“ ‘Woke’ is not a political movement, it’s
an optimal state of mind, and being.”
…………………………… —Roshi Bob
Some Never Awaken
You live like this, sheltered, in a
delicate world, and you believe
you are living.
Then you read a book…
or you take a trip…
and you discover that you
are not living, that you
are hibernating.
The symptoms of hibernating are
easily detectable: first, restlessness.
The second symptom (when hibernating
becomes dangerous and might
degenerate into death): absence
of pleasure.
That is all.
It appears like an innocuous illness.
Monotony, boredom, death.
Millions live like this (or die like this)
without knowing it.
They work in offices.
They drive a car.
They picnic with their families.
They raise children.
And then some shock treatment
takes place, a person, a book, a song,
and it awakens them and saves them
from death.
Some never awaken.
by Anais Nin
from The Diary of Anaïs Nin, Vol. 1: 1931-1934

 TAKE A GOOD LOOK
TAKE A GOOD LOOK Michael Levin: Pretty much everything, birth defects, traumatic injury, aging, degenerative disease, cancer, all of these things boil down to the problem of a group of cells not knowing how or not being able to build the right thing. If we have the answer to this, how do you communicate an anatomical goals to a collection of cells? You could fix all of these things.
Michael Levin: Pretty much everything, birth defects, traumatic injury, aging, degenerative disease, cancer, all of these things boil down to the problem of a group of cells not knowing how or not being able to build the right thing. If we have the answer to this, how do you communicate an anatomical goals to a collection of cells? You could fix all of these things. “For generations in the mind of America, the Negro has been more of a formula than a human being—a something to be argued about, condemned or defended, to be ‘kept down,’ or ‘in his place,’ or ‘helped up,’ to be worried with or worried over, harassed or patronized, a social bogey or a social burden.” So wrote Alain Locke in the anthology The New Negro (1925), often considered the founding document of the Harlem Renaissance, the artistic movement of which Locke is generally recognized as intellectual impresario. “The thinking Negro even has been induced to share this same general attitude, to focus his attention on controversial issues, to see himself in the distorted perspective of a social problem. His shadow, so to speak, has been more real to him than his personality.”
“For generations in the mind of America, the Negro has been more of a formula than a human being—a something to be argued about, condemned or defended, to be ‘kept down,’ or ‘in his place,’ or ‘helped up,’ to be worried with or worried over, harassed or patronized, a social bogey or a social burden.” So wrote Alain Locke in the anthology The New Negro (1925), often considered the founding document of the Harlem Renaissance, the artistic movement of which Locke is generally recognized as intellectual impresario. “The thinking Negro even has been induced to share this same general attitude, to focus his attention on controversial issues, to see himself in the distorted perspective of a social problem. His shadow, so to speak, has been more real to him than his personality.” Modern pro wrestling branches off from vaudeville, loops back through the circus, launches off a theater balcony, and takes a detour past Muscle Beach before hammering together a space all its own. It’s held onto its malleability and perennial status as a home for misfits and weirdos who don’t quite fit in anywhere else. As an accessible working-class art form, it’s become a magnet for generations of performers who came into wrestling with little more than a dream and a high pain threshold. It’s not a coincidence that pro wrestling is one of the few theatrical arts in which a performer can still succeed wholly on their own merits. You don’t need rich parents or a degree from a prestigious institution to don the tights and become a star; it’ll still cost you and the view from backstage isn’t always pretty, but the barrier to entry is far lower. How do you get to Wrestlemania? Practice.
Modern pro wrestling branches off from vaudeville, loops back through the circus, launches off a theater balcony, and takes a detour past Muscle Beach before hammering together a space all its own. It’s held onto its malleability and perennial status as a home for misfits and weirdos who don’t quite fit in anywhere else. As an accessible working-class art form, it’s become a magnet for generations of performers who came into wrestling with little more than a dream and a high pain threshold. It’s not a coincidence that pro wrestling is one of the few theatrical arts in which a performer can still succeed wholly on their own merits. You don’t need rich parents or a degree from a prestigious institution to don the tights and become a star; it’ll still cost you and the view from backstage isn’t always pretty, but the barrier to entry is far lower. How do you get to Wrestlemania? Practice. In 2022, researchers at the Bee Sensory and Behavioral Ecology Lab at Queen Mary University of London observed bumblebees doing something remarkable: The diminutive, fuzzy creatures were engaging in activity that
In 2022, researchers at the Bee Sensory and Behavioral Ecology Lab at Queen Mary University of London observed bumblebees doing something remarkable: The diminutive, fuzzy creatures were engaging in activity that 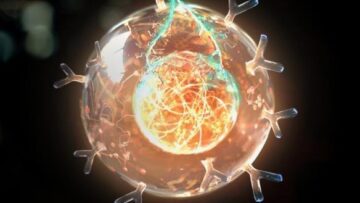 Dubbed “living drugs,” CAR T cells are bioengineered from a patient’s own immune cells to make them better able to hunt and destroy cancer. The treatment is successfully tackling previously untreatable blood cancers. Six therapies are already approved by the FDA.
Dubbed “living drugs,” CAR T cells are bioengineered from a patient’s own immune cells to make them better able to hunt and destroy cancer. The treatment is successfully tackling previously untreatable blood cancers. Six therapies are already approved by the FDA.  Years ago, for reasons I still don’t fully understand, I found myself writing about flight. It started as just a few paragraphs, a bit of spontaneous fiction jotted down in a notebook: a man stood on the roof of a barn, wearing a pair of enormous wings built from wood and cloth. His friend on the ground—the narrator—looked on nervously, ready to call an ambulance. And then the man jumped. Somehow, he flew.
Years ago, for reasons I still don’t fully understand, I found myself writing about flight. It started as just a few paragraphs, a bit of spontaneous fiction jotted down in a notebook: a man stood on the roof of a barn, wearing a pair of enormous wings built from wood and cloth. His friend on the ground—the narrator—looked on nervously, ready to call an ambulance. And then the man jumped. Somehow, he flew. After they were released from prison in Paris in the late autumn of 1794, both having narrowly escaped the guillotine, new bosom friends Rose de Beauharnais and Térézia Tallien found they had nothing to wear. Dressmakers and milliners had all but disappeared from a city still reeling from the Reign of Terror. In an era of desperate need and rampant inflation, a time when even the most prosperous took candles and bread with them when they went out to dinner, who could afford a silk dress, still less stays, hoops, acres of petticoats and several maids to sew you into it?
After they were released from prison in Paris in the late autumn of 1794, both having narrowly escaped the guillotine, new bosom friends Rose de Beauharnais and Térézia Tallien found they had nothing to wear. Dressmakers and milliners had all but disappeared from a city still reeling from the Reign of Terror. In an era of desperate need and rampant inflation, a time when even the most prosperous took candles and bread with them when they went out to dinner, who could afford a silk dress, still less stays, hoops, acres of petticoats and several maids to sew you into it? ‘At a quarter to eleven on August 12, 2022, on a sunny Friday morning in upstate New York, I was attacked and almost killed by a young man with a knife,” begins Salman Rushdie’s new memoir.
‘At a quarter to eleven on August 12, 2022, on a sunny Friday morning in upstate New York, I was attacked and almost killed by a young man with a knife,” begins Salman Rushdie’s new memoir. NASA’s interstellar explorer Voyager 1 is finally communicating with ground control in an understandable way again. On Saturday (April 20), Voyager 1 updated ground control about its health status for the first time in 5 months. While the
NASA’s interstellar explorer Voyager 1 is finally communicating with ground control in an understandable way again. On Saturday (April 20), Voyager 1 updated ground control about its health status for the first time in 5 months. While the  Kwame Anthony Appiah is a British-Ghanaian philosopher, Professor of Philosophy and Law and New York University, and the “Ethicist” columnist for The New York Times Magazine.
Kwame Anthony Appiah is a British-Ghanaian philosopher, Professor of Philosophy and Law and New York University, and the “Ethicist” columnist for The New York Times Magazine.