Moribund
The animals are dying.
All the beautiful women are dying too.
Elizabeth Kolbert writes you can see the sixth
mass extinction unraveling in your own backyard.
Out the fourteenth-story windows of the hotel
I watch as an unraveling of women
pull themselves from a small blue rectangle
to dry their skin. This must be the most
beautiful thing. First, women, and second, women
as a diorama of themselves. In a 1969 lecture available
online, physicist Albert Bartlett tells us, The greatest
shortcoming of the human race is our inability to understand
the exponential function. Jenifer Wightman quotes this in
her paper
on bacterial pointillism, a type of painting technique whereby mud
is colonized by pigmented bacteria to produce an evolving color-
field of living pigments, a Rothko-like landscape whose subject is
generations of sequential doublings. Always there is what
scientists call
the background rate of extinction, that little death hum of
one to five
species per year, and today it’s
a thousand to ten thousand times that. They’re dying
before we know they exist. Can you see that? The hotel room rises
fourteen stories, 196 stories, 2,744 stories, and the women in
the pool
are multiplying into a Rothko painting. On the news, I watch
Syrian women haul bundled children through Aleppo’s
smoldering fossil. They are dying, as are their children.
Syrian mothers write appeals followed by farewells
on social media. Final message, one reads. I am very sad
no one is helping us in this world, no one is evacuating me &
my daughter,
goodbye. Blue is the opposite of red, oxygen molecules
binding to hemoglobin as a blue thing exposed
reddens. On the day after Christmas in 2015 the New York Times
posts
a video of a twenty-seven-year-old Muslim woman in Kabul
accused of burning
the Quran. A male mob swells. The policemen stand back as
poles &
bricks are held above her. Then, at a certain velocity, lowered
to break her. It is hundreds of men crying Allahu Akbar
as she whimpers Allahu Akbar from the ground. I watch this video
stitched from cellphone footage on a tablet held
between my father’s hands. They kill her. They run
her over. They burn her against a stone wall on a riverbank.
She was never burning a Quran, anyone could’ve seen that.
A year later, I recall the video and in order to find it,
the specificities blurred by now, I type into the search bar
Muslim woman red scarf burning Quran.
Only midway through the video do I realize
her face is so blood-drenched I have in my memory replaced it
with a red scarf. In fact, by the time the men get to burning her,
her body is so blood-drenched they must use their own scarves
to light her. But those halving miracles
derived from her marrow, exponentially
going extinct against the stone wall on the riverbank—
I couldn’t. I didn’t. When the men burned her,
the policemen said, Be careful of the fire.
.
by Hannah Perrin King
from Narrative Magazine
 “Complexity” was the term that Ralph Ellison deployed most often to describe black life and culture. And it is the term best suited to convey the character of this brilliant, often disapproving and unsparing man. Decades before Toni Morrison’s “Beloved” and “Song of Solomon,” “Invisible Man” (1952) singularly defined the meaning of literary achievement. As a critic, Ellison was no less significant a thinker and stylist. Always, he was a philosopher of black expressive form and an astute cultural analyst.
“Complexity” was the term that Ralph Ellison deployed most often to describe black life and culture. And it is the term best suited to convey the character of this brilliant, often disapproving and unsparing man. Decades before Toni Morrison’s “Beloved” and “Song of Solomon,” “Invisible Man” (1952) singularly defined the meaning of literary achievement. As a critic, Ellison was no less significant a thinker and stylist. Always, he was a philosopher of black expressive form and an astute cultural analyst.
 Dear imagined future self,
Dear imagined future self, False words, phony videos, doctored photos, and violent content are regular features on the online ecosystem worldwide. India is no exception, where such content, which often attracts millions of views, has led to
False words, phony videos, doctored photos, and violent content are regular features on the online ecosystem worldwide. India is no exception, where such content, which often attracts millions of views, has led to  Accusations of antisemitism
Accusations of antisemitism  I often think that my obsession with
I often think that my obsession with  Unlike Armstrong or Cukor, who stay true to Alcott’s timeline, Gerwig begins in the middle of the narrative, depicting the second half of the book while weaving in scenes drawn from the first. We open on the March sisters in their late teens or early twenties. The women in question are no longer very little, and the Civil War that cast a shadow over their youth has ended. We find the eldest, Meg, searching for contentment in her new life as the wife of a poor tutor (James Norton). Played by Emma Watson, she is the picture of grace if not always the voice, her Yankee accent at times on the brink. Tomboyish Jo—Ronan, offering a perfect compromise between Ryder’s timidity and Hepburn’s ham—is in New York avoiding an unwanted marriage proposal from her best friend, Laurie (Timothée Chalamet), and chasing after her dream of becoming a writer. Amy (Florence Pugh), the bratty baby, is in Europe to hone her painting skills and find a society husband. Only sweet, sickly Beth (Eliza Scanlen) remains at home, though she will soon depart on an adventure of a more permanent kind, as she learns to accept her slowly impending death, the consequence of childhood scarlet fever. As she says of her fate in one of Alcott’s most poetic lines, delivered with solemn elegance by Scanlen, who makes the most of Beth’s limited part: “It’s like the tide . . . when it turns, it goes slowly, but it can’t be stopped.”
Unlike Armstrong or Cukor, who stay true to Alcott’s timeline, Gerwig begins in the middle of the narrative, depicting the second half of the book while weaving in scenes drawn from the first. We open on the March sisters in their late teens or early twenties. The women in question are no longer very little, and the Civil War that cast a shadow over their youth has ended. We find the eldest, Meg, searching for contentment in her new life as the wife of a poor tutor (James Norton). Played by Emma Watson, she is the picture of grace if not always the voice, her Yankee accent at times on the brink. Tomboyish Jo—Ronan, offering a perfect compromise between Ryder’s timidity and Hepburn’s ham—is in New York avoiding an unwanted marriage proposal from her best friend, Laurie (Timothée Chalamet), and chasing after her dream of becoming a writer. Amy (Florence Pugh), the bratty baby, is in Europe to hone her painting skills and find a society husband. Only sweet, sickly Beth (Eliza Scanlen) remains at home, though she will soon depart on an adventure of a more permanent kind, as she learns to accept her slowly impending death, the consequence of childhood scarlet fever. As she says of her fate in one of Alcott’s most poetic lines, delivered with solemn elegance by Scanlen, who makes the most of Beth’s limited part: “It’s like the tide . . . when it turns, it goes slowly, but it can’t be stopped.” Jugaad is a hack, a hustle, a fix. It’s a lot from a little, the best with what you’ve got—which is likely not much, if you need jugaad. A “very DU word,” a Delhi University grad once explained to me, and I thought about how college students as a rule and around the world turn nothing into something (e.g., instant noodles).
Jugaad is a hack, a hustle, a fix. It’s a lot from a little, the best with what you’ve got—which is likely not much, if you need jugaad. A “very DU word,” a Delhi University grad once explained to me, and I thought about how college students as a rule and around the world turn nothing into something (e.g., instant noodles). A facility that saw 53,000 emergency room visits per year disappeared from Philadelphia this summer with the prolonged and still-unfinished closure of Hahnemann University Hospital. The 496-bed hospital employed 2,700 people and saw 17,000 admissions in 2017, its last year under the management of the Tenet Healthcare Corporation. Tenet, one of the nation’s largest for-profit hospital conglomerates, owned ninety-six hospitals and nearly 500 outpatient centers in the United States that year. Not all of them turned a profit. Hahnemann, for example, booked $790 million in revenue in 2017, $115 million short of breaking even. So Tenet embarked on an international restructuring program, liquidating seventeen low-margin hospitals in the United States and the United Kingdom. In Philadelphia, Tenet sold Hahnemann to Joel Freedman, a man from Los Angeles who sat on the advisory board of the University of Southern California’s Leonard D. Schaeffer Center for Health Policy and Economics (his name has since been removed from the center’s website) and managed an investment fund, Paladin Capital, with interests in “the world’s most innovative cyber companies,” according to its website. By spring 2019 Freedman was still losing $3 to $5 million a month on Hahnemann. He had burned through four CEOs in fifteen months. In June, hospital administrators announced that the facility was shutting down.
A facility that saw 53,000 emergency room visits per year disappeared from Philadelphia this summer with the prolonged and still-unfinished closure of Hahnemann University Hospital. The 496-bed hospital employed 2,700 people and saw 17,000 admissions in 2017, its last year under the management of the Tenet Healthcare Corporation. Tenet, one of the nation’s largest for-profit hospital conglomerates, owned ninety-six hospitals and nearly 500 outpatient centers in the United States that year. Not all of them turned a profit. Hahnemann, for example, booked $790 million in revenue in 2017, $115 million short of breaking even. So Tenet embarked on an international restructuring program, liquidating seventeen low-margin hospitals in the United States and the United Kingdom. In Philadelphia, Tenet sold Hahnemann to Joel Freedman, a man from Los Angeles who sat on the advisory board of the University of Southern California’s Leonard D. Schaeffer Center for Health Policy and Economics (his name has since been removed from the center’s website) and managed an investment fund, Paladin Capital, with interests in “the world’s most innovative cyber companies,” according to its website. By spring 2019 Freedman was still losing $3 to $5 million a month on Hahnemann. He had burned through four CEOs in fifteen months. In June, hospital administrators announced that the facility was shutting down. There is no escape from this dilemma – either all matter is conscious, or consciousness is something distinct from matter”: Alfred Russel Wallace put the point succinctly in 1870, and it is hard to see how his colleague
There is no escape from this dilemma – either all matter is conscious, or consciousness is something distinct from matter”: Alfred Russel Wallace put the point succinctly in 1870, and it is hard to see how his colleague  During the past eight years, many astute people, inside and outside the scientific community, have worried about the quality of scientific research. They warn of a “replication crisis.” In biomedicine and psychology in particular, it seems that a high proportion of published results cannot be reproduced. The absolute number of retractions for articles in these fields are rising. Whether or not it is right to talk of crisis, it is certainly reasonable to be concerned. What is going on?
During the past eight years, many astute people, inside and outside the scientific community, have worried about the quality of scientific research. They warn of a “replication crisis.” In biomedicine and psychology in particular, it seems that a high proportion of published results cannot be reproduced. The absolute number of retractions for articles in these fields are rising. Whether or not it is right to talk of crisis, it is certainly reasonable to be concerned. What is going on?
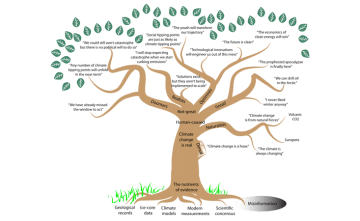 As a paleoclimatologist, I often find myself wondering why more people aren’t listening to the warnings, the data, the messages of climate woes—it’s not just a storm on the horizon, it’s here, knocking on the front door. In fact, it’s not even the front door anymore. You are on the roof, waiting for a helicopter to rescue you from your submerged house. The data is clear: The rates of current carbon dioxide release are 10 times greater than even the most rapid natural carbon catastrophe1 in the geological records, which brought about a miserable hothouse world of acidic oceans lacking oxygen, triggering a pulse of extinctions.2 Despite the evidence for anthropogenic climate change, views about the severity and impact of global warming diverge like branch points on a gnarly old oak tree (below).
As a paleoclimatologist, I often find myself wondering why more people aren’t listening to the warnings, the data, the messages of climate woes—it’s not just a storm on the horizon, it’s here, knocking on the front door. In fact, it’s not even the front door anymore. You are on the roof, waiting for a helicopter to rescue you from your submerged house. The data is clear: The rates of current carbon dioxide release are 10 times greater than even the most rapid natural carbon catastrophe1 in the geological records, which brought about a miserable hothouse world of acidic oceans lacking oxygen, triggering a pulse of extinctions.2 Despite the evidence for anthropogenic climate change, views about the severity and impact of global warming diverge like branch points on a gnarly old oak tree (below). Madison was never expected to live this long. The doctors had told her parents she would probably die at birth. Surprising everyone but her mother, she seized and trembled, and refused to suckle—but she didn’t die. Madison never learned to walk. Her four limbs were spastic. She remained small for her age, and she never learned to speak, not even to say Mama or milk, or no. But she saw and experienced many things beyond seizures, infections, breathing and feeding tubes; beyond Christmases and Easters and birthdays, and the everyday intimacies of childhood. She was her mother’s joy, and knew a fierce and indelible love, breathed over her in a nightly vigil. It imbued Madison with the quiet beauty of a survivor. Whatever trials she endured, there was a sense that she was lit from inside by something sacred.
Madison was never expected to live this long. The doctors had told her parents she would probably die at birth. Surprising everyone but her mother, she seized and trembled, and refused to suckle—but she didn’t die. Madison never learned to walk. Her four limbs were spastic. She remained small for her age, and she never learned to speak, not even to say Mama or milk, or no. But she saw and experienced many things beyond seizures, infections, breathing and feeding tubes; beyond Christmases and Easters and birthdays, and the everyday intimacies of childhood. She was her mother’s joy, and knew a fierce and indelible love, breathed over her in a nightly vigil. It imbued Madison with the quiet beauty of a survivor. Whatever trials she endured, there was a sense that she was lit from inside by something sacred. These days it is highly fashionable to label consciousness an ‘illusion’. This in turn fosters the impression, especially among the general public, that the way we normally think of our mental life has been shown by science to be drastically mistaken. While this is true in a very specific and technical sense, consciousness remains arguably the most distinctive evolved feature of humanity, enabling us not only to experience the world, like other animal species do, but to deliberately reflect on our experiences and to change the course of our lives accordingly.
These days it is highly fashionable to label consciousness an ‘illusion’. This in turn fosters the impression, especially among the general public, that the way we normally think of our mental life has been shown by science to be drastically mistaken. While this is true in a very specific and technical sense, consciousness remains arguably the most distinctive evolved feature of humanity, enabling us not only to experience the world, like other animal species do, but to deliberately reflect on our experiences and to change the course of our lives accordingly. Dennis, let’s start out by asking about the
Dennis, let’s start out by asking about the