Clifford Thompson at Commonweal:
 Why abstract art? The question is not rhetorical, especially as a point of entry into the visionary work of Jack Whitten, whose career spanned six decades before he died in 2018. One possible answer: the need to say what cannot be said according to the usual rules—rules for perspective, light, scale, and all the rest, but also, and maybe most importantly, rules for representing the world in a way that the world has already recognized. What looks real, what is real, may not be the same for you as it is for me. That makes it vitally important for artists to paint, sculpt, or draw the world as they see it, regardless of the rules. And that is particularly true when the rules—inside the world of art schools, galleries, and museums and, most especially, outside it—constitute the very evil that makes their work necessary.
Why abstract art? The question is not rhetorical, especially as a point of entry into the visionary work of Jack Whitten, whose career spanned six decades before he died in 2018. One possible answer: the need to say what cannot be said according to the usual rules—rules for perspective, light, scale, and all the rest, but also, and maybe most importantly, rules for representing the world in a way that the world has already recognized. What looks real, what is real, may not be the same for you as it is for me. That makes it vitally important for artists to paint, sculpt, or draw the world as they see it, regardless of the rules. And that is particularly true when the rules—inside the world of art schools, galleries, and museums and, most especially, outside it—constitute the very evil that makes their work necessary.
That was certainly true for Whitten, the African American son of a coal miner and a seamstress, born in 1939 and raised in segregated Bessemer, Alabama. Here is how segregated: Whitten and other Black students were prohibited from visiting art museums, so they toured the area’s coal mines and steel mills instead. The first member of his family to attend college, Whitten became a premed student at Alabama’s Tuskegee Institute before shifting his focus in 1959—ironically, given the restrictions placed on him during boyhood—to art.
more here.
Enjoying the content on 3QD? Help keep us going by donating now.

 Why abstract art? The question is not rhetorical, especially as a point of entry into the visionary work of Jack Whitten, whose career spanned six decades before he died in 2018. One possible answer: the need to say what cannot be said according to the usual rules—rules for perspective, light, scale, and all the rest, but also, and maybe most importantly, rules for representing the world in a way that the world has already recognized. What looks real, what is real, may not be the same for you as it is for me. That makes it vitally important for artists to paint, sculpt, or draw the world as they see it, regardless of the rules. And that is particularly true when the rules—inside the world of art schools, galleries, and museums and, most especially, outside it—constitute the very evil that makes their work necessary.
Why abstract art? The question is not rhetorical, especially as a point of entry into the visionary work of Jack Whitten, whose career spanned six decades before he died in 2018. One possible answer: the need to say what cannot be said according to the usual rules—rules for perspective, light, scale, and all the rest, but also, and maybe most importantly, rules for representing the world in a way that the world has already recognized. What looks real, what is real, may not be the same for you as it is for me. That makes it vitally important for artists to paint, sculpt, or draw the world as they see it, regardless of the rules. And that is particularly true when the rules—inside the world of art schools, galleries, and museums and, most especially, outside it—constitute the very evil that makes their work necessary. In April 1649, the earth of
In April 1649, the earth of  Through a stroke of good fortune, Elon Musk’s otherwise disastrous purchase of Twitter has turned into one of the great business acquisitions of all time. Buying control of a president was a start. What if the deal bought him something even more valuable?
Through a stroke of good fortune, Elon Musk’s otherwise disastrous purchase of Twitter has turned into one of the great business acquisitions of all time. Buying control of a president was a start. What if the deal bought him something even more valuable? Autism spectrum disorder, or autism, is a neurodevelopmental disorder. People with the disorder may have deficits in social communication and interaction and restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities. Autism is really a construct, an idea that there is something different about people who have very basic deficits or difficulties in social communication, starting very young, and also certain repetitive or sensory differences compared to neurotypical people.
Autism spectrum disorder, or autism, is a neurodevelopmental disorder. People with the disorder may have deficits in social communication and interaction and restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities. Autism is really a construct, an idea that there is something different about people who have very basic deficits or difficulties in social communication, starting very young, and also certain repetitive or sensory differences compared to neurotypical people. The term “first-world problem” is used to describe the type of minor nuisance that occupies the minds of the bourgeoisie. You dropped an AirPod in the urinal. You spilled chardonnay on the divan. Whole Foods was out of pomegranates. And so forth. These are perfectly real frustrations, but they only afflict the comfortable. We might define a parallel quandary in the field of moral philosophy: the first-world ethical problem. These are dilemmas about right and wrong that don’t actually touch any of the major ethical crises of our time or issues of structural injustice. They’re problems that only arise or seem worthy of spending time on once you reach a certain level of wealth and privilege. The New York Times advice column,
The term “first-world problem” is used to describe the type of minor nuisance that occupies the minds of the bourgeoisie. You dropped an AirPod in the urinal. You spilled chardonnay on the divan. Whole Foods was out of pomegranates. And so forth. These are perfectly real frustrations, but they only afflict the comfortable. We might define a parallel quandary in the field of moral philosophy: the first-world ethical problem. These are dilemmas about right and wrong that don’t actually touch any of the major ethical crises of our time or issues of structural injustice. They’re problems that only arise or seem worthy of spending time on once you reach a certain level of wealth and privilege. The New York Times advice column, 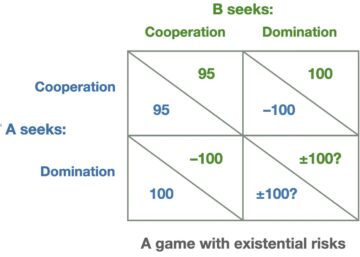 Advanced AI will transform possibilities, and our future will depend on which become real. Deep uncertainties make an AI arms race risky for all sides, yet AI also creates opportunities for unprecedented security. The key challenge isn’t technical feasibility — advanced AI can do that heavy lifting — but navigating from competition to cooperation against the friction of reality: institutional inertia, expectations rooted in thousands of years of state conflict, and sheer failure to recognize unprecedented options.
Advanced AI will transform possibilities, and our future will depend on which become real. Deep uncertainties make an AI arms race risky for all sides, yet AI also creates opportunities for unprecedented security. The key challenge isn’t technical feasibility — advanced AI can do that heavy lifting — but navigating from competition to cooperation against the friction of reality: institutional inertia, expectations rooted in thousands of years of state conflict, and sheer failure to recognize unprecedented options. Clara Collier: To start, do you want to give us a quick background of the book and your research?
Clara Collier: To start, do you want to give us a quick background of the book and your research? O
O U
U Koethe’s taste for self-contradiction or self-revision, and for rambling free-associative structures of “meditation gone awry” (as he puts it in the poem “Naturalism”) that move around in strange eddies before circling back to some revised perception of their starting point, may seem surprising in a poet whose day job has been in a philosophy department, where logical consistency and a rigorous organization of argument are valued. But then this is the philosopher-poet who once proclaimed, flatly, “I don’t like poems about philosophy.” His poetry seems to be the place for everything philosophy doesn’t know what to do with, for what in “Against Materialism” he calls, “Things so commonplace it’s easy to forget how strange they are” but which “Make up the furniture of the world, and if none of them pass muster metaphysically, / So what?”
Koethe’s taste for self-contradiction or self-revision, and for rambling free-associative structures of “meditation gone awry” (as he puts it in the poem “Naturalism”) that move around in strange eddies before circling back to some revised perception of their starting point, may seem surprising in a poet whose day job has been in a philosophy department, where logical consistency and a rigorous organization of argument are valued. But then this is the philosopher-poet who once proclaimed, flatly, “I don’t like poems about philosophy.” His poetry seems to be the place for everything philosophy doesn’t know what to do with, for what in “Against Materialism” he calls, “Things so commonplace it’s easy to forget how strange they are” but which “Make up the furniture of the world, and if none of them pass muster metaphysically, / So what?” Amis’s writing is stylish and screwy and grotesque and vulgar. The jokes come at an unhinged pace. He was an exquisite writer of the male body and the horrors of inhabiting one: “My hair hung on my head as if it were a cut-price toupée,” Charles Highway (Charles Highway!) reflects in Amis’s debut novel The Rachel Papers. That same character savages the “Big Boys” that are his pimples and speaks of “laundering my orifices,” as “they went all to hell if not scrupulously maintained.” A genital region is referred to as a “rig.” The names, across his books, are insane. Amis calls characters things like Spunk, 13, Fart Klaeber, Sod. A female cop (or as she calls herself “a police”) is named Mike Hoolihan. A quartet of violent dogs are Joe, Joel, Jeff, and Jon. That he called a writer-character Martin Amis, or so the
Amis’s writing is stylish and screwy and grotesque and vulgar. The jokes come at an unhinged pace. He was an exquisite writer of the male body and the horrors of inhabiting one: “My hair hung on my head as if it were a cut-price toupée,” Charles Highway (Charles Highway!) reflects in Amis’s debut novel The Rachel Papers. That same character savages the “Big Boys” that are his pimples and speaks of “laundering my orifices,” as “they went all to hell if not scrupulously maintained.” A genital region is referred to as a “rig.” The names, across his books, are insane. Amis calls characters things like Spunk, 13, Fart Klaeber, Sod. A female cop (or as she calls herself “a police”) is named Mike Hoolihan. A quartet of violent dogs are Joe, Joel, Jeff, and Jon. That he called a writer-character Martin Amis, or so the  In 1944 after the liberation of Majdanek, where the soviet troops discovered warehouses of shoes and human hair, the term “death factory” gained general currency. Through wartime propaganda channels the Soviet pamphlet, Majdanek the death factory near Lublin by Konstantin Simonov acquired a circulation in the West. In the exhibitionary complex of the holocaust, the shoes from the Majdanek warehouse have become another icon, especially since a large collection of them were donated to the Holocaust memorial museum in Washington DC.
In 1944 after the liberation of Majdanek, where the soviet troops discovered warehouses of shoes and human hair, the term “death factory” gained general currency. Through wartime propaganda channels the Soviet pamphlet, Majdanek the death factory near Lublin by Konstantin Simonov acquired a circulation in the West. In the exhibitionary complex of the holocaust, the shoes from the Majdanek warehouse have become another icon, especially since a large collection of them were donated to the Holocaust memorial museum in Washington DC. One July afternoon in 2024,
One July afternoon in 2024,  Among the cognitive debilities that occur over time is rigidity in one’s fundamental outlook and assumptions about life. One’s outlook is usually set relatively early in life; usually by early adulthood you are either a liberal or a conservative; a nationalist or an internationalist; a risk-taker or someone habitually fearful and cautious. There is a lot of happy talk among gerontologists about how people can remain open to new ideas and able to reinvent their lives late in life, and that certainly happens with some individuals. But the truth of the matter is that fundamental change in mental outlooks becomes much less likely with age.
Among the cognitive debilities that occur over time is rigidity in one’s fundamental outlook and assumptions about life. One’s outlook is usually set relatively early in life; usually by early adulthood you are either a liberal or a conservative; a nationalist or an internationalist; a risk-taker or someone habitually fearful and cautious. There is a lot of happy talk among gerontologists about how people can remain open to new ideas and able to reinvent their lives late in life, and that certainly happens with some individuals. But the truth of the matter is that fundamental change in mental outlooks becomes much less likely with age. I
I