McKenzie Prillaman in Nature:
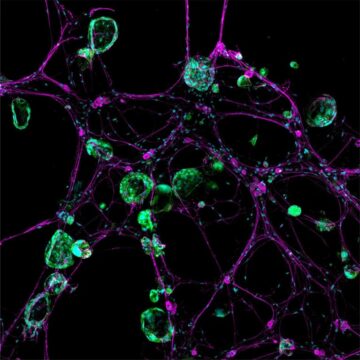 Lightning bolts of lime green flashed chaotically across the computer screen, a sight that stunned cancer neuroscientist Humsa Venkatesh. It was late 2017, and she was watching a storm of electrical activity in cells from a human brain tumour called a glioma. Venkatesh was expecting a little background chatter between the cancerous brain cells, just as there is between healthy ones. But the conversations were continuous, and rapid-fire. “I could see these tumour cells just lighting up,” says Venkatesh, who was then a postdoctoral researcher at Stanford University School of Medicine in Stanford, California. “They were so clearly electrically active.”
Lightning bolts of lime green flashed chaotically across the computer screen, a sight that stunned cancer neuroscientist Humsa Venkatesh. It was late 2017, and she was watching a storm of electrical activity in cells from a human brain tumour called a glioma. Venkatesh was expecting a little background chatter between the cancerous brain cells, just as there is between healthy ones. But the conversations were continuous, and rapid-fire. “I could see these tumour cells just lighting up,” says Venkatesh, who was then a postdoctoral researcher at Stanford University School of Medicine in Stanford, California. “They were so clearly electrically active.”
She immediately began to think about the implications. Scientists just hadn’t considered that cancer cells — even those in the brain — could communicate with each other to this extent. Perhaps the tumour’s constant electrical communication was helping it to survive, or even to grow. “This is cancer that we’re working on — not neurons, not any other cell type.” To see the cells fizz with so much activity was “truly mind blowing,” says Venkatesh, who is now at Harvard Medical School in Boston, Massachusetts. Venkatesh’s work formed part of a 2019 paper in Nature1, which was published alongside another article2 that came to the same conclusion: gliomas are electrically active. The tumours can even wire themselves into neural circuits and receive stimulation directly from neurons, which helps them to grow.
More here.

 As we embark on
As we embark on  Last week, a
Last week, a Neuralink was founded in 2016 by
Neuralink was founded in 2016 by 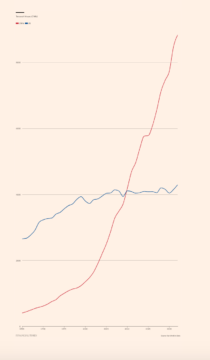 As data from the IEA confirm, the scale of China’s green energy push in the last couple of years dwarfs the much ballyhooed green energy programs in the West – NextGenEU, IRA etc.
As data from the IEA confirm, the scale of China’s green energy push in the last couple of years dwarfs the much ballyhooed green energy programs in the West – NextGenEU, IRA etc. There was a brief period in the later part of the Covid-19 pandemic, between the moment when Glenn Youngkin swept into the Virginia governorship and the full political return of Donald Trump, when I became convinced that American liberalism was headed for a truly epochal defeat in 2024.
There was a brief period in the later part of the Covid-19 pandemic, between the moment when Glenn Youngkin swept into the Virginia governorship and the full political return of Donald Trump, when I became convinced that American liberalism was headed for a truly epochal defeat in 2024. M
M I
I Back in 2001, immunologist Pere Santamaria was exploring a new way to study diabetes. Working in mice, he and his collaborators developed a method that uses iron oxide nanoparticles to track the key immune cells involved in the disorder.
Back in 2001, immunologist Pere Santamaria was exploring a new way to study diabetes. Working in mice, he and his collaborators developed a method that uses iron oxide nanoparticles to track the key immune cells involved in the disorder. We hypothesize that fictional stories are highly successful in human cultures partly because they activate evolved cognitive mechanisms, for instance for finding mates (e.g., in romance fiction), exploring the world (e.g., in adventure and speculative fiction), or avoiding predators (e.g., in horror fiction). In this paper, we put forward a comprehensive framework to study fiction through this evolutionary lens.The primary goal of this framework is to carve fictional stories at their cognitive joints using an evolutionary framework. Reviewing a wide range of adaptive variations in human psychology–in personality and developmental psychology, behavioral ecology, and evolutionary biology, among other disciplines –, this framework also addresses the question of interindividual differences in preferences for different features in fictional stories. It generates a wide range of predictions about the patterns of combinations of such features, according to the patterns of variations in the mechanisms triggered by fictional stories. As a result of a highly collaborative effort, we present a comprehensive review of evolved cognitive mechanisms that fictional stories activate.To generate this review, we (1) listed more than 70 adaptive challenges humans faced in the course of their evolution, (2) identified the adaptive psychological mechanisms that evolved in response to such challenges, (3) specified four sources of adaptive variability for the sensitivity of each mechanism(i.e., personality traits, sex, age, and ecological conditions), and (4) linked these mechanisms to the story features that trigger them. This comprehensive framework lays the ground for a theory-driven research program for the study of fictional stories, their content, distribution, structure, and cultural evolution.
We hypothesize that fictional stories are highly successful in human cultures partly because they activate evolved cognitive mechanisms, for instance for finding mates (e.g., in romance fiction), exploring the world (e.g., in adventure and speculative fiction), or avoiding predators (e.g., in horror fiction). In this paper, we put forward a comprehensive framework to study fiction through this evolutionary lens.The primary goal of this framework is to carve fictional stories at their cognitive joints using an evolutionary framework. Reviewing a wide range of adaptive variations in human psychology–in personality and developmental psychology, behavioral ecology, and evolutionary biology, among other disciplines –, this framework also addresses the question of interindividual differences in preferences for different features in fictional stories. It generates a wide range of predictions about the patterns of combinations of such features, according to the patterns of variations in the mechanisms triggered by fictional stories. As a result of a highly collaborative effort, we present a comprehensive review of evolved cognitive mechanisms that fictional stories activate.To generate this review, we (1) listed more than 70 adaptive challenges humans faced in the course of their evolution, (2) identified the adaptive psychological mechanisms that evolved in response to such challenges, (3) specified four sources of adaptive variability for the sensitivity of each mechanism(i.e., personality traits, sex, age, and ecological conditions), and (4) linked these mechanisms to the story features that trigger them. This comprehensive framework lays the ground for a theory-driven research program for the study of fictional stories, their content, distribution, structure, and cultural evolution. Some of the largest and most notable prediction markets to date have been around elections. The only problem? Prediction markets simply aren’t very good at political predictions. Markets for major U.S. elections are some of the deepest prediction markets anywhere: billions of dollars bet, millions of daily trades, and huge amounts of press. In theory, the larger the market, the more accurate the predictions. But in the markets with the biggest spotlight, we see a lot of strange stuff. Predictions that don’t line up with common sense. Odds that seem to defy reality. Obviously noncredible market movements. To figure out why, we’ll have to explore the underlying mechanisms that make markets work, and why the typical user of political prediction markets may not behave in the ways we expect.
Some of the largest and most notable prediction markets to date have been around elections. The only problem? Prediction markets simply aren’t very good at political predictions. Markets for major U.S. elections are some of the deepest prediction markets anywhere: billions of dollars bet, millions of daily trades, and huge amounts of press. In theory, the larger the market, the more accurate the predictions. But in the markets with the biggest spotlight, we see a lot of strange stuff. Predictions that don’t line up with common sense. Odds that seem to defy reality. Obviously noncredible market movements. To figure out why, we’ll have to explore the underlying mechanisms that make markets work, and why the typical user of political prediction markets may not behave in the ways we expect. Coming upon an Andre as you turn a corner in a gallery can be a lovely surprise. But for all the smaller controversies it has generated, it has become almost impossible to look down at Andre’s bricks, to tread his floors of metal plates, or gaze at his constructions of cut ash and cedar timbers, without thinking of the death of the
Coming upon an Andre as you turn a corner in a gallery can be a lovely surprise. But for all the smaller controversies it has generated, it has become almost impossible to look down at Andre’s bricks, to tread his floors of metal plates, or gaze at his constructions of cut ash and cedar timbers, without thinking of the death of the  The biggest recent find in classical music was the discovery that in 1940, Sergei Rachmaninoff was privately recorded by the conductor Eugene Ormandy. Seated at Ormandy’s piano, he played through his new Symphonic Dances, which Ormandy would soon premiere with the Philadelphia Orchestra. Singularly, Rachmaninoff never permitted his public performances to be broadcast—so this surreptitious home recording is the best evidence we have of what Rachmaninoff’s legendary pianism sounded like outside the confines of recording studios sucked clean of the oxygen a body of listeners can activate.
The biggest recent find in classical music was the discovery that in 1940, Sergei Rachmaninoff was privately recorded by the conductor Eugene Ormandy. Seated at Ormandy’s piano, he played through his new Symphonic Dances, which Ormandy would soon premiere with the Philadelphia Orchestra. Singularly, Rachmaninoff never permitted his public performances to be broadcast—so this surreptitious home recording is the best evidence we have of what Rachmaninoff’s legendary pianism sounded like outside the confines of recording studios sucked clean of the oxygen a body of listeners can activate.