Megan O’Grady in the New York Times:
 Perhaps no author has made more art of dispossession than Ruth Prawer Jhabvala. The author of a dozen novels and twice as many screenplays — she’s the only person to have won both the Booker Prize (for her eighth and best-known novel, “Heat and Dust”) and an Academy Award (twice, for best adapted screenplay) — Jhabvala was 12 when she fled Nazi Germany with her family in 1939. After the war, when her father learned the fate of the relatives left behind, he killed himself.
Perhaps no author has made more art of dispossession than Ruth Prawer Jhabvala. The author of a dozen novels and twice as many screenplays — she’s the only person to have won both the Booker Prize (for her eighth and best-known novel, “Heat and Dust”) and an Academy Award (twice, for best adapted screenplay) — Jhabvala was 12 when she fled Nazi Germany with her family in 1939. After the war, when her father learned the fate of the relatives left behind, he killed himself.
But even before her “disinheritance,” as she would later call these fundamental losses, Jhabvala was writing stories — first in German, and after they had settled in London, in English. She was studying English literature when she met Cyrus Jhabvala, an architect, and in 1951, they married and moved to Delhi. India was her home and subject until 1975, when she moved to New York’s Upper East Side, buying an apartment near her friends and creative partners, Ismail Merchant and James Ivory, as her career as a screenwriter flourished. There, as if closing a circle, she wrote fiction inspired by the European émigrés she met, people who understood what it meant to be homesick for a way of life that no longer existed. In a 1979 lecture, Jhabvala described herself as “blown about from country to country, culture to culture,” a “cuckoo forever insinuating itself into other’s nests.”
In this country, she’s best known as the screenwriting talent behind so many Merchant-Ivory films, among them the sumptuous, Oscar-winning adaptations of E. M. Forster’s “A Room With a View” and “Howards End” (a film of her own novel “The Householder” was their first collaboration).
More here.


 “We are in considerable doubt that you will develop into our professional stereotype of what an experimental psychologist should be.” When the Harvard psychology department kicked Judith Rich Harris out of their PhD program in 1960, they could not have known how true the words in their expulsion letter would turn out to be.
“We are in considerable doubt that you will develop into our professional stereotype of what an experimental psychologist should be.” When the Harvard psychology department kicked Judith Rich Harris out of their PhD program in 1960, they could not have known how true the words in their expulsion letter would turn out to be.
 When
When  Having read his book carefully, I believe it’s crucially important to take Pinker to task for some dangerously erroneous arguments he makes. Pinker is, after all, an intellectual darling of the most powerful echelons of global society. He
Having read his book carefully, I believe it’s crucially important to take Pinker to task for some dangerously erroneous arguments he makes. Pinker is, after all, an intellectual darling of the most powerful echelons of global society. He  Issuing a clarion call against the Modi government, an estimated 200 million workers across various sectors successfully carried out a
Issuing a clarion call against the Modi government, an estimated 200 million workers across various sectors successfully carried out a 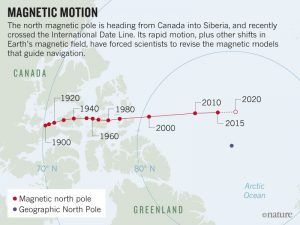 Something strange is going on at the top of the world. Earth’s north magnetic pole has been skittering away from Canada and towards Siberia, driven by liquid iron sloshing within the planet’s core. The magnetic pole is moving so quickly that it has forced the world’s geomagnetism experts into a rare move. On 15 January, they are set to update the World Magnetic Model, which describes
Something strange is going on at the top of the world. Earth’s north magnetic pole has been skittering away from Canada and towards Siberia, driven by liquid iron sloshing within the planet’s core. The magnetic pole is moving so quickly that it has forced the world’s geomagnetism experts into a rare move. On 15 January, they are set to update the World Magnetic Model, which describes  In 1987, my first year in college, I happened upon a notice outside of the English department for a winter session opportunity: escorting a visiting artist during a week-long interdisciplinary conference held at my school, the University of Rochester. I ran my finger down the list of artists’ names until it stopped on one: Ursula K. Le Guin.
In 1987, my first year in college, I happened upon a notice outside of the English department for a winter session opportunity: escorting a visiting artist during a week-long interdisciplinary conference held at my school, the University of Rochester. I ran my finger down the list of artists’ names until it stopped on one: Ursula K. Le Guin. In recent years many prominent people have expressed worries about artificial intelligence (AI). Elon Musk thinks it’s the “
In recent years many prominent people have expressed worries about artificial intelligence (AI). Elon Musk thinks it’s the “ Iraq has endured decades of sanctions, war, invasion, regime change and dysfunctional government. These span Saddam Hussein’s dictatorship, a devastating eight-year war with Iran in the 1980s and crippling UN sanctions throughout the 1990s. Those difficult years gave way to the traumas of the 2003 U.S.-led invasion and its chaotic aftermath, which brought the insurgents of the Islamic State to the outskirts of the Iraqi capital Baghdad in 2014.
Iraq has endured decades of sanctions, war, invasion, regime change and dysfunctional government. These span Saddam Hussein’s dictatorship, a devastating eight-year war with Iran in the 1980s and crippling UN sanctions throughout the 1990s. Those difficult years gave way to the traumas of the 2003 U.S.-led invasion and its chaotic aftermath, which brought the insurgents of the Islamic State to the outskirts of the Iraqi capital Baghdad in 2014. Few issues in economics have generated such heated debates as the nature of money and its role in the economy. What is money? How is it related to debt? How does it influence economic activity? The recent mainstream economic literature is an unfortunate exception. Bar a few who have sailed into these waters, money has been allowed to sink by the macroeconomics profession. And with little or no regrets.
Few issues in economics have generated such heated debates as the nature of money and its role in the economy. What is money? How is it related to debt? How does it influence economic activity? The recent mainstream economic literature is an unfortunate exception. Bar a few who have sailed into these waters, money has been allowed to sink by the macroeconomics profession. And with little or no regrets. It was slightly more than a century ago, in November 1918, that revolution swept through Germany, bringing chaos to a country that, in the final days of World War I, was already in desperate straits and verging on collapse. Although it was obvious to nearly everyone that the war was lost, the fighting staggered on, even as a growing pacifist movement issued the cry for “Peace, Freedom, Bread!” In Kiel on the Baltic Sea, sailors at the docks refused the order for a last battle and went into open mutiny, while soldiers and revolutionary workers in Berlin called for a general strike. Kaiser Wilhelm II, an absurd and incompetent militarist, at last faced the truth that his time was up and abdicated the throne, leaving confusion in his wake. On November 9, Philipp Scheidemann, a member of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SDP), seized the moment to declare the founding of a new republic.
It was slightly more than a century ago, in November 1918, that revolution swept through Germany, bringing chaos to a country that, in the final days of World War I, was already in desperate straits and verging on collapse. Although it was obvious to nearly everyone that the war was lost, the fighting staggered on, even as a growing pacifist movement issued the cry for “Peace, Freedom, Bread!” In Kiel on the Baltic Sea, sailors at the docks refused the order for a last battle and went into open mutiny, while soldiers and revolutionary workers in Berlin called for a general strike. Kaiser Wilhelm II, an absurd and incompetent militarist, at last faced the truth that his time was up and abdicated the throne, leaving confusion in his wake. On November 9, Philipp Scheidemann, a member of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SDP), seized the moment to declare the founding of a new republic. Speaker Nancy Pelosi and the
Speaker Nancy Pelosi and the 
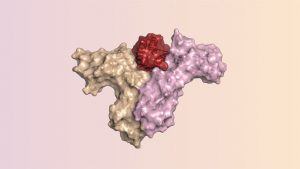 For patients with aggressive kidney and skin cancers, an immune-boosting protein called interleukin-2 (IL-2) can be a lifesaver. But the dose at which it fights cancer can also produce life-threatening side effects. Now, scientists have used computer modeling to design a new protein from scratch that mimics IL-2’s immune-enhancing abilities, while avoiding its dangerous side effects. The protein has so far been tested only in animals, but it may soon enter human trials. IL-2 plays a key role in directing the body’s immune response to outside invaders. The protein, a signaling molecule called a cytokine, ramps up the activity of white blood cells known as T lymphocytes by binding simultaneously to their IL-2β and IL-2γ receptors. In cells where a third type of receptor, IL-2α, is present, IL-2 binds collectively to all three. In other white blood cells, this dampens the body’s immune response. But it can also occur in cells in blood vessels, causing those vessels to leak, a potentially deadly condition.
For patients with aggressive kidney and skin cancers, an immune-boosting protein called interleukin-2 (IL-2) can be a lifesaver. But the dose at which it fights cancer can also produce life-threatening side effects. Now, scientists have used computer modeling to design a new protein from scratch that mimics IL-2’s immune-enhancing abilities, while avoiding its dangerous side effects. The protein has so far been tested only in animals, but it may soon enter human trials. IL-2 plays a key role in directing the body’s immune response to outside invaders. The protein, a signaling molecule called a cytokine, ramps up the activity of white blood cells known as T lymphocytes by binding simultaneously to their IL-2β and IL-2γ receptors. In cells where a third type of receptor, IL-2α, is present, IL-2 binds collectively to all three. In other white blood cells, this dampens the body’s immune response. But it can also occur in cells in blood vessels, causing those vessels to leak, a potentially deadly condition.