Susan Pedersen at the LRB:
 Selina Todd’s biography of Delaney does two things well. It helps us understand how someone the press insisted on calling a ‘Salford teenager’ was able to create this remarkable work – and it shows how hard the people who brought the play to stage and screen worked to shift the spotlight away from that intense mother-daughter dynamic. There was a script, too, for ‘new writers’ in the late 1950s and 1960s: they were to be young, authentic and, if possible, working class; they were to be masculine, rebellious and shocking. When, in April 1958, Delaney sent her play to Joan Littlewood, the director of the avant-garde Theatre Workshop in East London, she adopted a naive, Northern persona that was more than a little misleading. ‘A fortnight ago I didn’t know the theatre existed,’ she gushed to Littlewood – but then a friend had taken her to see a play and she had discovered ‘something that meant more to me than myself’. She now knew she wanted to write plays, and in two weeks had produced the enclosed ‘epic’. ‘Please can you help me? I’m willing enough to help myself.’ Christened plain ‘Sheila’, she signed the letter ‘Shelagh Delaney’, the name by which she would be known from then on.
Selina Todd’s biography of Delaney does two things well. It helps us understand how someone the press insisted on calling a ‘Salford teenager’ was able to create this remarkable work – and it shows how hard the people who brought the play to stage and screen worked to shift the spotlight away from that intense mother-daughter dynamic. There was a script, too, for ‘new writers’ in the late 1950s and 1960s: they were to be young, authentic and, if possible, working class; they were to be masculine, rebellious and shocking. When, in April 1958, Delaney sent her play to Joan Littlewood, the director of the avant-garde Theatre Workshop in East London, she adopted a naive, Northern persona that was more than a little misleading. ‘A fortnight ago I didn’t know the theatre existed,’ she gushed to Littlewood – but then a friend had taken her to see a play and she had discovered ‘something that meant more to me than myself’. She now knew she wanted to write plays, and in two weeks had produced the enclosed ‘epic’. ‘Please can you help me? I’m willing enough to help myself.’ Christened plain ‘Sheila’, she signed the letter ‘Shelagh Delaney’, the name by which she would be known from then on.
more here.

 On Sunday, on Tuesday, and again on Wednesday, President
On Sunday, on Tuesday, and again on Wednesday, President 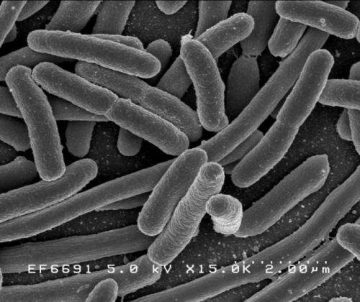 Bacteria have a cunning ability to survive in unfriendly environments. For example, through a complicated series of interactions, they can identify—and then build resistance to—
Bacteria have a cunning ability to survive in unfriendly environments. For example, through a complicated series of interactions, they can identify—and then build resistance to— There continues to be an impressive appetite for conceptual and philosophical explorations of psychiatry. The publishing field is now populated by a diverse array of backgrounds and perspectives. The general public seems mostly interested in decrying the medicalization of normal and the transformation of our woes into neatly packaged mental disorders. The academic literature is dominated by philosophers and philosophically-trained professionals; while the intellectual discourse is of high caliber, it unfortunately remains largely inaccessible to mental health professionals and much of the general public, and resultantly it has had little influence outside the academic community. There is also a cohort of individuals with a critical interest in the subject but whose philosophical focus remains stuck on classical critical figures such as Thomas Szasz, Michel Foucault and R.D. Laing, with little engagement with contemporary philosophy of science. The philosophical work of Kenneth Kendler and his various collaborators (John Campbell, Carl Craver, Kenneth Schaffner, Erik Engstrom, Rodrigo Munoz, George Murphy, and Peter Zachar) assembled in a specially curated volume occupies a unique and special position in this contemporary landscape and there is much to be said in its favor.
There continues to be an impressive appetite for conceptual and philosophical explorations of psychiatry. The publishing field is now populated by a diverse array of backgrounds and perspectives. The general public seems mostly interested in decrying the medicalization of normal and the transformation of our woes into neatly packaged mental disorders. The academic literature is dominated by philosophers and philosophically-trained professionals; while the intellectual discourse is of high caliber, it unfortunately remains largely inaccessible to mental health professionals and much of the general public, and resultantly it has had little influence outside the academic community. There is also a cohort of individuals with a critical interest in the subject but whose philosophical focus remains stuck on classical critical figures such as Thomas Szasz, Michel Foucault and R.D. Laing, with little engagement with contemporary philosophy of science. The philosophical work of Kenneth Kendler and his various collaborators (John Campbell, Carl Craver, Kenneth Schaffner, Erik Engstrom, Rodrigo Munoz, George Murphy, and Peter Zachar) assembled in a specially curated volume occupies a unique and special position in this contemporary landscape and there is much to be said in its favor.
 What would become known as the CARES Act
What would become known as the CARES Act 

 Two incidents separated by twelve hours and twelve hundred miles have taken on the appearance of the control and the variable in a grotesque experiment about race in America. On Monday morning, in New York City’s Central Park, a white woman named Amy Cooper called 911 and told the dispatcher that an African-American man was threatening her. The man she was talking about, Christian Cooper, who is no relation, filmed the call on his phone. They were in the Ramble, a part of the park favored by bird-watchers, including Christian Cooper, and he had simply requested that she leash her dog—something that is required in the area. In the video, before making the call, Ms. Cooper warns Mr. Cooper that she is “going to tell them there’s an African-American man threatening my life.” Her needless inclusion of the race of the man she fears serves only to summon the ancient impulse to protect white womanhood from the threats posed by black men. For anyone with a long enough memory or a recent enough viewing of the series “
Two incidents separated by twelve hours and twelve hundred miles have taken on the appearance of the control and the variable in a grotesque experiment about race in America. On Monday morning, in New York City’s Central Park, a white woman named Amy Cooper called 911 and told the dispatcher that an African-American man was threatening her. The man she was talking about, Christian Cooper, who is no relation, filmed the call on his phone. They were in the Ramble, a part of the park favored by bird-watchers, including Christian Cooper, and he had simply requested that she leash her dog—something that is required in the area. In the video, before making the call, Ms. Cooper warns Mr. Cooper that she is “going to tell them there’s an African-American man threatening my life.” Her needless inclusion of the race of the man she fears serves only to summon the ancient impulse to protect white womanhood from the threats posed by black men. For anyone with a long enough memory or a recent enough viewing of the series “ As many countries emerge from lockdowns, researchers are poised to use genome sequencing to avoid an expected second wave of COVID-19 infections. Since the first whole-genome sequence of the new coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, was
As many countries emerge from lockdowns, researchers are poised to use genome sequencing to avoid an expected second wave of COVID-19 infections. Since the first whole-genome sequence of the new coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, was  The combined total of inflation and unemployment used to be known as the “misery index”: Jimmy Carter cited it when he was campaigning in 1976 against Gerald Ford for the presidency. But the index was even higher in 1980, dooming Carter’s re-election bid. Barack Obama reduced the misery index during his two terms of office; indeed of all the Presidents since 1945, only Harry Truman left office with a lower misery index. But that didn’t seem to make voters happy; although Hillary Clinton (Obama’s party successor) won the popular vote, Donald Trump took enough key states to be elected. Similarly in 2016, British inflation was low and unemployment had been falling for years, yet voter anger resulted in Britain voting to leave the EU.
The combined total of inflation and unemployment used to be known as the “misery index”: Jimmy Carter cited it when he was campaigning in 1976 against Gerald Ford for the presidency. But the index was even higher in 1980, dooming Carter’s re-election bid. Barack Obama reduced the misery index during his two terms of office; indeed of all the Presidents since 1945, only Harry Truman left office with a lower misery index. But that didn’t seem to make voters happy; although Hillary Clinton (Obama’s party successor) won the popular vote, Donald Trump took enough key states to be elected. Similarly in 2016, British inflation was low and unemployment had been falling for years, yet voter anger resulted in Britain voting to leave the EU. Julia Wellner and other crew members for this year’s Thwaites Glacier Offshore Research Project stepped onto the deck of the research vessel/icebreaker (RV/IB) Nathaniel B. Palmer in January, leaving from a crowded pier in Punta Arenas, Chile, and sailing to west coast of Antarctica.
Julia Wellner and other crew members for this year’s Thwaites Glacier Offshore Research Project stepped onto the deck of the research vessel/icebreaker (RV/IB) Nathaniel B. Palmer in January, leaving from a crowded pier in Punta Arenas, Chile, and sailing to west coast of Antarctica. When in mid-March “
When in mid-March “