by Marie Snyder
 Lots of people discredit the Myers-Briggs as just a horoscope, but it’s significantly different and can be useful in recognizing that we’re all innately different kinds of people. This awareness can help us get along in this world and maybe even find love, or at least a better roommate.
Lots of people discredit the Myers-Briggs as just a horoscope, but it’s significantly different and can be useful in recognizing that we’re all innately different kinds of people. This awareness can help us get along in this world and maybe even find love, or at least a better roommate.
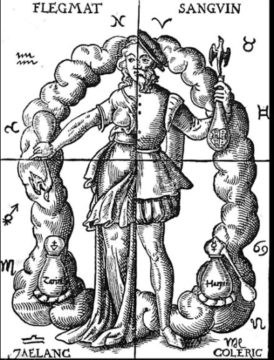
Dividing people into types based on intrinsic tendencies has been around for millennia, born of scrutinized observations of human nature. Ayurvedic Doshas were recorded about 3,000 years ago identifying people who are Vata (energetic but scattered), Pitta (systematic and ambitious, but dogmatic), or Kapha (methodical but slow moving). The four humours came around 500 years later with Alcmaeon of Croton to differentiate those who tend to be sanguine, phlegmatic, choleric, or melancholic. If you think of those categories long enough, you can easily find yourself playing a game of slotting your friends and family under each term.
Then Jung wrote Psychological Types in 1921, outlining opposing traits along three continuums: extraverted/introverted, sensing/intuitive, and thinking/feeling. (That last one might be better updated to task-oriented/people-oriented.) Although it produces only nine specific types, the continuum set-up provides infinite possibilities within each set of four letters. It’s similar to being mainly melancholic with a touch of sanguine, or having a primary and secondary dosha. Jung explains his stance on innate personality:
“The fact that, in spite of the greatest possible similarity of external conditions, one child will assume this type while another that, must, of course, in the last resort be ascribed to individual disposition.”
This typology was popularized by Katharine Cook Briggs and her daughter, Isabel Briggs Myers who added the perception/judgment continuum and found a market for attaching types to careers. Later the Big 5 added another continuum: sensitive/resilient, and now it’s used by data miners. The fact that companies like Cambridge Analytica use psychographic marketing to influence our purchasing and decisions (and possibly our voting choices), means there’s likely something to understanding people under categories. Read more »
