P. Kishore Saval in American Affairs:
 For thousands of years, the liberal arts were not liberal, and that is why they are increasingly unwelcome in our time. An honest study of the past is unsettling in a liberal age, because a person who learns to venerate earlier cultural traditions, from Homer to the baroque, may come to venerate the values to which those traditions are devoted. And those values are a direct rebuke to the substance of liberalism.
For thousands of years, the liberal arts were not liberal, and that is why they are increasingly unwelcome in our time. An honest study of the past is unsettling in a liberal age, because a person who learns to venerate earlier cultural traditions, from Homer to the baroque, may come to venerate the values to which those traditions are devoted. And those values are a direct rebuke to the substance of liberalism.
“Liberalism” here does not refer to the modern American distinction between liberals and conservatives, both of whom are liberals in every important respect. Liberalism is a governing idea dedicated to the priority of the autonomous, rights-bearing individual—an individual defined against, rather than constituted by, a community and its inherited traditions. In the early centuries of liberalism, the commitment to this idea of the individual appeared to release enormous creativity and achieve real benefits. But few can fail to notice that liberal societies are at the end of their vitality and creative energy. It has now become apparent to many that liberalism does not work—that it has degraded our spiritual freedom, impoverished the world of meaning, and dehumanized us before the power of money. But liberalism also prevents us from finding our way out of the mess that it has created. Liberalism is only a few centuries old, yet this recent governing order is now being treated as an eternal condition of humanity from which there can be no dissent or alternative. When we attempt to diagnose our disorder, we can only do so through a prejudicial history that falsifies the past, and therefore prevents any true understanding of the present. In such a context, the destruction of an authentic liberal arts tradition is not hard to understand.
More here.

 SKOOTER MCCOY WAS
SKOOTER MCCOY WAS  Look, we already know that Ishmael Reed hasn’t seen Hamilton.
Look, we already know that Ishmael Reed hasn’t seen Hamilton. “I love that,” said Thompson. “He’s for America 100%. It’s America or no way. I love that.” Thompson is an African American man in his early 20s. He was wearing a camouflage shirt under black overalls, with a large pin on his chest depicting a cartoon boy – a mashup of Calvin from Calvin and Hobbes and Trump himself – urinating on the CNN logo. People continued to walk past us en route to the rally. Mothers and daughters in University of Texas-El Paso sweatshirts. A man wearing an Uncle Sam costume. Groups of young men and groups of young women, and couples holding hands and dressed up as if the rally were a night on the town. A middle-aged blond woman rushed by in a head-to‑toe suede outfit, fringes flying as she crossed the street, the lights of the Coliseum beckoning.
“I love that,” said Thompson. “He’s for America 100%. It’s America or no way. I love that.” Thompson is an African American man in his early 20s. He was wearing a camouflage shirt under black overalls, with a large pin on his chest depicting a cartoon boy – a mashup of Calvin from Calvin and Hobbes and Trump himself – urinating on the CNN logo. People continued to walk past us en route to the rally. Mothers and daughters in University of Texas-El Paso sweatshirts. A man wearing an Uncle Sam costume. Groups of young men and groups of young women, and couples holding hands and dressed up as if the rally were a night on the town. A middle-aged blond woman rushed by in a head-to‑toe suede outfit, fringes flying as she crossed the street, the lights of the Coliseum beckoning. Toni Morrison, the author and Nobel Prize winner, turned 88 on Feb. 18. I have never met Morrison. And while you’ll likely see a donkey fly before you see her stand before a bunch of Harvard undergraduates and sing on demand, the fact is Toni Morrison is very much like Ella Fitzgerald. Like Fitzgerald, she rose from humble beginnings to world prominence. Like Fitzgerald, she is intensely private. And like Fitzgerald, she has given every iota of her extraordinary American-born talent and intellect to the great American dream. Not the one with the guns and bombs bursting in air. The other one, the one with world peace, justice, racial harmony, art, literature, music and language that shows us how to be free wrapped in it. Morrison has, as they say in church, lived a life of service. Whatever awards and acclaim she has won, she has earned. She has paid in full. She owes us nothing.
Toni Morrison, the author and Nobel Prize winner, turned 88 on Feb. 18. I have never met Morrison. And while you’ll likely see a donkey fly before you see her stand before a bunch of Harvard undergraduates and sing on demand, the fact is Toni Morrison is very much like Ella Fitzgerald. Like Fitzgerald, she rose from humble beginnings to world prominence. Like Fitzgerald, she is intensely private. And like Fitzgerald, she has given every iota of her extraordinary American-born talent and intellect to the great American dream. Not the one with the guns and bombs bursting in air. The other one, the one with world peace, justice, racial harmony, art, literature, music and language that shows us how to be free wrapped in it. Morrison has, as they say in church, lived a life of service. Whatever awards and acclaim she has won, she has earned. She has paid in full. She owes us nothing. Were the humanists wrong to claim that art is good for us, “like Ovaltine and yoga”? Movies have been more like a secret vice, the first and most invasive of the technologies that have progressively estranged us from one another. As a Londoner resettled in San Francisco, Thomson is also keenly aware of the way the medium has duped Americans, convincing them that happy endings are inevitable so long as gun-toting men control the narrative. “Can’t we admit,” he asks, “how much American experience has been rooted in fear?” In one mind-bending paragraph he outlines an alternative pantheon of great American films – including
Were the humanists wrong to claim that art is good for us, “like Ovaltine and yoga”? Movies have been more like a secret vice, the first and most invasive of the technologies that have progressively estranged us from one another. As a Londoner resettled in San Francisco, Thomson is also keenly aware of the way the medium has duped Americans, convincing them that happy endings are inevitable so long as gun-toting men control the narrative. “Can’t we admit,” he asks, “how much American experience has been rooted in fear?” In one mind-bending paragraph he outlines an alternative pantheon of great American films – including  “Bloodlines” employs numbered sections, one of Carreira’s favored devices, to divide the poem into a triptych. She uses time and place to distinguish each, taking us from her adolescence in Portugal to early adulthood in New Jersey to the present moment. In the first, the adolescent version of Carreira feels shame about her body—not the first time we encounter, in heartbreaking fashion, the painful self-consciousness of a young narrator—while, at the same time yearning for physical connection. She wants “a God-fearing man,” but she observes that a young neighbor of hers is “a pretty boy.” The end of this section is marked by the advent of menstruation, a hallmark of maturity that doubles as a sign of heritage and hardship. While the neighbor boy collects the material possessions that “make for a good life,” the menstrual signature on the speaker’s bed sheets “promises thorns no bread or gold can dull.” The concrete trappings of health and prosperity are conflated with the promise of a bright future, but “blood,” in all its multi-layered meaning, complicates the simple promise of “bread or gold.” Profoundly, for Carreira, this duality echoes the divided heart of the Portuguese immigrant community in America—one heart striving and struggling forward in its quest for material security and the American Dream, while the other looks backward toward an idealized past that continues to drift further and further out of reach with the passage of time.
“Bloodlines” employs numbered sections, one of Carreira’s favored devices, to divide the poem into a triptych. She uses time and place to distinguish each, taking us from her adolescence in Portugal to early adulthood in New Jersey to the present moment. In the first, the adolescent version of Carreira feels shame about her body—not the first time we encounter, in heartbreaking fashion, the painful self-consciousness of a young narrator—while, at the same time yearning for physical connection. She wants “a God-fearing man,” but she observes that a young neighbor of hers is “a pretty boy.” The end of this section is marked by the advent of menstruation, a hallmark of maturity that doubles as a sign of heritage and hardship. While the neighbor boy collects the material possessions that “make for a good life,” the menstrual signature on the speaker’s bed sheets “promises thorns no bread or gold can dull.” The concrete trappings of health and prosperity are conflated with the promise of a bright future, but “blood,” in all its multi-layered meaning, complicates the simple promise of “bread or gold.” Profoundly, for Carreira, this duality echoes the divided heart of the Portuguese immigrant community in America—one heart striving and struggling forward in its quest for material security and the American Dream, while the other looks backward toward an idealized past that continues to drift further and further out of reach with the passage of time. Diderot is known to the casual reader chiefly as an editor of the Encyclopédie—it had no other name, for there was no other encyclopédie. Since the Encyclopédie was a massive compendium of knowledge of all kinds, organizing the entirety of human thought, Diderot persists vaguely in memory as a type of Enlightenment superman, the big bore with a big book. Yet in these two new works of biography he turns out to be not a severe rationalist, overseeing a totalitarianism of thought, but an inspired and lovable amateur, with an opinion on every subject and an appetite for every occasion.
Diderot is known to the casual reader chiefly as an editor of the Encyclopédie—it had no other name, for there was no other encyclopédie. Since the Encyclopédie was a massive compendium of knowledge of all kinds, organizing the entirety of human thought, Diderot persists vaguely in memory as a type of Enlightenment superman, the big bore with a big book. Yet in these two new works of biography he turns out to be not a severe rationalist, overseeing a totalitarianism of thought, but an inspired and lovable amateur, with an opinion on every subject and an appetite for every occasion. In 2015 I attended a workshop on political polarization with an eclectic group of scholars and activists. We swapped ideas on resolving battles over climate change, inequality, abortion and gay rights. One obstacle to compromise, a psychologist said, is that many Americans have a visceral, emotional reaction to issues like homosexuality.
In 2015 I attended a workshop on political polarization with an eclectic group of scholars and activists. We swapped ideas on resolving battles over climate change, inequality, abortion and gay rights. One obstacle to compromise, a psychologist said, is that many Americans have a visceral, emotional reaction to issues like homosexuality. In my 50s, too old to become a real expert, I have finally fallen in love with algebraic geometry. As the name suggests, this is the study of geometry using algebra. Around 1637, René Descartes laid the groundwork for this subject by taking a plane, mentally drawing a grid on it, as we now do with graph paper, and calling the coordinates x and y. We can write down an equation like x2+ y2 = 1, and there will be a curve consisting of points whose coordinates obey this equation. In this example, we get a circle!
In my 50s, too old to become a real expert, I have finally fallen in love with algebraic geometry. As the name suggests, this is the study of geometry using algebra. Around 1637, René Descartes laid the groundwork for this subject by taking a plane, mentally drawing a grid on it, as we now do with graph paper, and calling the coordinates x and y. We can write down an equation like x2+ y2 = 1, and there will be a curve consisting of points whose coordinates obey this equation. In this example, we get a circle! With his reckless “pre-emptive” airstrike on
With his reckless “pre-emptive” airstrike on  In 1974, after protracted legal efforts and sometimes violent protests, a US district court in Washington State upheld the treaties of the Columbia Plateau tribes. Known as the Boldt Decision, the ruling upended the fishing industry and still angers non-Indian fishermen. It gave tribal members the right to half of the river’s harvestable fish, and it was upheld by the Supreme Court in 1979. (The number considered harvestable varies. Fishery managers meet throughout the year to set limits that will allow weak populations to rebound and tributary stocks to spawn, but the shares are always kept equal between treaty and non-treaty fishers.) The tribes also have access to thirty-one fishing sites closed to others. A long stretch of the lower river is now divided into six fishing zones. The first five zones are in the 145 miles between the mouth of the Columbia and Bonneville Dam. Zone 6 runs above Bonneville for another 147 miles, and commercial fishing can only be done by the tribes there. The Boldt Decision affirmed the right to fish—but it didn’t bring back the fish. It did nothing to mitigate the desperate losses caused by dams, development, and overfishing. By 1995, there were about 750,000 salmon left in the entire Columbia River.
In 1974, after protracted legal efforts and sometimes violent protests, a US district court in Washington State upheld the treaties of the Columbia Plateau tribes. Known as the Boldt Decision, the ruling upended the fishing industry and still angers non-Indian fishermen. It gave tribal members the right to half of the river’s harvestable fish, and it was upheld by the Supreme Court in 1979. (The number considered harvestable varies. Fishery managers meet throughout the year to set limits that will allow weak populations to rebound and tributary stocks to spawn, but the shares are always kept equal between treaty and non-treaty fishers.) The tribes also have access to thirty-one fishing sites closed to others. A long stretch of the lower river is now divided into six fishing zones. The first five zones are in the 145 miles between the mouth of the Columbia and Bonneville Dam. Zone 6 runs above Bonneville for another 147 miles, and commercial fishing can only be done by the tribes there. The Boldt Decision affirmed the right to fish—but it didn’t bring back the fish. It did nothing to mitigate the desperate losses caused by dams, development, and overfishing. By 1995, there were about 750,000 salmon left in the entire Columbia River. Cheesemania ’93, as I’ve decided to call it, is a classic TV commercial. In a civilization organized primarily around the funneling of capital to corporations, commercials offer a space of transcendent communion with the objects of our dependence and desire. They take place in a realm understood to be ideational without quite being imaginary—existing not in any one person’s mind, but ambiently, on a level of reality we rarely think to question, encoded in the daily order of things as neatly as the peanut butter aisle of a suburban grocery store. (This bare proximity to capitalism’s exposed nerves, combined with a habitual callousness to human dignity, is I believe why, in the
Cheesemania ’93, as I’ve decided to call it, is a classic TV commercial. In a civilization organized primarily around the funneling of capital to corporations, commercials offer a space of transcendent communion with the objects of our dependence and desire. They take place in a realm understood to be ideational without quite being imaginary—existing not in any one person’s mind, but ambiently, on a level of reality we rarely think to question, encoded in the daily order of things as neatly as the peanut butter aisle of a suburban grocery store. (This bare proximity to capitalism’s exposed nerves, combined with a habitual callousness to human dignity, is I believe why, in the  Fiona MacCarthy met Walter Gropius (1883–1969) through Jack Pritchard, the British entrepreneur who built Lawn Road Flats in Hampstead, an experiment in modernist living where Gropius took up residence after escaping Nazi Germany in 1934. The Bauhaus, the school he founded in Weimar a century ago this year, had been closed by stormtroopers the previous year (by then it had moved to Berlin). In 1968, after the opening of a Bauhaus exhibition at the Royal Academy, MacCarthy was invited to dinner with Gropius at the Lawn Road Isobar, the block’s in-house dining room: ‘He was then eighty-five, small, upright, very courteous, retaining a Germanic formality of bearing,’ MacCarthy recalled. He ‘was still valiant and impressive, with a flickering of arrogance’.
Fiona MacCarthy met Walter Gropius (1883–1969) through Jack Pritchard, the British entrepreneur who built Lawn Road Flats in Hampstead, an experiment in modernist living where Gropius took up residence after escaping Nazi Germany in 1934. The Bauhaus, the school he founded in Weimar a century ago this year, had been closed by stormtroopers the previous year (by then it had moved to Berlin). In 1968, after the opening of a Bauhaus exhibition at the Royal Academy, MacCarthy was invited to dinner with Gropius at the Lawn Road Isobar, the block’s in-house dining room: ‘He was then eighty-five, small, upright, very courteous, retaining a Germanic formality of bearing,’ MacCarthy recalled. He ‘was still valiant and impressive, with a flickering of arrogance’.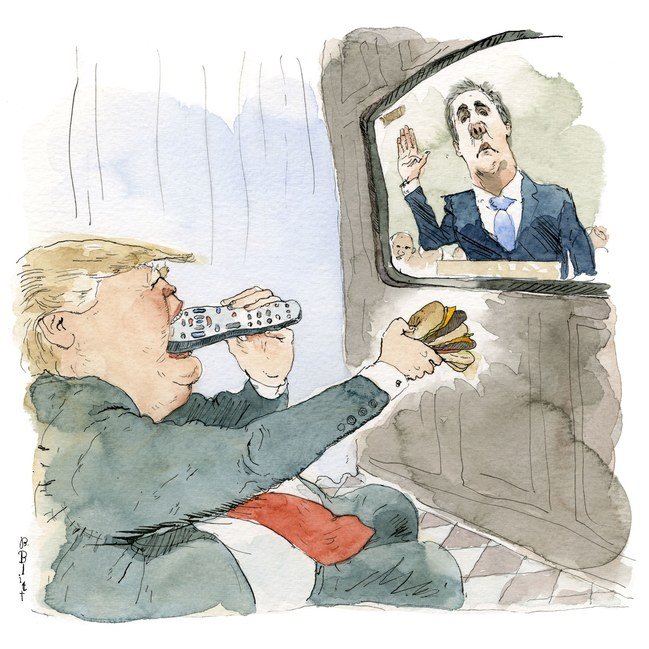
 Variations of the genome editor CRISPR have wowed biology labs around the world over the past few years because they can precisely change single DNA bases, promising deft repairs for genetic diseases and improvements in crop and livestock genomes. But such “base editors” can have a serious weakness. A pair of studies published online in Science this week
Variations of the genome editor CRISPR have wowed biology labs around the world over the past few years because they can precisely change single DNA bases, promising deft repairs for genetic diseases and improvements in crop and livestock genomes. But such “base editors” can have a serious weakness. A pair of studies published online in Science this week  During six years of singlehood in my 20s, I became a person I did not know. Before, I had always been a reader. I walked to the library several times a week as a kid and stayed up late into the night reading under my blankets with a flashlight. I checked out so many books and returned them so quickly the librarian once snapped, “Don’t take home so many books if you’re not going to read them all.”
During six years of singlehood in my 20s, I became a person I did not know. Before, I had always been a reader. I walked to the library several times a week as a kid and stayed up late into the night reading under my blankets with a flashlight. I checked out so many books and returned them so quickly the librarian once snapped, “Don’t take home so many books if you’re not going to read them all.”