of sexual attraction. Nature needs us to feel drawn to other human bodies, but evolution is imprecise. In order to go far enough, to make that feeling strong enough, it went too far. Others are powerfully lovely to us, but so, in a strangely different, strangely similar way, are flowers and sunsets. Art, in turn, this line of thought might go, is a response to natural beauty. Stunned by it, we seek to rival it, to reproduce it, to prolong it. Flowers fade, sunsets melt from moment to moment; the love of bodies brings us grief. Art abides. “When old age shall this generational waste, / Thou shalt remain.” In form, Francis Bacon’s New Atlantis is modeled loosely on Thomas More’s Utopia. A ship full of European sailors lands on a previously unknown island in the Americas where they find a civilized society in many ways superior to their own. The narrator describes the customs and institutions of this society, which in Bacon is called “Bensalem,” Hebrew for “son of peace.” Sometimes Bacon echoes, sometimes improves upon, More’s earlier work. But at the end of the story, Bacon turns to focus solely on the most original feature of the island, an institution called Solomon’s House, or the College of the Six Days Works.
In form, Francis Bacon’s New Atlantis is modeled loosely on Thomas More’s Utopia. A ship full of European sailors lands on a previously unknown island in the Americas where they find a civilized society in many ways superior to their own. The narrator describes the customs and institutions of this society, which in Bacon is called “Bensalem,” Hebrew for “son of peace.” Sometimes Bacon echoes, sometimes improves upon, More’s earlier work. But at the end of the story, Bacon turns to focus solely on the most original feature of the island, an institution called Solomon’s House, or the College of the Six Days Works. It’s been a year of endless einsteins. In March, a troupe of
It’s been a year of endless einsteins. In March, a troupe of  Natural Selection is the pressure that drives evolution up the slopes of Mount Improbable. Pressure really is rather a good metaphor. We speak of ‘selection pressure’, and you can almost feel it pushing a species to evolve, shoving it up the gradients of the mountain. Predators, we say, provided the selection pressure that drove antelopes to evolve their fast running legs. Even as we speak, though, we remember what this really means: genes for short legs are more likely to end up in predators’ bellies and therefore the world becomes less full of them. ‘Pressure’ from choosy females drove the evolution of male pheasants’ sumptuous feathers. What this means is that a gene for a beautiful feather is especially likely to find itself riding a sperm into a female’s body. But we think of it as a ‘pressure’ driving males towards greater beauty. No doubt predators provided a selection pressure in the opposite direction, towards duller plumage, since bright males would presumably attract predator, as well as female, eyes. Without the pressure from predators the cocks would be even brighter and more extravagant under pressure from females. Selection pressures, then, can push in opposite directions, or in the same direction or even (mathematicians can find ways of visualizing this) at any other ‘angle’ relative to one another, Selection pressures, moreover, can be ‘strong’ or ‘weak’, and the ordinary language meanings of these words fit well. The particular path up Mount Improbable that a lineage takes will be influenced by lots of different selection pressures, pushing and tugging in different directions and with different strengths, sometimes cooperating with each other, sometimes opposing.
Natural Selection is the pressure that drives evolution up the slopes of Mount Improbable. Pressure really is rather a good metaphor. We speak of ‘selection pressure’, and you can almost feel it pushing a species to evolve, shoving it up the gradients of the mountain. Predators, we say, provided the selection pressure that drove antelopes to evolve their fast running legs. Even as we speak, though, we remember what this really means: genes for short legs are more likely to end up in predators’ bellies and therefore the world becomes less full of them. ‘Pressure’ from choosy females drove the evolution of male pheasants’ sumptuous feathers. What this means is that a gene for a beautiful feather is especially likely to find itself riding a sperm into a female’s body. But we think of it as a ‘pressure’ driving males towards greater beauty. No doubt predators provided a selection pressure in the opposite direction, towards duller plumage, since bright males would presumably attract predator, as well as female, eyes. Without the pressure from predators the cocks would be even brighter and more extravagant under pressure from females. Selection pressures, then, can push in opposite directions, or in the same direction or even (mathematicians can find ways of visualizing this) at any other ‘angle’ relative to one another, Selection pressures, moreover, can be ‘strong’ or ‘weak’, and the ordinary language meanings of these words fit well. The particular path up Mount Improbable that a lineage takes will be influenced by lots of different selection pressures, pushing and tugging in different directions and with different strengths, sometimes cooperating with each other, sometimes opposing. At 11am local time on 13 December, countries adopted the text of an agreement that calls for “transitioning away from fossil fuels in energy systems, in a just, orderly and equitable manner, accelerating action in this critical decade, so as to achieve net zero by 2050 in keeping with the science.”
At 11am local time on 13 December, countries adopted the text of an agreement that calls for “transitioning away from fossil fuels in energy systems, in a just, orderly and equitable manner, accelerating action in this critical decade, so as to achieve net zero by 2050 in keeping with the science.”