Anil Ananthaswamy in Quanta:
 A theory developed by Sanjeev Arora of Princeton University and Anirudh Goyal, a research scientist at Google DeepMind, suggests that the largest of today’s LLMs are not stochastic parrots. The authors argue that as these models get bigger and are trained on more data, they improve on individual language-related abilities and also develop new ones by combining skills in a manner that hints at understanding — combinations that were unlikely to exist in the training data.
A theory developed by Sanjeev Arora of Princeton University and Anirudh Goyal, a research scientist at Google DeepMind, suggests that the largest of today’s LLMs are not stochastic parrots. The authors argue that as these models get bigger and are trained on more data, they improve on individual language-related abilities and also develop new ones by combining skills in a manner that hints at understanding — combinations that were unlikely to exist in the training data.
This theoretical approach, which provides a mathematically provable argument for how and why an LLM can develop so many abilities, has convinced experts like Hinton, and others. And when Arora and his team tested some of its predictions, they found that these models behaved almost exactly as expected. From all accounts, they’ve made a strong case that the largest LLMs are not just parroting what they’ve seen before.
More here.

 One unfortunate feature of American politics is that both Republicans and Democrats tend to work themselves into a frenzy over the other party’s presidential candidate, no matter who it is. To put it bluntly, both sides cry wolf all the time. Yes, I am a Democrat, but Democrats do this too — I’m old enough to remember when people I knew went crazy over poor old Mitt Romney saying that he had “
One unfortunate feature of American politics is that both Republicans and Democrats tend to work themselves into a frenzy over the other party’s presidential candidate, no matter who it is. To put it bluntly, both sides cry wolf all the time. Yes, I am a Democrat, but Democrats do this too — I’m old enough to remember when people I knew went crazy over poor old Mitt Romney saying that he had “ Greetings, gentle readers! Welcome to the very first installment of Am I the (Literary) Assh*le, a series where I get drunk and answer your burning (anonymous) questions about all things literary.
Greetings, gentle readers! Welcome to the very first installment of Am I the (Literary) Assh*le, a series where I get drunk and answer your burning (anonymous) questions about all things literary. On Monday, tens of millions across
On Monday, tens of millions across  There’s a scene in that modern classic of screwball existentialism,
There’s a scene in that modern classic of screwball existentialism,  DURING A HISTORY
DURING A HISTORY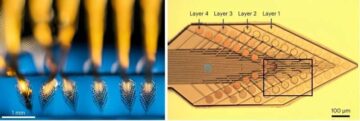 Recording the activity of large populations of single neurons in the brain over long periods of time is crucial to further our understanding of neural circuits, to enable novel medical device-based therapies and, in the future, for brain–computer interfaces requiring high-resolution electrophysiological information. But today there is a tradeoff between how much high-resolution information an implanted device can measure and how long it can maintain recording or stimulation performances. Rigid, silicon implants with many sensors, can collect a lot of information but can’t stay in the body for very long. Flexible, smaller devices are less intrusive and can last longer in the brain but only provide a fraction of the available neural information.
Recording the activity of large populations of single neurons in the brain over long periods of time is crucial to further our understanding of neural circuits, to enable novel medical device-based therapies and, in the future, for brain–computer interfaces requiring high-resolution electrophysiological information. But today there is a tradeoff between how much high-resolution information an implanted device can measure and how long it can maintain recording or stimulation performances. Rigid, silicon implants with many sensors, can collect a lot of information but can’t stay in the body for very long. Flexible, smaller devices are less intrusive and can last longer in the brain but only provide a fraction of the available neural information. For anyone who has seen or heard Watts at his best – courtesy, perhaps, of his podcast talks – ‘immeasurably alive’ is quite a good description of the man himself. It is easy to see how a basic understanding of God in these terms might have resonated with him. Watts also had moments when the sheer wonder of life around him made it feel as though it was not merely ‘there’, as brute fact, but was being poured out with extraordinary generosity. It seemed ‘given’, convincing Watts that there must be a giver and filling him with the desire to say ‘thank you’. He found backing for all of this in the writings of the 14th-century German theologian Meister Eckhart and the 6th-century Greek author Pseudo-Dionysius the Areopagite. It was there, too, in the ‘I-Thou’ thought of the modern Jewish philosopher
For anyone who has seen or heard Watts at his best – courtesy, perhaps, of his podcast talks – ‘immeasurably alive’ is quite a good description of the man himself. It is easy to see how a basic understanding of God in these terms might have resonated with him. Watts also had moments when the sheer wonder of life around him made it feel as though it was not merely ‘there’, as brute fact, but was being poured out with extraordinary generosity. It seemed ‘given’, convincing Watts that there must be a giver and filling him with the desire to say ‘thank you’. He found backing for all of this in the writings of the 14th-century German theologian Meister Eckhart and the 6th-century Greek author Pseudo-Dionysius the Areopagite. It was there, too, in the ‘I-Thou’ thought of the modern Jewish philosopher