Meara Sharma at Artforum:
 To encounter the work of Japanese photographer Daido Moriyama is to see the world not through his eyes but through his whole being. His angles are dizzyingly extreme, as if shot from the perspective of his knees, his toes, the back of his head. His subjects are blurred and warped, conjuring a sense of frenetic movement through space. His images—mostly black-and-white—are intensely high contrast, evocative of the sun’s unforgiving glare or the heightened realm of dreams. Rather than proposing an artfully constructed vision of the world, his photographs (whether of television screens or thronging beaches or fishnet-sheathed legs or discarded dolls) attempt to embody the fragmented experience of existence: its chaos, its precariousness, its fundamental inscrutability.
To encounter the work of Japanese photographer Daido Moriyama is to see the world not through his eyes but through his whole being. His angles are dizzyingly extreme, as if shot from the perspective of his knees, his toes, the back of his head. His subjects are blurred and warped, conjuring a sense of frenetic movement through space. His images—mostly black-and-white—are intensely high contrast, evocative of the sun’s unforgiving glare or the heightened realm of dreams. Rather than proposing an artfully constructed vision of the world, his photographs (whether of television screens or thronging beaches or fishnet-sheathed legs or discarded dolls) attempt to embody the fragmented experience of existence: its chaos, its precariousness, its fundamental inscrutability.
Moriyama’s signature style—known as are, bure, boke, which translates as “grainy, blurry, out of focus”—stems from a lifelong suspicion of photography’s capacity to capture reality, evident in the eighty-five-year-old artist’s potent retrospective at the Photographers’ Gallery.
more here.

 In the summer of 1933, Mark Rothko, who was then still known as Markus Rothkowitz, hitchhiked nearly three thousand miles from New York City to his hometown of Portland, Oregon. He had done this several times in recent years, having moved east in 1921 to attend Yale University before withdrawing and settling in New York in 1923.
In the summer of 1933, Mark Rothko, who was then still known as Markus Rothkowitz, hitchhiked nearly three thousand miles from New York City to his hometown of Portland, Oregon. He had done this several times in recent years, having moved east in 1921 to attend Yale University before withdrawing and settling in New York in 1923. Google cofounder Larry Page
Google cofounder Larry Page  Obviously, there already were differences between the lower and upper middle class in 1994—otherwise you couldn’t separate the two groups. But existing differences grew by a lot between 1994 and 2018. For the upper middle class, things generally got better in that timeframe: their wealth, health, and life expectancy improved. For the lower middle class, however,
Obviously, there already were differences between the lower and upper middle class in 1994—otherwise you couldn’t separate the two groups. But existing differences grew by a lot between 1994 and 2018. For the upper middle class, things generally got better in that timeframe: their wealth, health, and life expectancy improved. For the lower middle class, however, The blood cancer had returned, and Kevin Sander was running out of treatment options. A stem-cell transplant would offer the best chance for long-term survival, but to qualify for the procedure he would first need to reduce the extent of his tumour — a seemingly insurmountable goal, because successive treatments had all failed to keep the disease in check. As a last throw of the dice, he joined a landmark clinical trial. Led by haematologist Philipp Staber at the Medical University of Vienna, the study is exploring an innovative treatment strategy in which drugs are tested on the patient’s own cancer cells, cultured outside the body. In February 2022, researchers tried 130 compounds on cells grown from Sander’s cancer — essentially trying everything at their disposal to see what might work.
The blood cancer had returned, and Kevin Sander was running out of treatment options. A stem-cell transplant would offer the best chance for long-term survival, but to qualify for the procedure he would first need to reduce the extent of his tumour — a seemingly insurmountable goal, because successive treatments had all failed to keep the disease in check. As a last throw of the dice, he joined a landmark clinical trial. Led by haematologist Philipp Staber at the Medical University of Vienna, the study is exploring an innovative treatment strategy in which drugs are tested on the patient’s own cancer cells, cultured outside the body. In February 2022, researchers tried 130 compounds on cells grown from Sander’s cancer — essentially trying everything at their disposal to see what might work. If a cow said, ‘Don’t eat me’, we wouldn’t. We seem to regard the capacity for language (by which we mean our kind of language) as evidence of moral significance. But do animals talk? Many traditions assume they do, and understanding animal talk has sometimes been thought to indicate great human wisdom. The proverbially wise Solomon understood the language of the birds, and St Francis preached to them. Most of us have asked what a crow’s squawk or a dog’s whine means. Perhaps we ask because we feel that animals can tell us something we don’t know about the sort of place this world is.
If a cow said, ‘Don’t eat me’, we wouldn’t. We seem to regard the capacity for language (by which we mean our kind of language) as evidence of moral significance. But do animals talk? Many traditions assume they do, and understanding animal talk has sometimes been thought to indicate great human wisdom. The proverbially wise Solomon understood the language of the birds, and St Francis preached to them. Most of us have asked what a crow’s squawk or a dog’s whine means. Perhaps we ask because we feel that animals can tell us something we don’t know about the sort of place this world is.
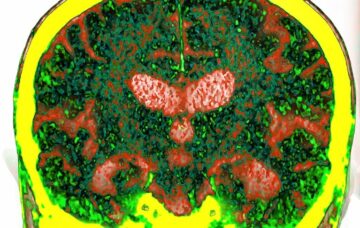 An analysis of around 1,500 blood proteins has identified biomarkers that can be used to predict the risk of developing dementia up to 15 years before diagnosis.
An analysis of around 1,500 blood proteins has identified biomarkers that can be used to predict the risk of developing dementia up to 15 years before diagnosis. When Tina Turner, years before she became rock ‘n’ roll royalty, lent her iconic voice to Phil Spector’s “River Deep, Mountain High” in 1966, the single ranked at No. 3 on the UK charts. But, on U.S. Billboard charts that same year, it didn’t get higher than 88. In the recent HBO documentary “Tina,” an archival clip of Ike Turner, who shares a credit for the song, explained that the song didn’t hold up in America because, during that time, “Black artists had to go Top 10 on the R&B charts before the top radio stations would touch it.” In the film, Ike added that the adventurous song, with its complex orchestration and lush, pop sound, was “too white for Black jockeys and too Black for white jockeys” in the U.S. Dan Lindsay, one of the co-directors of the documentary,
When Tina Turner, years before she became rock ‘n’ roll royalty, lent her iconic voice to Phil Spector’s “River Deep, Mountain High” in 1966, the single ranked at No. 3 on the UK charts. But, on U.S. Billboard charts that same year, it didn’t get higher than 88. In the recent HBO documentary “Tina,” an archival clip of Ike Turner, who shares a credit for the song, explained that the song didn’t hold up in America because, during that time, “Black artists had to go Top 10 on the R&B charts before the top radio stations would touch it.” In the film, Ike added that the adventurous song, with its complex orchestration and lush, pop sound, was “too white for Black jockeys and too Black for white jockeys” in the U.S. Dan Lindsay, one of the co-directors of the documentary,  SOMETIMES I STILL CAN’T BELIEVE
SOMETIMES I STILL CAN’T BELIEVE When Hannah Arendt looked at the man wearing an ill-fitting suit in the bulletproof dock inside a Jerusalem courtroom in 1961, she saw something different from everybody else. The prosecution, writes Lyndsey Stonebridge, ‘saw an ancient crime in modern garb, and portrayed Eichmann as the latest monster in the long history of anti-Semitism who had simply used novel methods to take hatred for Jews to a new level’. Arendt thought otherwise.
When Hannah Arendt looked at the man wearing an ill-fitting suit in the bulletproof dock inside a Jerusalem courtroom in 1961, she saw something different from everybody else. The prosecution, writes Lyndsey Stonebridge, ‘saw an ancient crime in modern garb, and portrayed Eichmann as the latest monster in the long history of anti-Semitism who had simply used novel methods to take hatred for Jews to a new level’. Arendt thought otherwise. In this second foray into the biology of death, I will examine programmed cell death or PCD. You might have heard of the process of apoptosis, but, as the previously reviewed
In this second foray into the biology of death, I will examine programmed cell death or PCD. You might have heard of the process of apoptosis, but, as the previously reviewed