Could Have
It could have happened.
It had to happen.
It happened earlier. Later.
Nearer. Farther off.
It happened, but not to you.
You were saved because you were the first.
You were saved because you were the last.
Alone. With others.
On the right. The left.
Because it was raining. Because of the shade.
Because the day was sunny.
You were in luck—there was a forest.
You were in luck—there were no trees
You were in luck—a rake, a hook, a beam, a brake,
a jamb, a turn, a quarter inch, an instant.
You were in luck—just then a straw went floating by.
As a result, because, although , despite.
What would have happened if a hand, a foot,
within an inch, a hairsbreadth from
an unfortunate coincidence.
So you’re here? Still dizzy from another dodge, close shave,
…. reprieve?
One hole in the net and you slipped through?
I couldn’t be more shocked or speechless.
Listen,
how your heart pounds inside me.
By Wistlawa Szymborska
from Poems new and Collected
Harvest Books, 1998
Enjoying the content on 3QD? Help keep us going by donating now.

 Parent less, play more.
Parent less, play more. People who experience kidney failure need either lifelong dialysis or a transplant to survive. Yet even for those lucky enough to get a transplant, that is by no means the end of the story. Kidneys from deceased donors last an average of 10 to 15 years, those from a living person 20 to 25. If (or rather, when) a transplant fails, the affected patient once again needs dialysis or a donated organ.
People who experience kidney failure need either lifelong dialysis or a transplant to survive. Yet even for those lucky enough to get a transplant, that is by no means the end of the story. Kidneys from deceased donors last an average of 10 to 15 years, those from a living person 20 to 25. If (or rather, when) a transplant fails, the affected patient once again needs dialysis or a donated organ. There is a scene in the movie version of Carl Sagan’s book Contact where the main character, an astronomer who has detected the first radio signal from an alien civilization, is being considered for the role of humanity’s representative to meet the aliens. The international panel interviewing her asks, “If you could ask [the aliens] just one question, what would it be?” Her reply is: “I’d ask them, ‘How did you do it? How did you evolve, how did you survive this technological adolescence without destroying yourself?” When I think about where humanity is now with AI—about what we’re on the cusp of—my mind keeps going back to that scene, because the question is so apt for our current situation, and I wish we had the aliens’ answer to guide us. I believe we are entering a rite of passage, both turbulent and inevitable, which will test who we are as a species. Humanity is about to be handed almost unimaginable power, and it is deeply unclear whether our social, political, and technological systems possess the maturity to wield it.
There is a scene in the movie version of Carl Sagan’s book Contact where the main character, an astronomer who has detected the first radio signal from an alien civilization, is being considered for the role of humanity’s representative to meet the aliens. The international panel interviewing her asks, “If you could ask [the aliens] just one question, what would it be?” Her reply is: “I’d ask them, ‘How did you do it? How did you evolve, how did you survive this technological adolescence without destroying yourself?” When I think about where humanity is now with AI—about what we’re on the cusp of—my mind keeps going back to that scene, because the question is so apt for our current situation, and I wish we had the aliens’ answer to guide us. I believe we are entering a rite of passage, both turbulent and inevitable, which will test who we are as a species. Humanity is about to be handed almost unimaginable power, and it is deeply unclear whether our social, political, and technological systems possess the maturity to wield it. The structure of Otrar is certainly all of a piece with German’s own work. But as a total film experience, it feels distinctly different from Khrustalyov, Ivan Lapshin, or German’s posthumously completed Hard to Be a God (2013, a years-in-the-making adaptation cowritten by German and Karmalita, traces of which can be felt in Otrar). “They were two of the most renowned filmmakers of Soviet cinema,” said Amirkulov in conversation with production designer Umirzak Shmanov. “We were, of course, very lucky to have them as the screenwriters. The script was extensive, extremely cumbersome, and completely uncompromising in the sense that they never settled for bypassing historical facts or circumstances, and they never came up with any easy solutions. On the one hand, it was very difficult to film. On the other hand, it was incredibly energizing because the script itself read like good literature. That’s why I’m grateful to fate for bringing me together with people like Alexei and Svetlana. I learned a great deal from their script because I had to put in a lot of effort, thought, and research to bring it to life. I even studied music, painting, read a lot of literature about the period, and watched films to match the material they had written.”
The structure of Otrar is certainly all of a piece with German’s own work. But as a total film experience, it feels distinctly different from Khrustalyov, Ivan Lapshin, or German’s posthumously completed Hard to Be a God (2013, a years-in-the-making adaptation cowritten by German and Karmalita, traces of which can be felt in Otrar). “They were two of the most renowned filmmakers of Soviet cinema,” said Amirkulov in conversation with production designer Umirzak Shmanov. “We were, of course, very lucky to have them as the screenwriters. The script was extensive, extremely cumbersome, and completely uncompromising in the sense that they never settled for bypassing historical facts or circumstances, and they never came up with any easy solutions. On the one hand, it was very difficult to film. On the other hand, it was incredibly energizing because the script itself read like good literature. That’s why I’m grateful to fate for bringing me together with people like Alexei and Svetlana. I learned a great deal from their script because I had to put in a lot of effort, thought, and research to bring it to life. I even studied music, painting, read a lot of literature about the period, and watched films to match the material they had written.” The U.S. should follow Canada’s lead on EV tariffs, slashing them to a very low level while initially limiting the number of annual imports. While Canada’s deal involved only vague promises of Chinese investment in the Canadian auto industry, the U.S. should require far more firm commitments, along with strong incentives for local sourcing of components like batteries and motors. And the dangers of espionage and sabotage can probably be minimized through additional measures.
The U.S. should follow Canada’s lead on EV tariffs, slashing them to a very low level while initially limiting the number of annual imports. While Canada’s deal involved only vague promises of Chinese investment in the Canadian auto industry, the U.S. should require far more firm commitments, along with strong incentives for local sourcing of components like batteries and motors. And the dangers of espionage and sabotage can probably be minimized through additional measures. Two years ago, I wrote about
Two years ago, I wrote about  Which animals came first? For more than a century, most evidence suggested that sponges, immobile filter-feeders that lack muscles, neurons and other specialized tissues, were the first animal lineages to emerge. Then, in 2008, a genomic study pointed to a head-scratching rival
Which animals came first? For more than a century, most evidence suggested that sponges, immobile filter-feeders that lack muscles, neurons and other specialized tissues, were the first animal lineages to emerge. Then, in 2008, a genomic study pointed to a head-scratching rival ‘H
‘H By the mid-1960s, Charles Bukowski had become a sort of king of the underground, the most published poet in the “littles,” as the magazines, alternative newspapers, and small presses that proliferated in the 1960s were known. John Martin read Bukowski’s poems in obscure, poorly printed zines and bought his thin, saddle-stapled chapbooks released in press runs of perhaps a couple hundred copies. Martin
By the mid-1960s, Charles Bukowski had become a sort of king of the underground, the most published poet in the “littles,” as the magazines, alternative newspapers, and small presses that proliferated in the 1960s were known. John Martin read Bukowski’s poems in obscure, poorly printed zines and bought his thin, saddle-stapled chapbooks released in press runs of perhaps a couple hundred copies. Martin  Through quantitative analysis and mechanistic interpretability methods applied to reasoning traces, we find that reasoning models like DeepSeek-R1 and QwQ-32B exhibit much greater perspective diversity than instruction-tuned models, activating broader conflict between heterogeneous personality- and expertise-related features during reasoning. This multi-agent structure manifests in conversational behaviors, including question-answering, perspective shifts, and the reconciliation of conflicting views, and in socio-emotional roles that characterize sharp back-and-forth conversations, together accounting for the accuracy advantage in reasoning tasks. Controlled reinforcement learning experiments reveal that base models increase conversational behaviors when rewarded solely for reasoning accuracy, and fine-tuning models with conversational scaffolding accelerates reasoning improvement over base models. These findings indicate that the social organization of thought enables effective exploration of solution spaces. We suggest that reasoning models establish a computational parallel to collective intelligence in human groups, where diversity enables superior problem-solving when systematically structured, which suggests new opportunities for agent organization to harness the wisdom of crowds.
Through quantitative analysis and mechanistic interpretability methods applied to reasoning traces, we find that reasoning models like DeepSeek-R1 and QwQ-32B exhibit much greater perspective diversity than instruction-tuned models, activating broader conflict between heterogeneous personality- and expertise-related features during reasoning. This multi-agent structure manifests in conversational behaviors, including question-answering, perspective shifts, and the reconciliation of conflicting views, and in socio-emotional roles that characterize sharp back-and-forth conversations, together accounting for the accuracy advantage in reasoning tasks. Controlled reinforcement learning experiments reveal that base models increase conversational behaviors when rewarded solely for reasoning accuracy, and fine-tuning models with conversational scaffolding accelerates reasoning improvement over base models. These findings indicate that the social organization of thought enables effective exploration of solution spaces. We suggest that reasoning models establish a computational parallel to collective intelligence in human groups, where diversity enables superior problem-solving when systematically structured, which suggests new opportunities for agent organization to harness the wisdom of crowds. When the United States summarily defected from the world order it had built since the end of World War II, effectively joining the revisionist powers of China and Russia, it was clear we were headed back to the kind of Great Power spheres of influence that characterized the 19th century. What was less clear was how all those left out of this equation would fare going forward.
When the United States summarily defected from the world order it had built since the end of World War II, effectively joining the revisionist powers of China and Russia, it was clear we were headed back to the kind of Great Power spheres of influence that characterized the 19th century. What was less clear was how all those left out of this equation would fare going forward.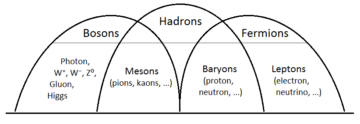 Everything around you – from tables and trees to distant stars and the great diversity of animal and plant life – is built from a small set of elementary particles. According to established scientific theories, these particles fall into two basic and deeply distinct categories: bosons and fermions.
Everything around you – from tables and trees to distant stars and the great diversity of animal and plant life – is built from a small set of elementary particles. According to established scientific theories, these particles fall into two basic and deeply distinct categories: bosons and fermions. Few things in life cause us more suffering than the confusions of love, all the wrong destinations at which we arrive by following a broken compass, having mistaken myriad things for love: admiration, desire, intellectual affinity, common ground.
Few things in life cause us more suffering than the confusions of love, all the wrong destinations at which we arrive by following a broken compass, having mistaken myriad things for love: admiration, desire, intellectual affinity, common ground.