Clive Thompson in OneZero:
 Macbeth is a creepy play.
Macbeth is a creepy play.
Actors have long been superstitious about acting in it. That’s partly because performances have been riddled with accidents and fatalities; indeed, actors consider it bad luck to even utter the name of the play. (They call it “The Scottish Tragedy”.) And it’s partly because the basic substance of the plot is eldritch: You’ve got black magic, witches, a gore-flecked ghost and walking forests.
But fans of Macbeth often say its freaky qualities are deeper than just the plot devices and characters. For centuries, people been unsettled by the very language of the play.
Actors and critics have long remarked that when you read Macbeth out loud, it feels like your voice and mouth and brain are doing something ever so slightly wrong. There’s something subconsciously off about the sound of the play, and it spooks people. It’s as if Shakespeare somehow wove a tiny bit of creepiness into every single line. The literary scholar George Walton Williams described the “continuous sense of menace” and “horror” that pervades even seemingly innocuous scenes.
For centuries, Shakespeare fans and theater folk have wondered about this, but could never quite explain it.
Then a clever bit of data analysis in 2014 uncovered the reason. (The paper is here.)
More here.

 Economies in the modern world are incredibly complex systems. But when we sit down to think about them in quantitative ways, it’s natural to keep things simple at first. We look for reliable relations between small numbers of variables, seek equilibrium configurations, and so forth. But those approaches don’t always work in complex systems, and sometimes we have to use methods that are specifically adapted to the challenges of complexity. That’s the perspective of W. Brian Arthur, a pioneer in the field of complexity economics, according to which economies are typically not in equilibrium, not made of homogeneous agents, and are being constantly updated. We talk about the basic ideas of complexity economics, how it differs from more standard approaches, and what it teaches us about the operation of real economies.
Economies in the modern world are incredibly complex systems. But when we sit down to think about them in quantitative ways, it’s natural to keep things simple at first. We look for reliable relations between small numbers of variables, seek equilibrium configurations, and so forth. But those approaches don’t always work in complex systems, and sometimes we have to use methods that are specifically adapted to the challenges of complexity. That’s the perspective of W. Brian Arthur, a pioneer in the field of complexity economics, according to which economies are typically not in equilibrium, not made of homogeneous agents, and are being constantly updated. We talk about the basic ideas of complexity economics, how it differs from more standard approaches, and what it teaches us about the operation of real economies. Encouraged by the election of Joe Biden, the COVID-19 vaccine, and the so-called “major opportunity” of smart technology, commentators and investors now predict that the economy will rebound from the pandemic downturn, or even accelerate, once the “exogenous” shock caused by the coronavirus has been absorbed. But is this a plausible future scenario?
Encouraged by the election of Joe Biden, the COVID-19 vaccine, and the so-called “major opportunity” of smart technology, commentators and investors now predict that the economy will rebound from the pandemic downturn, or even accelerate, once the “exogenous” shock caused by the coronavirus has been absorbed. But is this a plausible future scenario? In the popular imagination, the name Leonardo da Vinci conjures many things. In traditional textbooks, he epitomizes the concept of the “Renaissance man,” capable of knowing and doing everything. Another view has it that he was a prototypical engineer and scientist—inventor of tanks, helicopters, self-perpetuating machines, and urban infrastructure—and thus the forerunner of much of what we deem essential in our supposedly secular, technology-driven world. Art historians generally describe him as the key figure in a new phase in European painting, attuned to the portrayal of psychology and the subjectivity of sight, all while exercising an unparalleled naturalism. But, despite these things, there has always been another image of Leonardo, one that associated him with hidden things, esoteric knowledge beyond common perceptions. In Dan Brown’s The Da Vinci Code (2003), Leonardo figures as a guardian of a forbidden secret, keeping alive the dangerous knowledge that Christ married Mary Magdalene and had a child by her. In the context of Brown’s thriller, Leonardo is a knower of the unknown, a keeper of truths that must remain encrypted by means of his famous mirror writing. Because Leonardo’s secret could potentially overturn orthodox Christian beliefs, his perpetuation of it paradoxically meshes with his reputation as a harbinger of the modern world. Like a Nostradamus, he anticipates history, hiding the keys to understanding things that are beyond the grasp of his contemporaries and a challenge for more enlightened ages.
In the popular imagination, the name Leonardo da Vinci conjures many things. In traditional textbooks, he epitomizes the concept of the “Renaissance man,” capable of knowing and doing everything. Another view has it that he was a prototypical engineer and scientist—inventor of tanks, helicopters, self-perpetuating machines, and urban infrastructure—and thus the forerunner of much of what we deem essential in our supposedly secular, technology-driven world. Art historians generally describe him as the key figure in a new phase in European painting, attuned to the portrayal of psychology and the subjectivity of sight, all while exercising an unparalleled naturalism. But, despite these things, there has always been another image of Leonardo, one that associated him with hidden things, esoteric knowledge beyond common perceptions. In Dan Brown’s The Da Vinci Code (2003), Leonardo figures as a guardian of a forbidden secret, keeping alive the dangerous knowledge that Christ married Mary Magdalene and had a child by her. In the context of Brown’s thriller, Leonardo is a knower of the unknown, a keeper of truths that must remain encrypted by means of his famous mirror writing. Because Leonardo’s secret could potentially overturn orthodox Christian beliefs, his perpetuation of it paradoxically meshes with his reputation as a harbinger of the modern world. Like a Nostradamus, he anticipates history, hiding the keys to understanding things that are beyond the grasp of his contemporaries and a challenge for more enlightened ages.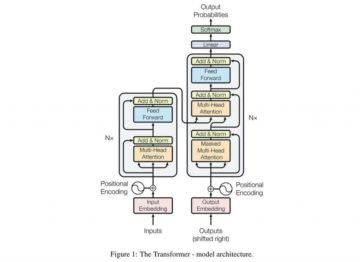 Last year I became fascinated with an artificial intelligence model that was being trained to write human-like text. The model was called GPT-3, short for Generative Pre-Trained Transformer 3; if you fed it a bit of text, it could complete a piece of writing, by predicting the words that should come next.
Last year I became fascinated with an artificial intelligence model that was being trained to write human-like text. The model was called GPT-3, short for Generative Pre-Trained Transformer 3; if you fed it a bit of text, it could complete a piece of writing, by predicting the words that should come next. Are you someone who enjoys the unsolicited opinions of strangers and acquaintances? If so, I can’t recommend cancer highly enough. You won’t even have the first pathology report in your hands before the advice comes pouring in. Laugh and the world laughs with you; get cancer and the world can’t shut its trap. Stop eating sugar; keep up your weight with milkshakes. Listen to a recent story on NPR; do not read a recent story in Time magazine. Exercise—but not too vigorously; exercise—hard, like Lance Armstrong. Join a support group, make a collage, make a collage in a support group, collage the shit out of your cancer. Do you live near a freeway or drink tap water or eat food microwaved on plastic plates? That’s what caused it. Do you ever think about suing? Do you ever wonder whether, if you’d just let some time pass, the cancer would have gone away on its own?
Are you someone who enjoys the unsolicited opinions of strangers and acquaintances? If so, I can’t recommend cancer highly enough. You won’t even have the first pathology report in your hands before the advice comes pouring in. Laugh and the world laughs with you; get cancer and the world can’t shut its trap. Stop eating sugar; keep up your weight with milkshakes. Listen to a recent story on NPR; do not read a recent story in Time magazine. Exercise—but not too vigorously; exercise—hard, like Lance Armstrong. Join a support group, make a collage, make a collage in a support group, collage the shit out of your cancer. Do you live near a freeway or drink tap water or eat food microwaved on plastic plates? That’s what caused it. Do you ever think about suing? Do you ever wonder whether, if you’d just let some time pass, the cancer would have gone away on its own? A major focus of modern medicine is treating existing conditions, but a promising approach is to try to detect elevated susceptibility to a condition before it becomes a diagnosable disease. “The pre-disease state, where someone has increased susceptibility to developing diseases, such as cancer, is widely considered the best period for intervening,” explains Yoshinori Kono, project leader at Kewpie. “Treating disease is important, but preventing disease before it strikes will reduce healthcare costs and improve quality of life.”
A major focus of modern medicine is treating existing conditions, but a promising approach is to try to detect elevated susceptibility to a condition before it becomes a diagnosable disease. “The pre-disease state, where someone has increased susceptibility to developing diseases, such as cancer, is widely considered the best period for intervening,” explains Yoshinori Kono, project leader at Kewpie. “Treating disease is important, but preventing disease before it strikes will reduce healthcare costs and improve quality of life.”
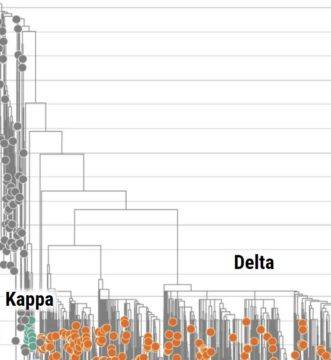 Edward Holmes does not like making predictions, but last year he hazarded a few. Again and again, people had asked Holmes, an expert on viral evolution at the University of Sydney, how he expected SARS-CoV-2 to change. In May 2020, 5 months into the pandemic, he started to include a slide with his best guesses in his talks. The virus would probably evolve to avoid at least some human immunity, he suggested. But it would likely make people less sick over time, he said, and there would be little change in its infectivity. In short, it sounded like evolution would not play a major role in the pandemic’s near future.
Edward Holmes does not like making predictions, but last year he hazarded a few. Again and again, people had asked Holmes, an expert on viral evolution at the University of Sydney, how he expected SARS-CoV-2 to change. In May 2020, 5 months into the pandemic, he started to include a slide with his best guesses in his talks. The virus would probably evolve to avoid at least some human immunity, he suggested. But it would likely make people less sick over time, he said, and there would be little change in its infectivity. In short, it sounded like evolution would not play a major role in the pandemic’s near future. Exactly one year ago, I did not die from poisoning by a chemical weapon, and it would seem that corruption played no small part in my survival. Having contaminated Russia’s state system, corruption has also contaminated the intelligence services. When a country’s senior management is preoccupied with protection rackets and extortion from businesses, the quality of covert operations inevitably suffers. A group of FSB agents applied the nerve agent to my underwear just as shoddily as they incompetently dogged my footsteps for three and a half years – in violation of all instructions from above – allowing
Exactly one year ago, I did not die from poisoning by a chemical weapon, and it would seem that corruption played no small part in my survival. Having contaminated Russia’s state system, corruption has also contaminated the intelligence services. When a country’s senior management is preoccupied with protection rackets and extortion from businesses, the quality of covert operations inevitably suffers. A group of FSB agents applied the nerve agent to my underwear just as shoddily as they incompetently dogged my footsteps for three and a half years – in violation of all instructions from above – allowing  Deep learning, the artificial-intelligence technology that powers voice assistants, autonomous cars, and Go champions, relies on complicated “neural network” software arranged in layers. A deep-learning system can live on a single computer, but the biggest ones are spread over thousands of machines wired together into “clusters,” which sometimes live at large data centers, like those operated by Google. In a big cluster, as many as forty-eight pizza-box-size servers slide into a rack as tall as a person; these racks stand in rows, filling buildings the size of warehouses. The neural networks in such systems can tackle daunting problems, but they also face clear challenges. A network spread across a cluster is like a brain that’s been scattered around a room and wired together. Electrons move fast, but, even so, cross-chip communication is slow, and uses extravagant amounts of energy.
Deep learning, the artificial-intelligence technology that powers voice assistants, autonomous cars, and Go champions, relies on complicated “neural network” software arranged in layers. A deep-learning system can live on a single computer, but the biggest ones are spread over thousands of machines wired together into “clusters,” which sometimes live at large data centers, like those operated by Google. In a big cluster, as many as forty-eight pizza-box-size servers slide into a rack as tall as a person; these racks stand in rows, filling buildings the size of warehouses. The neural networks in such systems can tackle daunting problems, but they also face clear challenges. A network spread across a cluster is like a brain that’s been scattered around a room and wired together. Electrons move fast, but, even so, cross-chip communication is slow, and uses extravagant amounts of energy. W
W