Paul Voosen in Science:
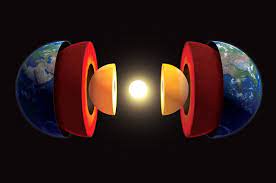 Earth’s magnetic field, nearly as old as the planet itself, protects life from damaging space radiation. But 565 million years ago, the field was sputtering, dropping to 10% of today’s strength, according to a recent discovery. Then, almost miraculously, over the course of just a few tens of millions of years, it regained its strength—just in time for the sudden profusion of complex multicellular life known as the Cambrian explosion.
Earth’s magnetic field, nearly as old as the planet itself, protects life from damaging space radiation. But 565 million years ago, the field was sputtering, dropping to 10% of today’s strength, according to a recent discovery. Then, almost miraculously, over the course of just a few tens of millions of years, it regained its strength—just in time for the sudden profusion of complex multicellular life known as the Cambrian explosion.
What could have caused the rapid revival? Increasingly, scientists believe it was the birth of Earth’s inner core, a sphere of solid iron that sits within the molten outer core, where churning metal generates the planet’s magnetic field. Once the inner core was born, possibly 4 billion years after the planet itself, its treelike growth—accreting a few millimeters per year at its surface—would have turbocharged motions in the outer core, reviving the faltering magnetic field and renewing the protective shield for life. “The inner core regenerated Earth’s magnetic field at a really interesting time in evolution,” says John Tarduno, a geophysicist at the University of Rochester. “What would have happened if it didn’t form?”
Just why and how the inner core was born at that moment is one of many lingering puzzles about the Pluto-size orb 5000 kilo meters underfoot. “The inner core is a planet within a planet,” says Hrvoje Tkalčić, a seismologist at Australian National University (ANU)—with its own topography, its own spin rate, its own structure. “It’s beneath our feet and yet we still don’t understand some big questions,” Tkalčić says.
But researchers are beginning to chip away at those questions. Using the rare seismic waves from earthquakes or nuclear tests that penetrate or reflect off the inner core, seismologists have discovered it spins independently from the rest of the planet. Armed with complex computer models, theorists have predicted the structure and weird behavior of iron alloys crushed by the weight of the world. And experimentalists are close to confirming some of those predictions in the lab by re-creating the extreme temperatures and pressures of the inner core.
More here.
 Many scholars agree that a subjectively meaningful existence often boils down to three factors: the feeling that one’s life is coherent and “makes sense,” the possession of clear and satisfying long-term goals and the belief that one’s life matters in the grand scheme of things. Psychologists call these three things coherence, purpose and existential mattering.
Many scholars agree that a subjectively meaningful existence often boils down to three factors: the feeling that one’s life is coherent and “makes sense,” the possession of clear and satisfying long-term goals and the belief that one’s life matters in the grand scheme of things. Psychologists call these three things coherence, purpose and existential mattering.
 Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis is both a Trump follower and possible Trump opponent, as he’s declined to say whether he’d face off against the former president for the 2024 GOP nomination. He’s pushed through a number of state bills that deal with hot button partisan issues, such as the recently enacted Parental Rights in Education, dubbed by critics the “don’t say gay” law, that bans school teaching of sexual topics deemed non-age-appropriate. Florida is “becoming redder all the time, and it has a very arch-conservative edge – a culture war edge,” says Orlando-based historian James Clark, author of “Hidden History of Florida.”
Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis is both a Trump follower and possible Trump opponent, as he’s declined to say whether he’d face off against the former president for the 2024 GOP nomination. He’s pushed through a number of state bills that deal with hot button partisan issues, such as the recently enacted Parental Rights in Education, dubbed by critics the “don’t say gay” law, that bans school teaching of sexual topics deemed non-age-appropriate. Florida is “becoming redder all the time, and it has a very arch-conservative edge – a culture war edge,” says Orlando-based historian James Clark, author of “Hidden History of Florida.” Van Etten often counters the sonic immensity of her new album, stacked with towering choruses, moody synths, and a lingering sense of despair, with lamplit views of the hearth. On the festival-ready “Anything,” she presents an image glowing with the warmth of an Edward Hopper painting, bellowing, “You love him by the stove light in your arms.” Talking about the song’s origin story, she remembers cooking dinner one night, and as the jazz pianist Bud Powell’s “
Van Etten often counters the sonic immensity of her new album, stacked with towering choruses, moody synths, and a lingering sense of despair, with lamplit views of the hearth. On the festival-ready “Anything,” she presents an image glowing with the warmth of an Edward Hopper painting, bellowing, “You love him by the stove light in your arms.” Talking about the song’s origin story, she remembers cooking dinner one night, and as the jazz pianist Bud Powell’s “ Roughly speaking, “The White Negro” contends that, in the aftermath of Auschwitz and Hiroshima, the human race as a whole now finds itself in the same psychic and physical predicament experienced by black people in America in the 1950s – that is, deindividualised, oppressed by violent systems of control, risking their lives every time they walked down the street. To live authentically in such a world, Mailer suggests, we must become “white Negroes”, or hipsters. Our morality must be psychopathic – radically free from inherited codes. Our philosophy must be existentialist. We must live like teenage hoodlums – weighing up the “therapeutic” value of “beat[ing] in the brains of a candy store keeper”.
Roughly speaking, “The White Negro” contends that, in the aftermath of Auschwitz and Hiroshima, the human race as a whole now finds itself in the same psychic and physical predicament experienced by black people in America in the 1950s – that is, deindividualised, oppressed by violent systems of control, risking their lives every time they walked down the street. To live authentically in such a world, Mailer suggests, we must become “white Negroes”, or hipsters. Our morality must be psychopathic – radically free from inherited codes. Our philosophy must be existentialist. We must live like teenage hoodlums – weighing up the “therapeutic” value of “beat[ing] in the brains of a candy store keeper”. The idea goes like this. Once upon a time, private property was unknown. Food went to those in need. Everyone was cared for. Then agriculture arose and, with it, ownership over land, labour and wild resources. The organic community splintered under the weight of competition. The story predates Marx and Engels. The patron saint of capitalism,
The idea goes like this. Once upon a time, private property was unknown. Food went to those in need. Everyone was cared for. Then agriculture arose and, with it, ownership over land, labour and wild resources. The organic community splintered under the weight of competition. The story predates Marx and Engels. The patron saint of capitalism,  “We’re doing a really terrible job of communicating risk,” said Katelyn Jetelina, an epidemiologist at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. “I think that’s also why people are throwing their hands up in the air and saying, ‘Screw it.’ They’re desperate for some sort of guidance.”
“We’re doing a really terrible job of communicating risk,” said Katelyn Jetelina, an epidemiologist at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston. “I think that’s also why people are throwing their hands up in the air and saying, ‘Screw it.’ They’re desperate for some sort of guidance.” In developing a nuclear arsenal that will soon rival those of Russia and the United States, China is not merely departing from its decades-old status as a minor nuclear state; it is also upending the bipolar nuclear power system. For the 73 years since the Soviet Union’s first nuclear test, that bipolar system, for all its flaws and moments of terror, has averted nuclear war. Now, by closing in on parity with the two existing great nuclear powers, China is heralding a paradigm shift to something much less stable: a tripolar nuclear system. In that world, there will be both a greater risk of a nuclear arms race and heightened incentives for states to resort to nuclear weapons in a crisis. With three competing great nuclear powers, many of the features that enhanced stability in the bipolar system will be rendered either moot or far less reliable.
In developing a nuclear arsenal that will soon rival those of Russia and the United States, China is not merely departing from its decades-old status as a minor nuclear state; it is also upending the bipolar nuclear power system. For the 73 years since the Soviet Union’s first nuclear test, that bipolar system, for all its flaws and moments of terror, has averted nuclear war. Now, by closing in on parity with the two existing great nuclear powers, China is heralding a paradigm shift to something much less stable: a tripolar nuclear system. In that world, there will be both a greater risk of a nuclear arms race and heightened incentives for states to resort to nuclear weapons in a crisis. With three competing great nuclear powers, many of the features that enhanced stability in the bipolar system will be rendered either moot or far less reliable. How do you like to pay? Do you prefer to tap, wave, insert, single-click or double-click – or are you a hold out for hard cash? If it’s the latter, you’re fast becoming the exception. Between our growing enthusiasm for online shopping, the ease and speed with which we can now make electronic bank transfers, and the inexorable rise of cards and the advent of digital wallets, more and more of us are shunning physical money. This is still a relatively recent trend.
How do you like to pay? Do you prefer to tap, wave, insert, single-click or double-click – or are you a hold out for hard cash? If it’s the latter, you’re fast becoming the exception. Between our growing enthusiasm for online shopping, the ease and speed with which we can now make electronic bank transfers, and the inexorable rise of cards and the advent of digital wallets, more and more of us are shunning physical money. This is still a relatively recent trend.  Kinase inhibitors are a type of targeted
Kinase inhibitors are a type of targeted  “What is writing good for if we can’t write a way out of this darkest timeline?” (264), Karen Cheung asks in this hauntingly moving memoir of her life in Hong Kong over these last two decades. Since the passage of the National Security Law (NSL) in the summer of 2020, “Hong Kong is dead” has become a common refrain in international news. Amid constant crackdowns and arrests, Hong Kong no longer fits the image of a vibrant cosmopolitan city where foreign corporations, tourists, and expatriates can enjoy unbridled freedom. Beginning with a scathing and acute interrogation of this narrative, Cheung’s memoir cannot write Hong Kong out of its darkest timeline, but it has succeeded in lifting up the deeds and voices of Hongkongers who have always dared to imagine and work towards a better collective future for the city.
“What is writing good for if we can’t write a way out of this darkest timeline?” (264), Karen Cheung asks in this hauntingly moving memoir of her life in Hong Kong over these last two decades. Since the passage of the National Security Law (NSL) in the summer of 2020, “Hong Kong is dead” has become a common refrain in international news. Amid constant crackdowns and arrests, Hong Kong no longer fits the image of a vibrant cosmopolitan city where foreign corporations, tourists, and expatriates can enjoy unbridled freedom. Beginning with a scathing and acute interrogation of this narrative, Cheung’s memoir cannot write Hong Kong out of its darkest timeline, but it has succeeded in lifting up the deeds and voices of Hongkongers who have always dared to imagine and work towards a better collective future for the city. Inside one of the buildings lies a wonder of modern technology: 285,000 CPU cores yoked together into one giant supercomputer, powered by solar arrays and cooled by industrial fans. The machines never sleep: Every second of every day, they churn through innumerable calculations, using state-of-the-art techniques in machine intelligence that go by names like ‘‘stochastic gradient descent’’ and ‘‘convolutional neural networks.’’ The whole system is believed to be one of the most powerful supercomputers on the planet.
Inside one of the buildings lies a wonder of modern technology: 285,000 CPU cores yoked together into one giant supercomputer, powered by solar arrays and cooled by industrial fans. The machines never sleep: Every second of every day, they churn through innumerable calculations, using state-of-the-art techniques in machine intelligence that go by names like ‘‘stochastic gradient descent’’ and ‘‘convolutional neural networks.’’ The whole system is believed to be one of the most powerful supercomputers on the planet. Earth’s magnetic field, nearly as old as the planet itself, protects life from damaging space radiation. But 565 million years ago, the field was sputtering, dropping to 10% of today’s strength, according to a recent discovery. Then, almost miraculously, over the course of just a few tens of millions of years, it regained its strength—just in time for the sudden profusion of complex multicellular life known as
Earth’s magnetic field, nearly as old as the planet itself, protects life from damaging space radiation. But 565 million years ago, the field was sputtering, dropping to 10% of today’s strength, according to a recent discovery. Then, almost miraculously, over the course of just a few tens of millions of years, it regained its strength—just in time for the sudden profusion of complex multicellular life known as  The basic charge against Imran Khan
The basic charge against Imran Khan  In May 2020, Omar Ruiz found himself with a broken heart. “My wife told me she was no longer in love with me,” and shortly thereafter, the couple, who had been married 11 years, separated. Not only was he crushed, he said, but as a marriage and family therapist, “this entire process challenged my professional identity,” said Mr. Ruiz, who is 36 and lives in Boston. “How could I help couples when my own marriage is falling apart?”
In May 2020, Omar Ruiz found himself with a broken heart. “My wife told me she was no longer in love with me,” and shortly thereafter, the couple, who had been married 11 years, separated. Not only was he crushed, he said, but as a marriage and family therapist, “this entire process challenged my professional identity,” said Mr. Ruiz, who is 36 and lives in Boston. “How could I help couples when my own marriage is falling apart?”