Dorsa Amir in Nautilus:
 The science-fiction writer Robert Heinlein once wrote, “Each generation thinks it invented sex.” He was presumably referring to the pride each generation takes in defining its own sexual practices and ethics. But his comment hit the mark in another sense: Every generation has to reinvent sex because the previous generation did a lousy job of teaching it. In the United States, the conversations we have with our children about sex are often awkward, limited, and brimming with euphemism. At school, if kids are lucky enough to live in a state that allows it, they’ll get something like 10 total hours of sex education.1 If they’re less lucky, they’ll instead experience the curious phenomenon of abstinence-only education, in which the goal is to avoid transmitting any information at all. In addition to being counterproductive—potentially leading to higher rates of teen pregnancy2 and sexually transmitted illnesses3—this practice is strange. Compare it to the practices of many small-scale societies, where children first learn about sex by observing their parents!
The science-fiction writer Robert Heinlein once wrote, “Each generation thinks it invented sex.” He was presumably referring to the pride each generation takes in defining its own sexual practices and ethics. But his comment hit the mark in another sense: Every generation has to reinvent sex because the previous generation did a lousy job of teaching it. In the United States, the conversations we have with our children about sex are often awkward, limited, and brimming with euphemism. At school, if kids are lucky enough to live in a state that allows it, they’ll get something like 10 total hours of sex education.1 If they’re less lucky, they’ll instead experience the curious phenomenon of abstinence-only education, in which the goal is to avoid transmitting any information at all. In addition to being counterproductive—potentially leading to higher rates of teen pregnancy2 and sexually transmitted illnesses3—this practice is strange. Compare it to the practices of many small-scale societies, where children first learn about sex by observing their parents!
One of the most distinctive features of the human species is its practice of cultural transmission. Our ability to retain, refine, and pass down cultural knowledge across generations has helped us survive in every habitat on the planet—and even in space. Three-hundred and fifty generations ago, we were making the switch from foraging to early agriculture. Now, the sum of human cultural knowledge, passed from parent to child for thousands of years, is a Google search away. So why is it that, despite having immediate access to virtually every area of knowledge, we Westerners paradoxically fail to directly share the most important of these insights with the next generation? Sometimes intentionally under the banner of protecting young minds, sometimes unintentionally as a result of the way our communities are structured, we dam critical information and force new generations to start from scratch, leaning on their own intuitions and the scant experience of their peers to chart a way forward. From birth and parenting to death and burial, we have built a knowledge dam that makes it harder to lead successful lives.
It doesn’t have to be this way—and, in fact, it wasn’t, until very recently.
More here.

 The dubious notion
The dubious notion The medical community has been aware of the placebo effect–the phenomenon in which a nontherapeutic treatment (like a sham pill) improves a patient’s physical condition–for centuries. But Ted Kaptchuk, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and one of the leading researchers on the placebo effect, wanted to take his research further. He was tired of letting the people in his studies think they were taking a real therapy and then watching what happened. Instead, he wondered, what if he was honest? His Harvard colleagues told Kaptchuk he was crazy, that letting people in a clinical trial know they were taking a placebo would defeat the purpose. Nevertheless, in 2009 the university’s teaching hospital, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, launched the first open-label placebo, or so-called honest placebo, trial to date, starting with people who had IBS, including Buonanno.
The medical community has been aware of the placebo effect–the phenomenon in which a nontherapeutic treatment (like a sham pill) improves a patient’s physical condition–for centuries. But Ted Kaptchuk, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and one of the leading researchers on the placebo effect, wanted to take his research further. He was tired of letting the people in his studies think they were taking a real therapy and then watching what happened. Instead, he wondered, what if he was honest? His Harvard colleagues told Kaptchuk he was crazy, that letting people in a clinical trial know they were taking a placebo would defeat the purpose. Nevertheless, in 2009 the university’s teaching hospital, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, launched the first open-label placebo, or so-called honest placebo, trial to date, starting with people who had IBS, including Buonanno. Ten years after the collapse of Lehman Brothers, the official economic statistics — the ones that fill news stories, television shows and presidential tweets — say that the American economy is fully recovered.
Ten years after the collapse of Lehman Brothers, the official economic statistics — the ones that fill news stories, television shows and presidential tweets — say that the American economy is fully recovered. I was born in 1955 and—apart from the Castilian (which you know as Spanish) spoken by a minority of speakers—Galician was the language spoken in Galicia. What can be done with a people of whom a majority speak an incorrect language? Francoism made the answer very clear; its policy of emigration/deportation was successful. Thousands of Galician speakers were proletarianized across a Europe in need of cheap labor after the Second World War. With its demographic policy of emigration, Franco’s government met several objectives. One of those was, precisely, to break the transmission of Galician from one generation to the next. I belong to an intermediate generation; my parents were native Galician speakers but always spoke to us in Castilian, as they didn’t want their children to have painful issues in adapting, as they’d had. Naturally, what my generation inherited from our parents was a linguistic conflict, of which I spoke in Secession. My native language is the fascist prohibition against speaking the language of my progenitors, of the women who preceded me. This is definitely the case.
I was born in 1955 and—apart from the Castilian (which you know as Spanish) spoken by a minority of speakers—Galician was the language spoken in Galicia. What can be done with a people of whom a majority speak an incorrect language? Francoism made the answer very clear; its policy of emigration/deportation was successful. Thousands of Galician speakers were proletarianized across a Europe in need of cheap labor after the Second World War. With its demographic policy of emigration, Franco’s government met several objectives. One of those was, precisely, to break the transmission of Galician from one generation to the next. I belong to an intermediate generation; my parents were native Galician speakers but always spoke to us in Castilian, as they didn’t want their children to have painful issues in adapting, as they’d had. Naturally, what my generation inherited from our parents was a linguistic conflict, of which I spoke in Secession. My native language is the fascist prohibition against speaking the language of my progenitors, of the women who preceded me. This is definitely the case.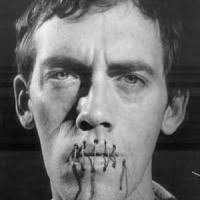 Today, David Wojnarowicz is known mostly as a martyr to the culture wars of the 1980s, another artist diagnosed with AIDS who fought along with so many to get the government to act, for a long time in vain, and who then, like so many others, died of the disease, a terrible tear in the fabric of art that was savagely exacted on gay men of that generation. Wojnarowicz came out of the same deeply downtown bohemianism of the early 1980s that fueled Jean-Michel Basquiat’s equally short, culture-altering arc through the art world: small cadres of like-minded underground characters and self-defined artists, desperate to act on the culture but denied the usual access to artistic power structures for reasons financial, psychological, racial, sexual. Wojnarowicz rose amid a gritty East Village aesthetic of graffiti, Expressionistic gestures, roughly assembled surfaces, funky found objects, one-night shows at clubs, and midnight guerrilla actions on the finer art. But in a way, Wojnarowicz’s tremendous, almost Rimbaud-like reputation suits, since he was an even better, more lucid freedom fighter than he was an artist.
Today, David Wojnarowicz is known mostly as a martyr to the culture wars of the 1980s, another artist diagnosed with AIDS who fought along with so many to get the government to act, for a long time in vain, and who then, like so many others, died of the disease, a terrible tear in the fabric of art that was savagely exacted on gay men of that generation. Wojnarowicz came out of the same deeply downtown bohemianism of the early 1980s that fueled Jean-Michel Basquiat’s equally short, culture-altering arc through the art world: small cadres of like-minded underground characters and self-defined artists, desperate to act on the culture but denied the usual access to artistic power structures for reasons financial, psychological, racial, sexual. Wojnarowicz rose amid a gritty East Village aesthetic of graffiti, Expressionistic gestures, roughly assembled surfaces, funky found objects, one-night shows at clubs, and midnight guerrilla actions on the finer art. But in a way, Wojnarowicz’s tremendous, almost Rimbaud-like reputation suits, since he was an even better, more lucid freedom fighter than he was an artist. Yet perhaps one of the greatest compliments I can give “On Color” is that despite the indisputable scholarly erudition found on every page, the clever edge to its witty prose and its own defiantly unclassifiable
Yet perhaps one of the greatest compliments I can give “On Color” is that despite the indisputable scholarly erudition found on every page, the clever edge to its witty prose and its own defiantly unclassifiable  In the world’s most famous thought experiment, physicist Erwin Schrödinger described how a cat in a box could be in an uncertain predicament. The peculiar rules of quantum theory meant that it could be both dead and alive, until the box was opened and the cat’s state measured. Now, two physicists have devised a modern version of the paradox by replacing the cat with a physicist doing experiments—with shocking implications. Quantum theory has a long history of thought experiments, and in most cases these are used to point to weaknesses in various interpretations of quantum mechanics. But the latest version, which involves multiple players, is unusual: it shows that if the standard interpretation of quantum mechanics is correct, then different experimenters can reach opposite conclusions about what the physicist in the box has measured. This means that quantum theory contradicts itself.
In the world’s most famous thought experiment, physicist Erwin Schrödinger described how a cat in a box could be in an uncertain predicament. The peculiar rules of quantum theory meant that it could be both dead and alive, until the box was opened and the cat’s state measured. Now, two physicists have devised a modern version of the paradox by replacing the cat with a physicist doing experiments—with shocking implications. Quantum theory has a long history of thought experiments, and in most cases these are used to point to weaknesses in various interpretations of quantum mechanics. But the latest version, which involves multiple players, is unusual: it shows that if the standard interpretation of quantum mechanics is correct, then different experimenters can reach opposite conclusions about what the physicist in the box has measured. This means that quantum theory contradicts itself. This thought kept blinking through my mind, like a neon sign on a dark street, as I read These Truths, the newest book by Harvard professor and The New Yorker contributor Jill Lepore. A 900-plus page tome, it is a full history of the United States, a country I was born in and soon after left. I was raised in a much younger country, Israel, which was handed over by a colonizing force to a people desperate for a home, back in the days—not so long ago, really—when colonizers could simply gift the land they’d taken as if it were theirs to give. The history I was taught from the ages of six to eighteen was both condensed and elongated, the history of a fledgling country full of war but also of an ancient people once enslaved and long persecuted.
This thought kept blinking through my mind, like a neon sign on a dark street, as I read These Truths, the newest book by Harvard professor and The New Yorker contributor Jill Lepore. A 900-plus page tome, it is a full history of the United States, a country I was born in and soon after left. I was raised in a much younger country, Israel, which was handed over by a colonizing force to a people desperate for a home, back in the days—not so long ago, really—when colonizers could simply gift the land they’d taken as if it were theirs to give. The history I was taught from the ages of six to eighteen was both condensed and elongated, the history of a fledgling country full of war but also of an ancient people once enslaved and long persecuted. ‘Red Birds’ marks the award-winning British-Pakistani author’s return to fiction after seven years, and is a potential instant classic.
‘Red Birds’ marks the award-winning British-Pakistani author’s return to fiction after seven years, and is a potential instant classic.
 During the slow recovery after the 2008 financial crisis, Larry Summers, the Director of President Barack Obama’s National Economic Council, argued that the US economy was in the grips of “secular stagnation”: neither full employment nor strong growth could be achieved under stable financial conditions.
During the slow recovery after the 2008 financial crisis, Larry Summers, the Director of President Barack Obama’s National Economic Council, argued that the US economy was in the grips of “secular stagnation”: neither full employment nor strong growth could be achieved under stable financial conditions. Our understanding of heredity and genetics is improving at blinding speed. It was only in the year 2000 that scientists obtained the first rough map of the human genome: 3 billion base pairs of DNA with about 20,000 functional genes. Today, you can send a bit of your DNA to companies such as
Our understanding of heredity and genetics is improving at blinding speed. It was only in the year 2000 that scientists obtained the first rough map of the human genome: 3 billion base pairs of DNA with about 20,000 functional genes. Today, you can send a bit of your DNA to companies such as  That the news in its traditional forms is the problem with journalism actually dawned on me much earlier, when in 2006 I joined the editorial department of a major Dutch newspaper. I was 24 and studying philosophy when I landed a job covering domestic affairs. As a philosophy student does, I immediately started asking: what is this thing called news that I’m supposed to make here? Scrutinizing the practices of my colleagues, I eventually distilled a definition that I think describes news pretty accurately.
That the news in its traditional forms is the problem with journalism actually dawned on me much earlier, when in 2006 I joined the editorial department of a major Dutch newspaper. I was 24 and studying philosophy when I landed a job covering domestic affairs. As a philosophy student does, I immediately started asking: what is this thing called news that I’m supposed to make here? Scrutinizing the practices of my colleagues, I eventually distilled a definition that I think describes news pretty accurately.
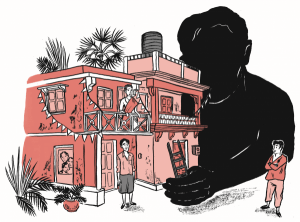 Filmistan Studios occupies five acres in Goregaon, India, which is technically an outer suburb of Mumbai, but denser than most New York City neighborhoods. If you take the train from the city proper and fight the foot traffic that crowds the bazaar area around the station, you’ll reach a pair of steel gates. Just on the other side are Filmistan’s soundstages, which have been in continuous operation since 1943. In the Golden Age of Hindi Film, up to the 1960s, the industry worked along lines similar to those of the old Hollywood studio system, with each production house fielding its own stable of talent. Unlike most of its former rivals, Filmistan has remained open for business as a production facility, and the grounds now accommodate eight stages and several outdoor shooting areas, including a Hindu temple, a jailhouse exterior, and a village. But Filmistan is more than a collection of sets. Behind the scenes, there are real people living there. I came to Filmistan as an anthropologist in training, with a research project that looked solid enough, on paper, to win a Fulbright grant. One thing about ethnography they don’t teach you in school, though, is how awkward it can be getting started. Reaching out to people to do research with—soliciting “informants”—can feel like approaching strangers for a date. Left to myself in Mumbai, with my sun-glasses and clumsy Hindi, I was a field-work wallflower
Filmistan Studios occupies five acres in Goregaon, India, which is technically an outer suburb of Mumbai, but denser than most New York City neighborhoods. If you take the train from the city proper and fight the foot traffic that crowds the bazaar area around the station, you’ll reach a pair of steel gates. Just on the other side are Filmistan’s soundstages, which have been in continuous operation since 1943. In the Golden Age of Hindi Film, up to the 1960s, the industry worked along lines similar to those of the old Hollywood studio system, with each production house fielding its own stable of talent. Unlike most of its former rivals, Filmistan has remained open for business as a production facility, and the grounds now accommodate eight stages and several outdoor shooting areas, including a Hindu temple, a jailhouse exterior, and a village. But Filmistan is more than a collection of sets. Behind the scenes, there are real people living there. I came to Filmistan as an anthropologist in training, with a research project that looked solid enough, on paper, to win a Fulbright grant. One thing about ethnography they don’t teach you in school, though, is how awkward it can be getting started. Reaching out to people to do research with—soliciting “informants”—can feel like approaching strangers for a date. Left to myself in Mumbai, with my sun-glasses and clumsy Hindi, I was a field-work wallflower R
R