Editor’s note: This is the introduction to “An occasional series commissioned by Huw Price where contemporary philosophers consider the tv discussion between Peter Strawson and Gareth Evans regarding the nature of Truth from 1973.” The other articles in the series can be read here as they become available.
Huw Price at 3:16 AM:
 I first discovered this fascinating conversation as a postdoc at ANU, Canberra, in the early 1980s. I was interested in truth, and looking for new things to read. Google was nearly 20 years in the future, so I had to rely on the library’s subject catalogue. This worked much like Google does today, with two differences. I had to look up ‘Truth’ in a large device called a card catalogue, rather than typing it into a search field. And the results – accessible instantaneously in the card file, just behind the ‘Truth’ card – were limited to items held by the library.
I first discovered this fascinating conversation as a postdoc at ANU, Canberra, in the early 1980s. I was interested in truth, and looking for new things to read. Google was nearly 20 years in the future, so I had to rely on the library’s subject catalogue. This worked much like Google does today, with two differences. I had to look up ‘Truth’ in a large device called a card catalogue, rather than typing it into a search field. And the results – accessible instantaneously in the card file, just behind the ‘Truth’ card – were limited to items held by the library.
In amongst the listings for books, there was one for a movie – as the card told me, a discussion between P F Strawson and Gareth Evans, recorded for The Open University in 1973. The library had a copy on 16mm. That sounded intriguing.
Fortunately, unlike some postdocs today, I knew how to use a 16mm projector – I was a projectionist first, a projectivist second. I organised a screening for colleagues and graduate students, and was delighted to discover that Strawson and Evans’ discussion connected to my own interests in truth and factuality.
More here. And here is the discussion between Strawson and Evans:

 It was only in the second volume of Warburg’s Gesammelte Schriften (Collected Writings), published in 2000, that the glass negatives created in 1929 were used to publish fragmentary pictorial evidence of the “Bilderatlas Mnemosyne.” Editors Martin Warnke and Claudia Brink produced black-and-white images from the negatives, printing them at a reduced size that tended to obscure their details. They also left off additional commentary, given the lack of extant captioning by Warburg himself. This publication was in no small part encouraged by the resurgence of interest in the works of Walter Benjamin (1892–1940), whose theories of media and history had come to seem prescient, particularly in the Anglophone world, with the 1969 Illuminations, edited and introduced by Hannah Arendt and subsequently popularized by John Berger in his 1972 TV series and book, Ways of Seeing. (While Warburg was only peripherally aware of Benjamin during his lifetime, Benjamin sent Warburg a copy of his thesis on Baroque Trauerspiel, or tragic drama, which cited Warburg.) Like Benjamin, who often engaged in leaps of thought and argument by way of metaphorical image rather than logical deduction, Warburg was concerned with Zwischenräume, the spaces in between, as well as something he termed Denkraum, or room for thought.
It was only in the second volume of Warburg’s Gesammelte Schriften (Collected Writings), published in 2000, that the glass negatives created in 1929 were used to publish fragmentary pictorial evidence of the “Bilderatlas Mnemosyne.” Editors Martin Warnke and Claudia Brink produced black-and-white images from the negatives, printing them at a reduced size that tended to obscure their details. They also left off additional commentary, given the lack of extant captioning by Warburg himself. This publication was in no small part encouraged by the resurgence of interest in the works of Walter Benjamin (1892–1940), whose theories of media and history had come to seem prescient, particularly in the Anglophone world, with the 1969 Illuminations, edited and introduced by Hannah Arendt and subsequently popularized by John Berger in his 1972 TV series and book, Ways of Seeing. (While Warburg was only peripherally aware of Benjamin during his lifetime, Benjamin sent Warburg a copy of his thesis on Baroque Trauerspiel, or tragic drama, which cited Warburg.) Like Benjamin, who often engaged in leaps of thought and argument by way of metaphorical image rather than logical deduction, Warburg was concerned with Zwischenräume, the spaces in between, as well as something he termed Denkraum, or room for thought. The style of To the Friend Who Did Not Save My Life is more restrained and controlled than these earlier works, but full of well-noticed contrasting details that combine to create an effect that Guibert—apropos of The Compassion Protocol, his last work before his suicide in 1991—characterized as “barbarous and delicate.” An ambulance pulls up to unload a patient in front of a half-abandoned hospital in the midst of shutting down: “slippers in a crate with ampules of potassium chloride . . . a basin from an intensive care unit with a coating of snow on the bottom.” At another hospital, the nurses who draw his blood for the dreaded regular T-cell count “slip on their latex gloves as though they were velvet gloves for a gala evening at the opera.” One of them comments on his cologne, “It’s Habit Rouge isn’t it? . . . I do like that perfume, and to catch a whiff of it on this gray morning, well, you know it’s really a little treat for me.” Disease, as those who’ve spent time in the presence of the sick know, is never quite dramatically life or death, but always life in death and death in life. No moment of one’s life as a terminally ill person or a carer for a terminally ill person passes without this double acknowledgment.
The style of To the Friend Who Did Not Save My Life is more restrained and controlled than these earlier works, but full of well-noticed contrasting details that combine to create an effect that Guibert—apropos of The Compassion Protocol, his last work before his suicide in 1991—characterized as “barbarous and delicate.” An ambulance pulls up to unload a patient in front of a half-abandoned hospital in the midst of shutting down: “slippers in a crate with ampules of potassium chloride . . . a basin from an intensive care unit with a coating of snow on the bottom.” At another hospital, the nurses who draw his blood for the dreaded regular T-cell count “slip on their latex gloves as though they were velvet gloves for a gala evening at the opera.” One of them comments on his cologne, “It’s Habit Rouge isn’t it? . . . I do like that perfume, and to catch a whiff of it on this gray morning, well, you know it’s really a little treat for me.” Disease, as those who’ve spent time in the presence of the sick know, is never quite dramatically life or death, but always life in death and death in life. No moment of one’s life as a terminally ill person or a carer for a terminally ill person passes without this double acknowledgment.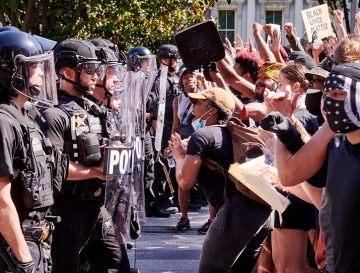 ALONE AND INSIDE IN THESE
ALONE AND INSIDE IN THESE  Human beings typically don’t leave the nest until well into our teenage years—a relatively rare strategy among animals. But corvids—a group of birds that includes jays, ravens, and crows—also spend a lot of time under their parents’ wings. Now, in a parallel to humans, researchers have found that ongoing tutelage by patient parents may explain how corvids have managed to achieve their smarts. Corvids are large, big-brained birds that often live in intimate social groups of related and unrelated individuals. They are known to be intelligent—capable of
Human beings typically don’t leave the nest until well into our teenage years—a relatively rare strategy among animals. But corvids—a group of birds that includes jays, ravens, and crows—also spend a lot of time under their parents’ wings. Now, in a parallel to humans, researchers have found that ongoing tutelage by patient parents may explain how corvids have managed to achieve their smarts. Corvids are large, big-brained birds that often live in intimate social groups of related and unrelated individuals. They are known to be intelligent—capable of  In The Weil Conjectures Karen Olsson presents her remarkable subjects as creatures from a fairy tale: “Once there were a brother and sister who devoted themselves to the search for truth. A brother who spent his long life solving problems. A sister who died before she could solve the problem of life.” The sister was Simone Weil (pronounced “vay”), a philosopher and political activist who died in 1943 at age thirty-four and gained fame with the posthumous publication of works, assembled from her voluminous notebooks, on society, justice, and the mystical life of faith. Her elder brother André, who lived to ninety-two, was a prodigy who became one of the twentieth century’s preeminent mathematicians.
In The Weil Conjectures Karen Olsson presents her remarkable subjects as creatures from a fairy tale: “Once there were a brother and sister who devoted themselves to the search for truth. A brother who spent his long life solving problems. A sister who died before she could solve the problem of life.” The sister was Simone Weil (pronounced “vay”), a philosopher and political activist who died in 1943 at age thirty-four and gained fame with the posthumous publication of works, assembled from her voluminous notebooks, on society, justice, and the mystical life of faith. Her elder brother André, who lived to ninety-two, was a prodigy who became one of the twentieth century’s preeminent mathematicians. Late one January
Late one January If we’re talking about culture that makes people happy, we have to start with the works of PG Wodehouse. There are two reasons why. One reason is that making people happy was Wodehouse’s overriding ambition. The other reason is that he was better at it than any other writer in history.
If we’re talking about culture that makes people happy, we have to start with the works of PG Wodehouse. There are two reasons why. One reason is that making people happy was Wodehouse’s overriding ambition. The other reason is that he was better at it than any other writer in history. What does it mean to be great? Whom shall we call great? How can we become great? Is greatness the same as goodness? These questions involve fundamental ethical assumptions, concepts and concerns. Like many who addressed such issues in the past, we often use virtues — courage, generosity, forbearance, etc. — in order to explain what greatness means, reflecting a common notion that greatness requires moral integrity. Virtues describe our ambitions and aspirations, as individuals and as communities. How we give credit for moral achievements is presumably also culturally conditioned, just as the way we relate to our accomplishments in general reflects social and historical context. Studies on the Dunning-Kruger effect suggest that while North Americans regularly overestimate their abilities, in Japan the opposite appears to be the case. Other variables too are sometimes debated. The self-citation rate among male scientists is often reported to be higher than among their female peers, which might reflect a higher estimation of their achievements. Differences are also believed to be generational and related to educational practices around appreciation and rewards. Recent public debates have shed light on the psychological and emotional costs of self-optimizing and the social and political dynamics of virtue-signaling. Likewise, who our role models should be and how they are selected often reveals the diverging views of greatness in a society. Even a brief survey of these and similar discussions suggests that the philosophical problem of greatness can be of significant interest to contemporary readers.
What does it mean to be great? Whom shall we call great? How can we become great? Is greatness the same as goodness? These questions involve fundamental ethical assumptions, concepts and concerns. Like many who addressed such issues in the past, we often use virtues — courage, generosity, forbearance, etc. — in order to explain what greatness means, reflecting a common notion that greatness requires moral integrity. Virtues describe our ambitions and aspirations, as individuals and as communities. How we give credit for moral achievements is presumably also culturally conditioned, just as the way we relate to our accomplishments in general reflects social and historical context. Studies on the Dunning-Kruger effect suggest that while North Americans regularly overestimate their abilities, in Japan the opposite appears to be the case. Other variables too are sometimes debated. The self-citation rate among male scientists is often reported to be higher than among their female peers, which might reflect a higher estimation of their achievements. Differences are also believed to be generational and related to educational practices around appreciation and rewards. Recent public debates have shed light on the psychological and emotional costs of self-optimizing and the social and political dynamics of virtue-signaling. Likewise, who our role models should be and how they are selected often reveals the diverging views of greatness in a society. Even a brief survey of these and similar discussions suggests that the philosophical problem of greatness can be of significant interest to contemporary readers. The cultured and literate Amedeo Modigliani (1884-1920) was passionately interested in and emotionally involved with Italian and French poetry of the past as well as with the work of his friends, Anna Ahkmatova, Max Jacob and Blaise Cendrars. On the 100th anniversary of his tragic death in 1920 we can see how the poets who fascinated him portrayed the pain of sex and love, the exaltation of art, the effect of narcotics on creativity and the need to suffer extreme experience. They encouraged his compulsion to live dangerously, and taught him to see the artist as victim, outcast and superman. They provided intellectual justification for the deliberate derangement of his senses and glorified his devotion to art. He didn’t just read poets. He lived according to their principles as if they were imprinted on his body as well as in his mind. These powerful poets both inspired his work and—as he was drawn to disaster and followed their maniacal descent–helped to destroy him.
The cultured and literate Amedeo Modigliani (1884-1920) was passionately interested in and emotionally involved with Italian and French poetry of the past as well as with the work of his friends, Anna Ahkmatova, Max Jacob and Blaise Cendrars. On the 100th anniversary of his tragic death in 1920 we can see how the poets who fascinated him portrayed the pain of sex and love, the exaltation of art, the effect of narcotics on creativity and the need to suffer extreme experience. They encouraged his compulsion to live dangerously, and taught him to see the artist as victim, outcast and superman. They provided intellectual justification for the deliberate derangement of his senses and glorified his devotion to art. He didn’t just read poets. He lived according to their principles as if they were imprinted on his body as well as in his mind. These powerful poets both inspired his work and—as he was drawn to disaster and followed their maniacal descent–helped to destroy him. Like most big-idea books, this one begins by absurdly overstating the novelty of its argument. The author promises to reveal “a radical idea” that has been “erased from the annals of world history”. It is, even, “a new view of humankind”. Some measure of bathos is presumably intended when we learn that this radical new view is that “most people, deep down, are pretty decent”. But there appears to be no authorial shame over the laughably bogus claim that this idea has been “erased” from history, presumably by a dark centuries-long conspiracy of secretive misanthropes, to some bafflingly obscure end. Not yet erased from the annals of history, for example, is the 18th-century philosopher
Like most big-idea books, this one begins by absurdly overstating the novelty of its argument. The author promises to reveal “a radical idea” that has been “erased from the annals of world history”. It is, even, “a new view of humankind”. Some measure of bathos is presumably intended when we learn that this radical new view is that “most people, deep down, are pretty decent”. But there appears to be no authorial shame over the laughably bogus claim that this idea has been “erased” from history, presumably by a dark centuries-long conspiracy of secretive misanthropes, to some bafflingly obscure end. Not yet erased from the annals of history, for example, is the 18th-century philosopher  Thousands of academics and major scientific organizations worldwide will stop work on 10 June as part of a global stand against anti-Black racism in science. More than 4,000 scientists as well as societies, universities and publishers, will join a call to “Strike for Black Lives,” halting their usual work activities to learn about systemic racism in the research community and to craft ways to address inequalities. The event is being planned by two ad hoc groups of scientists using hashtags such as
Thousands of academics and major scientific organizations worldwide will stop work on 10 June as part of a global stand against anti-Black racism in science. More than 4,000 scientists as well as societies, universities and publishers, will join a call to “Strike for Black Lives,” halting their usual work activities to learn about systemic racism in the research community and to craft ways to address inequalities. The event is being planned by two ad hoc groups of scientists using hashtags such as  After barreling through the relentlessly flat, verdant Punjabi hinterland in a rented Toyota, stopping briefly for naan, kebabs, and petrol, we hit town at three, four in the morning, and at three, four in the morning, music wafts through the still, sticky summer air. Millions gather each year for ten days in the hilly medieval town of Pakpattan, in Pakistan, to commemorate the death anniversary of the twelfth-century saint Baba Farid, celebrating the reunion of man and his maker with qawwali—call it Muslim soul. When Doc, a pal and Pakpattan regular, urged me to join him on the pilgrimage the night before—it’s Baba’s 776th death anniversary, he informs me—I decided to accompany him. I can’t refuse Doc: I’ve got his back; he’s got mine. And who knows? Perhaps Baba will bless me as well. But you have to believe to be blessed.
After barreling through the relentlessly flat, verdant Punjabi hinterland in a rented Toyota, stopping briefly for naan, kebabs, and petrol, we hit town at three, four in the morning, and at three, four in the morning, music wafts through the still, sticky summer air. Millions gather each year for ten days in the hilly medieval town of Pakpattan, in Pakistan, to commemorate the death anniversary of the twelfth-century saint Baba Farid, celebrating the reunion of man and his maker with qawwali—call it Muslim soul. When Doc, a pal and Pakpattan regular, urged me to join him on the pilgrimage the night before—it’s Baba’s 776th death anniversary, he informs me—I decided to accompany him. I can’t refuse Doc: I’ve got his back; he’s got mine. And who knows? Perhaps Baba will bless me as well. But you have to believe to be blessed. When protests erupted in the US in response to the killing of George Floyd on May 25, the anger over police brutality was also fuelled by a sense of simmering injustice over the impact of coronavirus. Not only have black people died from the disease in disproportionately high numbers: there are early signs they will bear the brunt of the economic fallout too.
When protests erupted in the US in response to the killing of George Floyd on May 25, the anger over police brutality was also fuelled by a sense of simmering injustice over the impact of coronavirus. Not only have black people died from the disease in disproportionately high numbers: there are early signs they will bear the brunt of the economic fallout too. A podcast only hits the century mark once! And for Mindscape, this is it. There have been holiday messages and bonus episodes and the like. But this is the 100th officially-numbered episode. To celebrate, I decided to treat myself to a solo episode in which I reflect, somewhat non-systematically, on the age-old question of the meaning of life. I end up spending a lot (most?) of the time talking about the meaning of “life,” i.e. what it means to be a living organism in a naturalistic universe. But then I go on to muse about the construction of human meaning in a world where values are not imposed on us or objectively grounded in physical facts.
A podcast only hits the century mark once! And for Mindscape, this is it. There have been holiday messages and bonus episodes and the like. But this is the 100th officially-numbered episode. To celebrate, I decided to treat myself to a solo episode in which I reflect, somewhat non-systematically, on the age-old question of the meaning of life. I end up spending a lot (most?) of the time talking about the meaning of “life,” i.e. what it means to be a living organism in a naturalistic universe. But then I go on to muse about the construction of human meaning in a world where values are not imposed on us or objectively grounded in physical facts.