Peter Balakian at Literary Hub:

Some books written decades ago return to us, with a renewed relevance, in critical times. Richard Hofstadter’s Pulitzer Prize-winning book of 1964 Anti-Intellectualism in American Life is one. The eminent American historian, who taught at Columbia University in the 1950s and 60s, analyzed a strain in American culture that can help us understand some of the underpinnings of Donald Trump’s assaults on higher education, intellectuals, culture, and free speech. Anti-intellectualism is more than a descriptive term, it’s a concept that Hofstadter developed having studied the roots of the “national disrespect of the mind.” His study was prompted by the virulent assaults on intellectuals, liberalism, and higher education unleashed by Senator Joseph McCarthy in the 1950s in his tyrannous, anti-communist crusade, in which he claimed “commies” were infiltrating the government (even President Eisenhower was a suspect).
Hofstadter traced anti-intellectualism to the following sources: 1) evangelical religion with its disdain for modernity, science, and rational thought, 2) pioneer individualism with its libertarian worship of practical skills and anti-institutionalism, and 3) businessman culture grounded in the practical life in pursuit of wealth and materialism.
More here.
Enjoying the content on 3QD? Help keep us going by donating now.

 There’s a quote I’m fond of, falsely attributed to Lenin, that “ethics are the aesthetics of the future.” It was in fact coined by Gorky, and as with so many misattributed phrases, it is also misquoted. I had always quietly reordered the line in my mind, preferring to have aesthetics in the first position, and when I finally went looking for it, and found it — in an essay Gorky wrote on Anatoly France — I was vindicated to discover that it actually read: “Aesthetics was [his] ethics — the ethics of the future.” That it’s thought to be authored by Lenin is perhaps understandable: it is a revolutionary sentiment after all, one that would have pleased the Romantics, the Surrealists, or any other radical avant-garde that aimed at transvaluation. It could also easily be, I think, the unofficial epigraph, the spiritual motto of Peter Weiss’s trilogy of novels, The Aesthetics of Resistance.
There’s a quote I’m fond of, falsely attributed to Lenin, that “ethics are the aesthetics of the future.” It was in fact coined by Gorky, and as with so many misattributed phrases, it is also misquoted. I had always quietly reordered the line in my mind, preferring to have aesthetics in the first position, and when I finally went looking for it, and found it — in an essay Gorky wrote on Anatoly France — I was vindicated to discover that it actually read: “Aesthetics was [his] ethics — the ethics of the future.” That it’s thought to be authored by Lenin is perhaps understandable: it is a revolutionary sentiment after all, one that would have pleased the Romantics, the Surrealists, or any other radical avant-garde that aimed at transvaluation. It could also easily be, I think, the unofficial epigraph, the spiritual motto of Peter Weiss’s trilogy of novels, The Aesthetics of Resistance. Most of us wouldn’t consider the Middle Ages the epitome of medical sophistication, thanks to our perception of their barbaric and (from a modern perspective) ridiculous strategies for helping the ill. But against all prejudices, medieval medicine was actually more advanced and science-based than we might think.
Most of us wouldn’t consider the Middle Ages the epitome of medical sophistication, thanks to our perception of their barbaric and (from a modern perspective) ridiculous strategies for helping the ill. But against all prejudices, medieval medicine was actually more advanced and science-based than we might think. On one side, advocates for legalised assisted dying invoke patients’ rights to make their own medical choices. Making it possible for doctors to assist their patients to die, they propose, allows us to avoid pointless suffering and to die ‘with dignity’. While assisted dying represents a departure from recent medical practice, it accords with values that the medical community holds dear, including compassion and beneficence.
On one side, advocates for legalised assisted dying invoke patients’ rights to make their own medical choices. Making it possible for doctors to assist their patients to die, they propose, allows us to avoid pointless suffering and to die ‘with dignity’. While assisted dying represents a departure from recent medical practice, it accords with values that the medical community holds dear, including compassion and beneficence. Researchers have been sneaking secret messages into their papers in an effort to trick artificial intelligence (AI) tools into giving them a positive peer-review report.
Researchers have been sneaking secret messages into their papers in an effort to trick artificial intelligence (AI) tools into giving them a positive peer-review report.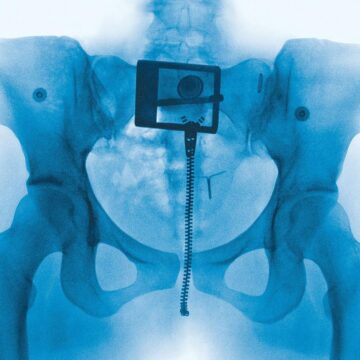 The press cycle preceding Lorde’s new album, Virgin, was one of the most scrutinized of its kind in some time. She has been pressed, during junkets, for more information after saying she doesn’t feel like a man or woman. Fans, editors, and news aggregators gobble up the two or three throwaway lines published in short profiles in magazines like Rolling Stone, Vogue, and GQ. No one mentions the journalists soliciting these quotes—unless fans take them to task for portraying their idols in a negative light. Hero worship can easily obscure the dirt beneath the mythology of a pop star.
The press cycle preceding Lorde’s new album, Virgin, was one of the most scrutinized of its kind in some time. She has been pressed, during junkets, for more information after saying she doesn’t feel like a man or woman. Fans, editors, and news aggregators gobble up the two or three throwaway lines published in short profiles in magazines like Rolling Stone, Vogue, and GQ. No one mentions the journalists soliciting these quotes—unless fans take them to task for portraying their idols in a negative light. Hero worship can easily obscure the dirt beneath the mythology of a pop star. Around the world, governments are racing to build world-class universities. From Germany’s Exzellenzinitiative to India’s “Institutes of Eminence,” the goal is the same: to cultivate institutions that attract and nurture top global talent, conduct cutting-edge research, and drive innovation and growth. But the stakes are particularly high in the United States and China, given the escalating competition between the world’s two largest economies.
Around the world, governments are racing to build world-class universities. From Germany’s Exzellenzinitiative to India’s “Institutes of Eminence,” the goal is the same: to cultivate institutions that attract and nurture top global talent, conduct cutting-edge research, and drive innovation and growth. But the stakes are particularly high in the United States and China, given the escalating competition between the world’s two largest economies. My faith first wavers
My faith first wavers Keith Krehbiel lived with Parkinson’s disease for nearly 25 years before agreeing to try a brain implant that might alleviate his symptoms. He had long been reluctant to submit to the surgery. “It was a big move,” he says. But by 2020, his symptoms had become so severe that he grudgingly agreed to go ahead.
Keith Krehbiel lived with Parkinson’s disease for nearly 25 years before agreeing to try a brain implant that might alleviate his symptoms. He had long been reluctant to submit to the surgery. “It was a big move,” he says. But by 2020, his symptoms had become so severe that he grudgingly agreed to go ahead. Not long ago, Dr. Richard Menger, a neurosurgeon, was ready to operate on a 16-year-old with complex scoliosis. A team of doctors had spent months preparing for the surgery, consulting orthopedists and cardiologists, even printing a 3D model of the teen’s spine. The surgery was scheduled for a Friday when Menger got the news: the teen’s insurer, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Alabama, had denied coverage of the surgery.
Not long ago, Dr. Richard Menger, a neurosurgeon, was ready to operate on a 16-year-old with complex scoliosis. A team of doctors had spent months preparing for the surgery, consulting orthopedists and cardiologists, even printing a 3D model of the teen’s spine. The surgery was scheduled for a Friday when Menger got the news: the teen’s insurer, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Alabama, had denied coverage of the surgery. “It appears early life got trapped in a minima of metabolic efficiency. Everything on that planet is starving. Meaning they can’t run their brains for a full day-night cycle. So they just… turn themselves off. Their consciousness dies. Then they reboot with the same memories in the morning. Of course, the memories are integrated differently each time into an entirely new standing consciousness wave.”
“It appears early life got trapped in a minima of metabolic efficiency. Everything on that planet is starving. Meaning they can’t run their brains for a full day-night cycle. So they just… turn themselves off. Their consciousness dies. Then they reboot with the same memories in the morning. Of course, the memories are integrated differently each time into an entirely new standing consciousness wave.” Recently, I found myself pouring my heart out, not to a human, but to a chatbot named Wysa on my phone. It nodded – virtually – asked me how I was feeling and gently suggested trying breathing exercises.
Recently, I found myself pouring my heart out, not to a human, but to a chatbot named Wysa on my phone. It nodded – virtually – asked me how I was feeling and gently suggested trying breathing exercises. The Democratic Party is in crisis, and it goes far beyond the stereotypical “Dems in Disarray” headlines. The party’s popularity numbers are abysmal: a
The Democratic Party is in crisis, and it goes far beyond the stereotypical “Dems in Disarray” headlines. The party’s popularity numbers are abysmal: a  As it emerged after the overthrow of Reconstruction, when black voices were again being silenced in public and civic spheres, the blues became an alternative form of communication. As Shelby “Poppa Jazz” Brown reminded the noted folklorist William Ferris,
As it emerged after the overthrow of Reconstruction, when black voices were again being silenced in public and civic spheres, the blues became an alternative form of communication. As Shelby “Poppa Jazz” Brown reminded the noted folklorist William Ferris,