Zoé Samudzi at Artforum:
 In his 2019 book Monuments of Power, Tycho van der Hoog notes that midcentury North Korean public art and architectonics differ from versions in the Soviet Union and China because of the “near total destruction of Pyongyang during the Korean War,” which “meant a tabula rasa for city planners.” The image of North Korea literally constructing itself from the rubble of devastating aerial bombing campaigns by the United States undoubtedly resonated with African nationalist leaders, who were also attempting to chart a course for their infant nations. And in supporting anti-imperialist movements in Asia, Latin America, and Africa through its modeling of “proletarian internationalism,” the state hoped to gain allies in the United Nations as it attempted to end US domination both within the institution and on the Korean peninsula. The Mansudae Overseas Project was opened in 1974 as a sub-bureau of the larger studio, tasked with creating statues as gifts to African states. (Countries are presently billed for the monuments because they are a critical source of earning the state foreign currency.)
In his 2019 book Monuments of Power, Tycho van der Hoog notes that midcentury North Korean public art and architectonics differ from versions in the Soviet Union and China because of the “near total destruction of Pyongyang during the Korean War,” which “meant a tabula rasa for city planners.” The image of North Korea literally constructing itself from the rubble of devastating aerial bombing campaigns by the United States undoubtedly resonated with African nationalist leaders, who were also attempting to chart a course for their infant nations. And in supporting anti-imperialist movements in Asia, Latin America, and Africa through its modeling of “proletarian internationalism,” the state hoped to gain allies in the United Nations as it attempted to end US domination both within the institution and on the Korean peninsula. The Mansudae Overseas Project was opened in 1974 as a sub-bureau of the larger studio, tasked with creating statues as gifts to African states. (Countries are presently billed for the monuments because they are a critical source of earning the state foreign currency.)
more here.

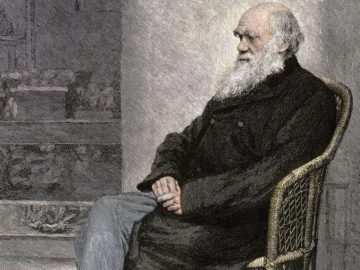 “If I have seen further,” Isaac Newton wrote to his fellow scientist Robert Hooke in 1675, “it is by standing on the shoulders of Giants.” Long seen as our greatest scientist’s greatest line, it may have been a sarcastic joke: Hooke, a rival who had claimed credit for Newton’s discoveries and whom Newton came to dislike intensely, was a short man. It was true, however, that Newton was supported by people who remained unseen. This was very much the case with his finances: Newton was an investor in the slave trade. He bought thousands of shares in the South Sea Company, the principal enterprise of which was to transport people from Africa to the Americas. Newton invested in this business for over a decade, making a significant profit (and then losing it in the crash of 1720).
“If I have seen further,” Isaac Newton wrote to his fellow scientist Robert Hooke in 1675, “it is by standing on the shoulders of Giants.” Long seen as our greatest scientist’s greatest line, it may have been a sarcastic joke: Hooke, a rival who had claimed credit for Newton’s discoveries and whom Newton came to dislike intensely, was a short man. It was true, however, that Newton was supported by people who remained unseen. This was very much the case with his finances: Newton was an investor in the slave trade. He bought thousands of shares in the South Sea Company, the principal enterprise of which was to transport people from Africa to the Americas. Newton invested in this business for over a decade, making a significant profit (and then losing it in the crash of 1720). Hypomethylating agents (HMA) are currently used as a first-line treatment for patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), and increasingly in other diseases, but their mechanism of action is not clear. HMAs may affect many genes and could potentially activate an oncogene—a gene that contributes to the development of cancer—but this has not been clearly demonstrated to date. To test this, investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Stem Cell Institute and collaborators studied how HMA affects known oncogenes. They found that HMA activated the oncofetal protein SALL4 in up to 40 percent of
Hypomethylating agents (HMA) are currently used as a first-line treatment for patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), and increasingly in other diseases, but their mechanism of action is not clear. HMAs may affect many genes and could potentially activate an oncogene—a gene that contributes to the development of cancer—but this has not been clearly demonstrated to date. To test this, investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Stem Cell Institute and collaborators studied how HMA affects known oncogenes. They found that HMA activated the oncofetal protein SALL4 in up to 40 percent of  To speak of Italo Calvino’s popularity outside of Italy is to speak of Calvino in translation, given that he has been read and loved abroad in other languages and not in Italian. For an author who floats, as Calvino himself said, “a bit in mid-air,” translation—that twofold and intermediate space—was his destiny.
To speak of Italo Calvino’s popularity outside of Italy is to speak of Calvino in translation, given that he has been read and loved abroad in other languages and not in Italian. For an author who floats, as Calvino himself said, “a bit in mid-air,” translation—that twofold and intermediate space—was his destiny. The origin of life here on Earth was an important and fascinating event, but it was also a long time ago and hasn’t left many pieces of direct evidence concerning what actually happened. One set of clues we have comes from processes in current living organisms, especially those processes that seem extremely common. The Krebs cycle, the sequence of reactions that functions as a pathway for energy distribution in aerobic organisms, is such an example. I talk with biochemist about the importance of the Krebs cycle to contemporary biology, as well as its possible significance in understanding the origin of life.
The origin of life here on Earth was an important and fascinating event, but it was also a long time ago and hasn’t left many pieces of direct evidence concerning what actually happened. One set of clues we have comes from processes in current living organisms, especially those processes that seem extremely common. The Krebs cycle, the sequence of reactions that functions as a pathway for energy distribution in aerobic organisms, is such an example. I talk with biochemist about the importance of the Krebs cycle to contemporary biology, as well as its possible significance in understanding the origin of life. Great civilizations can wither—even when built on the material and human foundations of a potential superpower. Today the civilizations of India, China, the West, and Islam are all in jeopardy. But what has happened to Russia, the world’s largest state and fulcrum of Eurasia? Tsarist Russia, for all that was cruel and backward about it, had redeeming features. It gave rise to some of the greatest music, dance, and literature in human history—a flowering that struggled for air in Soviet times but has nearly stopped breathing under Vladimir Putin’s petrostate.
Great civilizations can wither—even when built on the material and human foundations of a potential superpower. Today the civilizations of India, China, the West, and Islam are all in jeopardy. But what has happened to Russia, the world’s largest state and fulcrum of Eurasia? Tsarist Russia, for all that was cruel and backward about it, had redeeming features. It gave rise to some of the greatest music, dance, and literature in human history—a flowering that struggled for air in Soviet times but has nearly stopped breathing under Vladimir Putin’s petrostate. CHRIS KRAUS DID NOT LOVE KATHY ACKER, did not even “like” her, though love and like are mean props in the perpetual war of letters. Kraus did think that this woman, who had slept with her (eventually ex-) husband (Sylvère Lotringer), was “kind of frightening and awesome.” Lotringer of course founded Semiotext(e), the publishing house that Kraus still helms with him and Hedi El Kholti, which also published Acker’s e-mails to Wark cited above and Kraus’s debut novel (I Love Dick,1997) as well as her most recent book (After Kathy Acker, 2017). “To Sylvère, The Best Fuck In The World (At Least To My Knowledge) Love, Kathy Acker,” reads an inscription in a book Kraus finds in Sylvère’s library in I Love Dick. “Pretty stiff competition,” Kraus says. Although Kraus was present for Acker’s life, even inspired by her work, she is not what you would call a “partisan,” and because of this she has written the smartest, cruelest, most intimately clinical, which is to say the best, biography of Acker one could hope for.
CHRIS KRAUS DID NOT LOVE KATHY ACKER, did not even “like” her, though love and like are mean props in the perpetual war of letters. Kraus did think that this woman, who had slept with her (eventually ex-) husband (Sylvère Lotringer), was “kind of frightening and awesome.” Lotringer of course founded Semiotext(e), the publishing house that Kraus still helms with him and Hedi El Kholti, which also published Acker’s e-mails to Wark cited above and Kraus’s debut novel (I Love Dick,1997) as well as her most recent book (After Kathy Acker, 2017). “To Sylvère, The Best Fuck In The World (At Least To My Knowledge) Love, Kathy Acker,” reads an inscription in a book Kraus finds in Sylvère’s library in I Love Dick. “Pretty stiff competition,” Kraus says. Although Kraus was present for Acker’s life, even inspired by her work, she is not what you would call a “partisan,” and because of this she has written the smartest, cruelest, most intimately clinical, which is to say the best, biography of Acker one could hope for. The record is an unusual proposition: A rare fusion of pow wow—an Indigenous culture of music and dance—and experimental electronic production that pairs Rainey’s singing with Broder’s synths and wildly abstract beats. Holding it all together are sampled live recordings of pow wow singing and drumming stretching back decades, many of them made by Rainey himself.
The record is an unusual proposition: A rare fusion of pow wow—an Indigenous culture of music and dance—and experimental electronic production that pairs Rainey’s singing with Broder’s synths and wildly abstract beats. Holding it all together are sampled live recordings of pow wow singing and drumming stretching back decades, many of them made by Rainey himself.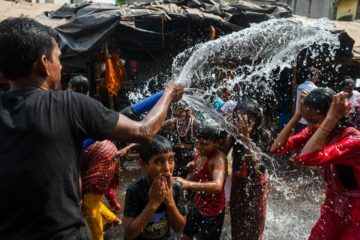 Human-induced climate change made the deadly heatwave that gripped India and Pakistan in March and April 30 times more likely, according to a
Human-induced climate change made the deadly heatwave that gripped India and Pakistan in March and April 30 times more likely, according to a  Mallory McMorrow
Mallory McMorrow Pity literary biographers. There are few writers less appreciated, there are none more despised. There they sit, with their church bulletins of family trees and their dental records, their interviews with ex-lovers, mad uncles, and discarded children, and go about “reconstructing” the life of someone they never knew, or knew just barely. To George Eliot, biographers were a “disease of English literature,” while Auden thought all literary biographies “superfluous and usually in bad taste.” Even Ian Hamilton, the intrepid chronicler of Robert Lowell, J. D. Salinger, and Matthew Arnold, thought that there was “some necessary element of sleaze” to the whole enterprise.
Pity literary biographers. There are few writers less appreciated, there are none more despised. There they sit, with their church bulletins of family trees and their dental records, their interviews with ex-lovers, mad uncles, and discarded children, and go about “reconstructing” the life of someone they never knew, or knew just barely. To George Eliot, biographers were a “disease of English literature,” while Auden thought all literary biographies “superfluous and usually in bad taste.” Even Ian Hamilton, the intrepid chronicler of Robert Lowell, J. D. Salinger, and Matthew Arnold, thought that there was “some necessary element of sleaze” to the whole enterprise. Both countries are English-speaking democracies with similar demographic profiles. In Australia and in the United States, the
Both countries are English-speaking democracies with similar demographic profiles. In Australia and in the United States, the  In 2005, Britain’s then–Labour chancellor of the exchequer, Gordon Brown, chose the backdrop of Tanzania to make a dramatic statement about his nation’s unmatched record of imperial conquest and rule. “The time is long gone,” he said, “when Britain needs to apologize for its colonial history.” The choice of locale for such a proclamation was, to be charitable, curious. A braver stage would have been Kenya, to pick an African nation that had experienced horrific violence during its independence struggle from British colonial rule, or India or Malaya, where extreme and brutal measures to sustain imperial control had been carried out on an even greater scale. But here we were, nonetheless.
In 2005, Britain’s then–Labour chancellor of the exchequer, Gordon Brown, chose the backdrop of Tanzania to make a dramatic statement about his nation’s unmatched record of imperial conquest and rule. “The time is long gone,” he said, “when Britain needs to apologize for its colonial history.” The choice of locale for such a proclamation was, to be charitable, curious. A braver stage would have been Kenya, to pick an African nation that had experienced horrific violence during its independence struggle from British colonial rule, or India or Malaya, where extreme and brutal measures to sustain imperial control had been carried out on an even greater scale. But here we were, nonetheless. Apparently Anna Wintour wants to be seen as human, and Amy Odell’s biography goes some way to helping her achieve that aim. Nearly all the photographs show her smiling, looking friendly, even girlish. And the text quite often mentions her crying. On 9 November 2016 she cried in front of her entire staff because Hillary Clinton lost the election. But then she immediately set about trying to persuade Melania Trump to do a Vogue shoot. Melania, another tough cookie, refused unless she was guaranteed the cover.
Apparently Anna Wintour wants to be seen as human, and Amy Odell’s biography goes some way to helping her achieve that aim. Nearly all the photographs show her smiling, looking friendly, even girlish. And the text quite often mentions her crying. On 9 November 2016 she cried in front of her entire staff because Hillary Clinton lost the election. But then she immediately set about trying to persuade Melania Trump to do a Vogue shoot. Melania, another tough cookie, refused unless she was guaranteed the cover.