Luke Savage in The Walrus:
 Jordan Peterson’s marketability has always been a bit surprising given his weirdness. He speaks exclusively in a glottal cadence that sounds like Kermit the Frog after a night of heavy drinking. He calls hostile interlocutors “bucko.” He breaks down in tears when discussing children’s cartoons and has occasionally been known to dress like the Joker. But these days, the reactionary right is miserably bereft of real intellectuals, and a decade or so ago, Peterson stepped into this void and was rewarded with global success.
Jordan Peterson’s marketability has always been a bit surprising given his weirdness. He speaks exclusively in a glottal cadence that sounds like Kermit the Frog after a night of heavy drinking. He calls hostile interlocutors “bucko.” He breaks down in tears when discussing children’s cartoons and has occasionally been known to dress like the Joker. But these days, the reactionary right is miserably bereft of real intellectuals, and a decade or so ago, Peterson stepped into this void and was rewarded with global success.
That success, improbably, comes from a unique fusion of obscurantism and conservative pomposity. There’s a certain genre of left-coded writing, for example, that’s rightly derided for its convolution, even meaninglessness. Perhaps the most common hallmark of this style is the incessant bracketing of words in scare quotes, a tactic that often allows the author (or “author”) to assert ideas or concepts while remaining aloof and evasive about what it is they’re actually saying. Sometimes, there are random capitalizations as well, or particular sentences are italicized for no discernible reason. In this genre, everything—right down to the very act of writing itself—plays out in linguistic abstraction, and at a convenient remove from anything tangible or concrete.
More there.
Enjoying the content on 3QD? Help keep us going by donating now.

 Eight times a week at the Majestic Theater in Manhattan, the entire, harrowing arc of a classic tragedy is delivered in 4½ minutes that are as exhilarating as they are upsetting. All the textbook components of tragedy according to Aristotle are vigorously at work here: self-delusion and self-knowledge, pity and terror, and the sense that what is happening is somehow both unexpected and inevitable.
Eight times a week at the Majestic Theater in Manhattan, the entire, harrowing arc of a classic tragedy is delivered in 4½ minutes that are as exhilarating as they are upsetting. All the textbook components of tragedy according to Aristotle are vigorously at work here: self-delusion and self-knowledge, pity and terror, and the sense that what is happening is somehow both unexpected and inevitable.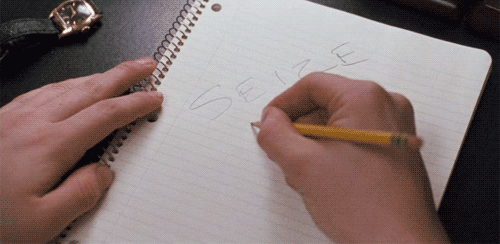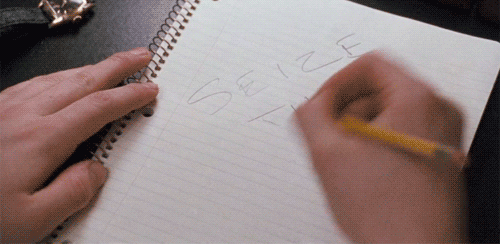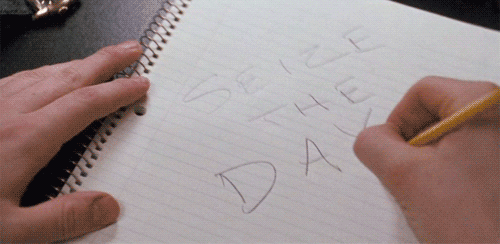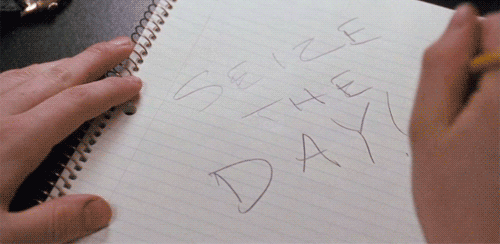 Dear Reader,
Dear Reader, I had read about the Santa Ana winds in a Joan Didion essay but had incorrectly understood them to be a mood-altering phenomenon, something with positive ions that made people feel on edge. It did not occur to me that they were a very real weather event, not just a vibe. That day, January 7, the fires had already started in the Pacific Palisades, which is more than 20 miles from Highland Park, where I live, but even so, I was not overly concerned. At my daughter’s school, they’d kept the kids inside during recess. That seemed excessive—and when my friend texted me some X account, with a crudely circled map, warning about the winds, it sounded overblown. That evening, when I walked to pick my daughter up from her class, there were gusts of wind and palm fronds littering the road. It felt spooky, but also slightly exciting. A weather event! The L.A. version of a snowstorm.
I had read about the Santa Ana winds in a Joan Didion essay but had incorrectly understood them to be a mood-altering phenomenon, something with positive ions that made people feel on edge. It did not occur to me that they were a very real weather event, not just a vibe. That day, January 7, the fires had already started in the Pacific Palisades, which is more than 20 miles from Highland Park, where I live, but even so, I was not overly concerned. At my daughter’s school, they’d kept the kids inside during recess. That seemed excessive—and when my friend texted me some X account, with a crudely circled map, warning about the winds, it sounded overblown. That evening, when I walked to pick my daughter up from her class, there were gusts of wind and palm fronds littering the road. It felt spooky, but also slightly exciting. A weather event! The L.A. version of a snowstorm. In 1994, an earthquake of a proof shook up the mathematical world. The mathematician Andrew Wiles had finally settled
In 1994, an earthquake of a proof shook up the mathematical world. The mathematician Andrew Wiles had finally settled  The “HUGEst” political alliance of the century is breaking apart before our eyes in suitably spectacular fashion.
The “HUGEst” political alliance of the century is breaking apart before our eyes in suitably spectacular fashion. Twombly (1928–2011) has been a polarizing figure. He is best known for his large scrawly works in grayscale, sometimes called “blackboard paintings,” that resemble the marks of a second grader trying to learn cursive and failing. The artist has drawn (ha!) admiration from some of the greatest writers and critics of our era, from Roland Barthes and Robert Motherwell to Octavio Paz and Anne Carson. Yet few artists have also been on the end of more ridicule. Donald Judd called an early exhibit of Twombly’s “a fiasco.” Jackson Arn
Twombly (1928–2011) has been a polarizing figure. He is best known for his large scrawly works in grayscale, sometimes called “blackboard paintings,” that resemble the marks of a second grader trying to learn cursive and failing. The artist has drawn (ha!) admiration from some of the greatest writers and critics of our era, from Roland Barthes and Robert Motherwell to Octavio Paz and Anne Carson. Yet few artists have also been on the end of more ridicule. Donald Judd called an early exhibit of Twombly’s “a fiasco.” Jackson Arn  Most of us like to see ourselves as good, morally decent individuals. What’s more, we largely agree on what it means to be a decent person. You don’t just have to pay your taxes and not harm others. You have to go beyond that by, for instance, being kind, treating others with respect, and supporting your friends, family and neighbours. What our modern secular society lacks, however, is a clear idea of how a decent person should give to charity. We live in a world of staggering inequality and extreme need. There will always be more we could do. When have we given enough – not to be a saint, but to clear the bar of decency?
Most of us like to see ourselves as good, morally decent individuals. What’s more, we largely agree on what it means to be a decent person. You don’t just have to pay your taxes and not harm others. You have to go beyond that by, for instance, being kind, treating others with respect, and supporting your friends, family and neighbours. What our modern secular society lacks, however, is a clear idea of how a decent person should give to charity. We live in a world of staggering inequality and extreme need. There will always be more we could do. When have we given enough – not to be a saint, but to clear the bar of decency? In Vienna, in late February 1895, a 30-year-old woman, Emma Eckstein, is about to undergo an operation. She has recently complained of a few health problems – mostly stomach pain and discomfort, some sadness, especially around her period. Luckily, a young Berlin doctor by the name of Wilhelm Fliess is there to help. He comes highly recommended by a long-time trusted family friend, himself a reputable physician, Sigmund Freud. They agree that Eckstein’s menstrual stomach issues can be addressed through a simple surgery on an altogether different body part – Fliess removes a bit of bone from inside her nose.
In Vienna, in late February 1895, a 30-year-old woman, Emma Eckstein, is about to undergo an operation. She has recently complained of a few health problems – mostly stomach pain and discomfort, some sadness, especially around her period. Luckily, a young Berlin doctor by the name of Wilhelm Fliess is there to help. He comes highly recommended by a long-time trusted family friend, himself a reputable physician, Sigmund Freud. They agree that Eckstein’s menstrual stomach issues can be addressed through a simple surgery on an altogether different body part – Fliess removes a bit of bone from inside her nose. What does it mean to say, “I am aware,” when that sentence might be as much a performance as a report?
What does it mean to say, “I am aware,” when that sentence might be as much a performance as a report? The world is still recovering from the COVID-19 pandemic, which many researchers say probably started, or was at least amplified, at
The world is still recovering from the COVID-19 pandemic, which many researchers say probably started, or was at least amplified, at  O
O