Eli Zaretsky in Sidecar:
As if demonstrating that the repressed does return, politics has erupted in the supposedly apolitical world of American psychoanalysis. An advocacy group, Black Psychoanalysts Speak, and a documentary film, Psychoanalysis in El Barrio, seek to redress the racial and class biases of analysis. Unbehagen, a psychoanalytic list-serve, features a roiling debate over whether it is necessary to match the analyst’s gender, race, ethnicity and sexual orientation with the patient’s. The American Psychoanalytic Association itself has been shaken by political recriminations, purges, resignations and denunciations. An article by Donald Moss, published in the association’s journal, provided the catalyst in this case. According to its abstract:
Whiteness is a condition one first acquires and then one has – a malignant, parasitic-like condition to which ‘white’ people have a particular susceptibility. The condition is foundational, generating characteristic ways of being in one’s body, in one’s mind, and in one’s world. Parasitic Whiteness renders its hosts’ appetites voracious, insatiable and perverse.
The reaction to the article was sharply divided. Some saw it as a valuable extension of psychoanalytic theory, while others believed it neglected vital determining factors of racialization, such as deindustrialization, union discrimination and the inequities of the real estate market. In response to the controversy, an internal body was appointed, the Holmes Commission, to ‘investigate systemic racism and its underlying determinants embedded within APsaA, and to offer remedies for all aspects of identified racism’. Among the repercussions has been a debate over anti-Semitism precipitated by a speaking invitation to a controversial Lebanese psychoanalytic therapist, which led to the resignation of the President of the Association, Kerry Sulkowicz.
These developments are noteworthy in themselves, but they also raise wider questions about the relation between psychoanalysis and politics. What is striking about the politicization of contemporary psychoanalysis is the extent to which it conforms to the liberal identitarianism, sometimes termed ‘wokeness’, prevailing in the broader culture, which views systematic wrongs such as racism as emanating from individual psyches, along the model of sin.
More here.

 Surgeons in Baltimore have transplanted the heart of a genetically altered pig into a man with terminal heart disease who had no other hope for treatment, the University of Maryland Medical Center announced on Friday. It is the
Surgeons in Baltimore have transplanted the heart of a genetically altered pig into a man with terminal heart disease who had no other hope for treatment, the University of Maryland Medical Center announced on Friday. It is the  Of all the forms of human intellect that one might expect
Of all the forms of human intellect that one might expect  It is Mumbai in November, which is to say: hot.
It is Mumbai in November, which is to say: hot. In an attempt to address climate change and other environmental problems, governments are increasingly turning to economic solutions. The underlying message is clear: capitalism might have created the problem, but capitalism can solve it. Adrienne Buller, a Senior Fellow with progressive think tank Common Wealth, is, to put it mildly, sceptical of this. From carbon credits to biodiversity offsets, she unmasks these policies for the greenwashing that they are. The Value of a Whale is a necessary corrective that is as eye-opening as it is shocking.
In an attempt to address climate change and other environmental problems, governments are increasingly turning to economic solutions. The underlying message is clear: capitalism might have created the problem, but capitalism can solve it. Adrienne Buller, a Senior Fellow with progressive think tank Common Wealth, is, to put it mildly, sceptical of this. From carbon credits to biodiversity offsets, she unmasks these policies for the greenwashing that they are. The Value of a Whale is a necessary corrective that is as eye-opening as it is shocking. The past few years have seen an abundance of works of popular science about a variety of human beings who once inhabited Eurasia: “Neanderthals”. They died out, it appears, 40,000 years ago. That number – 40,000 – is as totemic to Neanderthal specialists as that better known figure, 65 million, is to dinosaur fanciers.
The past few years have seen an abundance of works of popular science about a variety of human beings who once inhabited Eurasia: “Neanderthals”. They died out, it appears, 40,000 years ago. That number – 40,000 – is as totemic to Neanderthal specialists as that better known figure, 65 million, is to dinosaur fanciers. To understand the origins of any franchise, look first to rights—who owns the intellectual property, how it is managed, and where the revenue generated from its exploitation is set to flow.
To understand the origins of any franchise, look first to rights—who owns the intellectual property, how it is managed, and where the revenue generated from its exploitation is set to flow. There are five fundamental operations in mathematics,” the German mathematician Martin Eichler supposedly said. “Addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and modular forms.”
There are five fundamental operations in mathematics,” the German mathematician Martin Eichler supposedly said. “Addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and modular forms.” Huda Dahbour was 35 years old when she moved with her husband and three children to the West Bank in September 1995. It was the second anniversary of the Oslo accords, which established pockets of Palestinian self-government in the occupied territories. Jerusalem was still relatively open when they arrived in East Sawahre, a neighbourhood just outside the areas of Jerusalem that
Huda Dahbour was 35 years old when she moved with her husband and three children to the West Bank in September 1995. It was the second anniversary of the Oslo accords, which established pockets of Palestinian self-government in the occupied territories. Jerusalem was still relatively open when they arrived in East Sawahre, a neighbourhood just outside the areas of Jerusalem that 
 In The Odyssey, Odysseus and his crew are forced to navigate a strait bounded by two equally dangerous obstacles: Scylla, a six-headed sea serpent, and Charybdis, an underwater horror that sucks down ships through a massive whirlpool. Judging Charybdis to be a greater danger to the crew as a whole, Odysseus orders his crew to try and pass through on Scylla’s side. They make it, but six sailors are eaten in the crossing. In their new book Tyranny of the Minority, Harvard political scientists Steven Levitsky and Daniel Ziblatt — the authors of How Democracies Die — argue America’s founders faced an analogous problem: navigating between two types of dictatorship that threatened to devour the new country.
In The Odyssey, Odysseus and his crew are forced to navigate a strait bounded by two equally dangerous obstacles: Scylla, a six-headed sea serpent, and Charybdis, an underwater horror that sucks down ships through a massive whirlpool. Judging Charybdis to be a greater danger to the crew as a whole, Odysseus orders his crew to try and pass through on Scylla’s side. They make it, but six sailors are eaten in the crossing. In their new book Tyranny of the Minority, Harvard political scientists Steven Levitsky and Daniel Ziblatt — the authors of How Democracies Die — argue America’s founders faced an analogous problem: navigating between two types of dictatorship that threatened to devour the new country.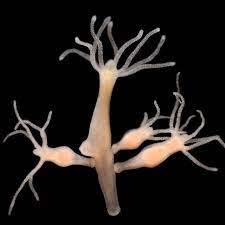 A strange, immortal tube-shaped animal has been discovered to regenerate a whole new body from only its mouth to avoid getting old. This creature, named Hydractinia symbiolongicarpus, a tiny invertebrate that lives on the shells of crabs, is usually immune to aging altogether, but was found to use aging within its body to grow an entirely new body, a study published in the
A strange, immortal tube-shaped animal has been discovered to regenerate a whole new body from only its mouth to avoid getting old. This creature, named Hydractinia symbiolongicarpus, a tiny invertebrate that lives on the shells of crabs, is usually immune to aging altogether, but was found to use aging within its body to grow an entirely new body, a study published in the Justin H. Vassallo in American Affairs:
Justin H. Vassallo in American Affairs: