Eric Kaufmann in the New York Times:
 Amid the uproar over the Ralph Northam blackface photograph, a Washington Post poll asked Virginians if he should remain governor. The results were striking: Only 48 percent of whites felt that he should stay in office. That percentage was exceeded by the nearly 60 percent of black Virginians who thought Mr. Northam should remain.
Amid the uproar over the Ralph Northam blackface photograph, a Washington Post poll asked Virginians if he should remain governor. The results were striking: Only 48 percent of whites felt that he should stay in office. That percentage was exceeded by the nearly 60 percent of black Virginians who thought Mr. Northam should remain.
In another survey, part of my own research, I asked Americans whether President Trump’s wall is racist. White Democrats overwhelmingly said it was, virtually no Republicans did — and minorities placed in the middle.
We find this pattern across numerous issues. And taken as a whole, it reveals something about the United States in the Trump era: The country is not divided by racial conflict, but by conflict over racial ideology. This is a crucial difference — and it is also grounds for optimism.
More here.

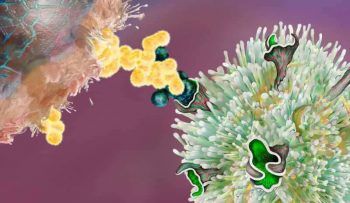 Medicine has great hopes for personalised cancer immunotherapy. The idea is to have a vaccine prompt the immune system to fight a tumour. Scientists at ETH Zurich have developed a method that allows them to determine which molecules are suited to patient-specific immunisation. Cells belonging to the body’s own
Medicine has great hopes for personalised cancer immunotherapy. The idea is to have a vaccine prompt the immune system to fight a tumour. Scientists at ETH Zurich have developed a method that allows them to determine which molecules are suited to patient-specific immunisation. Cells belonging to the body’s own  “What the hell is wrong with Michael?” Chris Rock
“What the hell is wrong with Michael?” Chris Rock  Elephants have bigger brains than humans, so why aren’t they smarter than we are?
Elephants have bigger brains than humans, so why aren’t they smarter than we are? In Becoming, Obama describes the value of telling one’s story this way: “Even when it’s not pretty or perfect. Even when it’s more real than you want it to be. Your story is what you have, what you will always have. It is something to own.” For Obama, a person’s story is an affirmation of their space in the world, the right to be and belong. “In sharing my story,” she says, “I hope to help create space for other stories and other voices, to widen the pathway for who belongs and why. . . . Let’s invite one another in. Maybe then we can begin to fear less, to make fewer wrong assumptions, to let go of biases and stereotypes that unnecessarily divide us.” The root of discrimination, Obama implies, including the ugly discrimination she faced as first lady, is misunderstanding. Sharing personal narratives, then, offers a way for people to fully see each other and to overcome our differences.
In Becoming, Obama describes the value of telling one’s story this way: “Even when it’s not pretty or perfect. Even when it’s more real than you want it to be. Your story is what you have, what you will always have. It is something to own.” For Obama, a person’s story is an affirmation of their space in the world, the right to be and belong. “In sharing my story,” she says, “I hope to help create space for other stories and other voices, to widen the pathway for who belongs and why. . . . Let’s invite one another in. Maybe then we can begin to fear less, to make fewer wrong assumptions, to let go of biases and stereotypes that unnecessarily divide us.” The root of discrimination, Obama implies, including the ugly discrimination she faced as first lady, is misunderstanding. Sharing personal narratives, then, offers a way for people to fully see each other and to overcome our differences.
 Death is a recurring theme in Jaeggy’s work. When the narrator of the story ‘I Am the Brother of XX’ says, ‘I want to die when I grow up’, it’s not meant to shock but to remind us of the death drive that sleeps next to our own child selves, buried inside us. Another important motif is cold: a necessary condition for feeling, thinking, expressing yourself. In Sweet Days, one of the protagonist’s happiest memories is of a night she spent in her friend’s bare, freezing room. The friend burns some alcohol in a saucepan on the floor, and when the flame dies the cold returns, biting into their bones as they stand by the window watching the dawn. This is not hardship but ‘a spiritual or aesthetic exercise’. Being cold, physically and emotionally, brings you closer to that perfect state, nothingness, which shouldn’t be confused with emptiness, for ‘what we do not possess belongs to us’.
Death is a recurring theme in Jaeggy’s work. When the narrator of the story ‘I Am the Brother of XX’ says, ‘I want to die when I grow up’, it’s not meant to shock but to remind us of the death drive that sleeps next to our own child selves, buried inside us. Another important motif is cold: a necessary condition for feeling, thinking, expressing yourself. In Sweet Days, one of the protagonist’s happiest memories is of a night she spent in her friend’s bare, freezing room. The friend burns some alcohol in a saucepan on the floor, and when the flame dies the cold returns, biting into their bones as they stand by the window watching the dawn. This is not hardship but ‘a spiritual or aesthetic exercise’. Being cold, physically and emotionally, brings you closer to that perfect state, nothingness, which shouldn’t be confused with emptiness, for ‘what we do not possess belongs to us’. The horror of a video showing a toddler tugging at her mother’s unconscious form in a supermarket conveys more easily the horror of the corruption, avarice, poverty and stupidity that created the problem in the first place. How this happened – how the number of deaths from opiate overdoses increased by a factor of six in the US between 1999 and 2017 – is the subject of several recent books. Dopesick, by Beth Macy, describes the effects of opiate use in Appalachia, where she worked as a newspaper reporter. Dreamland, by Sam Quinones, describes the rise of a super-efficient network of dealers of Mexican black tar heroin in the US and its effects on one particular town in Ohio. American Overdose, by Chris McGreal, a correspondent for the Guardian, offers a more detailed view of the corruption that enabled the spread of opiates to go unchecked by the healthcare industry, government or law enforcement.
The horror of a video showing a toddler tugging at her mother’s unconscious form in a supermarket conveys more easily the horror of the corruption, avarice, poverty and stupidity that created the problem in the first place. How this happened – how the number of deaths from opiate overdoses increased by a factor of six in the US between 1999 and 2017 – is the subject of several recent books. Dopesick, by Beth Macy, describes the effects of opiate use in Appalachia, where she worked as a newspaper reporter. Dreamland, by Sam Quinones, describes the rise of a super-efficient network of dealers of Mexican black tar heroin in the US and its effects on one particular town in Ohio. American Overdose, by Chris McGreal, a correspondent for the Guardian, offers a more detailed view of the corruption that enabled the spread of opiates to go unchecked by the healthcare industry, government or law enforcement. A review of books on ageing is inevitably filtered through the age, health and optimism quotient of the reviewer. Thirty years ago I wrote an essay for the New York Times, cheerfully titled “Old Age Is Not What It Used To Be”, full of encouraging news from the newly burgeoning field of gerontology. In those days, “old age” usually referred to people in their sixties and seventies, with some outliers in their eighties and even a few in their nineties. (Bernice Neugarten and other gerontologists had recently begun to speak of the “young old”, who are healthy and mentally competent, and the “old old”, who aren’t.) My essay was populated with thriving old people who were as witty, active, happy, sexually active and intellectually engaged as they had ever been, and by researchers assuring us that we won’t “lose it” so long as we remain witty, active, happy, sexually active and intellectually engaged. All very nice, cynics muttered, but how are we supposed to retain those satisfactions when every joint aches, we have lost a life partner and too many close friends, mental sharpness blurs, hearing declines, the grown-up children have decamped to foreign lands, the identities that provided meaning are gone, and we start to feel like a bump on the log of life?
A review of books on ageing is inevitably filtered through the age, health and optimism quotient of the reviewer. Thirty years ago I wrote an essay for the New York Times, cheerfully titled “Old Age Is Not What It Used To Be”, full of encouraging news from the newly burgeoning field of gerontology. In those days, “old age” usually referred to people in their sixties and seventies, with some outliers in their eighties and even a few in their nineties. (Bernice Neugarten and other gerontologists had recently begun to speak of the “young old”, who are healthy and mentally competent, and the “old old”, who aren’t.) My essay was populated with thriving old people who were as witty, active, happy, sexually active and intellectually engaged as they had ever been, and by researchers assuring us that we won’t “lose it” so long as we remain witty, active, happy, sexually active and intellectually engaged. All very nice, cynics muttered, but how are we supposed to retain those satisfactions when every joint aches, we have lost a life partner and too many close friends, mental sharpness blurs, hearing declines, the grown-up children have decamped to foreign lands, the identities that provided meaning are gone, and we start to feel like a bump on the log of life? The Mueller investigation was fully worth it, despite its conclusions. In early 2017, with a clearly corrupt president in place, but both houses of Congress dominated by the Republicans, there would have been no way to launch a legislative-branch inquiry into his misdeeds. The Special Prosecutor’s probe served as a fortuitous substitute. Even though it was implausible from the start that collusion with Russia by Trump and his team swung the election, there were enough signs of deals with Russian political operatives and business figures to justify a probe. The appointment of a Department of Justice Special Prosecutor, though not initiated by the Democrats, was a gift to them.
The Mueller investigation was fully worth it, despite its conclusions. In early 2017, with a clearly corrupt president in place, but both houses of Congress dominated by the Republicans, there would have been no way to launch a legislative-branch inquiry into his misdeeds. The Special Prosecutor’s probe served as a fortuitous substitute. Even though it was implausible from the start that collusion with Russia by Trump and his team swung the election, there were enough signs of deals with Russian political operatives and business figures to justify a probe. The appointment of a Department of Justice Special Prosecutor, though not initiated by the Democrats, was a gift to them. Norman Triplett was a pioneer in the psychology of magic, and back in 1900, he published a wonderful scientific paper on magic that, among many other things, discusses an experiment on an intriguing magical illusion. A magician sat at a table in front of a group of schoolchildren and threw a ball up in the air a few times. Before the final throw, his hand secretly went under the table, letting the ball fall onto his lap, after which he proceeded to throw an imaginary ball up in the air. Described like this, it does not sound like an amazing trick, but what was truly surprising is that more than half of the children claimed to have seen an illusory ball—what Triplett referred to as a “ghost ball”—leave the magician’s hand and disappear somewhere midway between the magician and the ceiling. This was clearly an illusion because on the final throw, no ball had left his hand; the children had perceived an event that never took place. Triplett carried out several studies using this illusion, and he came to some rather interesting, though not necessarily correct, conclusions. He thought that the illusion resulted from retinal afterimages, or in his own words, “What the audience sees is an image of repetition, which is undoubtedly partly the effect of a residual stimulation in the eye, partly a central excitation.”
Norman Triplett was a pioneer in the psychology of magic, and back in 1900, he published a wonderful scientific paper on magic that, among many other things, discusses an experiment on an intriguing magical illusion. A magician sat at a table in front of a group of schoolchildren and threw a ball up in the air a few times. Before the final throw, his hand secretly went under the table, letting the ball fall onto his lap, after which he proceeded to throw an imaginary ball up in the air. Described like this, it does not sound like an amazing trick, but what was truly surprising is that more than half of the children claimed to have seen an illusory ball—what Triplett referred to as a “ghost ball”—leave the magician’s hand and disappear somewhere midway between the magician and the ceiling. This was clearly an illusion because on the final throw, no ball had left his hand; the children had perceived an event that never took place. Triplett carried out several studies using this illusion, and he came to some rather interesting, though not necessarily correct, conclusions. He thought that the illusion resulted from retinal afterimages, or in his own words, “What the audience sees is an image of repetition, which is undoubtedly partly the effect of a residual stimulation in the eye, partly a central excitation.” A little old man came out of a fabric store and lit a stick of incense. He had a pronounced lower lip, which dangled more than a foot from the bottom of his face. He shook and brandished his wondrous lip and the young men around him trembled and approached. He held his left hand low and made a gesture with his palm toward the ground and shook his lip once more. The young men scattered back into the store. Then he spoke some kind of offering, a prayer to the sky above. Then he blew his nose and went back inside.
A little old man came out of a fabric store and lit a stick of incense. He had a pronounced lower lip, which dangled more than a foot from the bottom of his face. He shook and brandished his wondrous lip and the young men around him trembled and approached. He held his left hand low and made a gesture with his palm toward the ground and shook his lip once more. The young men scattered back into the store. Then he spoke some kind of offering, a prayer to the sky above. Then he blew his nose and went back inside. He never stood a chance. His first mistake was looking for food alone; perhaps things would have turned out differently if he’d been with someone else. The second, bigger mistake was wandering too far up the valley into a dangerous wooded area. This was where he risked running into the Others, the ones from the ridge above the valley. At first, there were two of them, and he tried to fight, but another four crept up behind him and he was surrounded. They left him there to bleed to death and later returned to mutilate his body. Eventually, nearly 20 such killings took place, until there was no one left, and the Others took over the whole valley.
He never stood a chance. His first mistake was looking for food alone; perhaps things would have turned out differently if he’d been with someone else. The second, bigger mistake was wandering too far up the valley into a dangerous wooded area. This was where he risked running into the Others, the ones from the ridge above the valley. At first, there were two of them, and he tried to fight, but another four crept up behind him and he was surrounded. They left him there to bleed to death and later returned to mutilate his body. Eventually, nearly 20 such killings took place, until there was no one left, and the Others took over the whole valley. So, I ask fellow non-supernaturalists, will the irascible attacks and mean-spirited memes “preach” to anyone but those caught in the echo chamber or the bubble of unbelief? Seriously, who are people talking to, if anyone other than the online “atheist crowd”? Who’s even hearing MY voice right now? A select group of Patheists (Patheos readers)?
So, I ask fellow non-supernaturalists, will the irascible attacks and mean-spirited memes “preach” to anyone but those caught in the echo chamber or the bubble of unbelief? Seriously, who are people talking to, if anyone other than the online “atheist crowd”? Who’s even hearing MY voice right now? A select group of Patheists (Patheos readers)? No other item of religious clothing has ignited passions and prejudice among politicians and media commentators as much as the burqa, worn by a minority of Muslim women. In 2006, then leader of the House of Commons Jack Straw wrote of his “concerns” after a meeting with a veiled Muslim woman in his Blackburn constituency – he later apologised. Tony Blair, who was then prime minister, said the wearing of veils was a “mark of separation”. More than a decade later,
No other item of religious clothing has ignited passions and prejudice among politicians and media commentators as much as the burqa, worn by a minority of Muslim women. In 2006, then leader of the House of Commons Jack Straw wrote of his “concerns” after a meeting with a veiled Muslim woman in his Blackburn constituency – he later apologised. Tony Blair, who was then prime minister, said the wearing of veils was a “mark of separation”. More than a decade later,