The Blades
In the new world, as the goddess dictated,
each time a man touched a woman against
her will, each time he exposed himself,
each time he whistled, dropped something
in her drink, photographed her in secret
she sprouted a wing from her spine. Not feathered,
like birds or angels, not cellular, translucent,
veined like dragonflies, but a wing
like a blade, like a sword hammered flat,
thin as paper. One wing per wrong.
At first, the women lamented. All their dresses
needed altering, their blankets shredded,
their own hair sliced off like a whisper
if it grew down their backs. And those
misused by fathers, bosses, drunken strangers
evening after evening were blade-ridden,
their statures curved downward like sorrow
under such weight. But this was not the old world
of red letters or mouthfuls of unspoken names,
not the old world of women folded
around their secrets like envelopes, of stark
rooms where men asked what they’d done
to deserve this. And the goddess whispered
to the women in their dreams, and they awakened,
startled, and knew the truth.
They pinned up their hair, walked out into the morning,
their blades glittering in the sun, sistering
them to each other. They searched for the woman
with the most blades, found her unable to stand,
left for dead, nearly crushed beneath the blades’ weight.
They called her queen. They lifted her with hands
gentle as questions, flung her into the air,
saw her snap straight, beat the wings at last,
and they followed her, a swarm of them, terrible
and thrumming, to put the blades to use.
by Katie Bickham
from Rattle, #62 Winter 2018

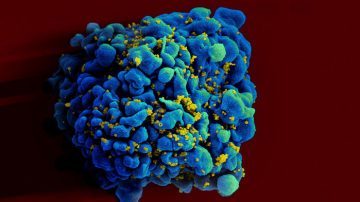 Drugs work stunningly well to control HIV—but not in everyone, and not without side effects. That’s why a small cadre of patients known as elite controllers has long fascinated researchers: Their immune system alone naturally suppresses HIV for decades without drugs. Now one team, inspired by success in mice, hopes to endow HIV-infected people with tailormade immune cells that target HIV, in effect creating elite controllers in the clinic. The immune strategy has risks, but it builds on increasingly popular cancer treatments with T cells engineered to have surface proteins, called chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), that can recognize markers on the surfaces of tumor cells and destroy the cancer. Such CAR T cells can also be tailored to identify and eliminate HIV-infected cells. This approach was tested in HIV-infected humans long before CAR T cells proved their worth against cancer, but it roundly failed. The field wants “to move what’s been learned from cancer back to HIV, completing the circle,” says Steven Deeks, an HIV/AIDS clinician at the University of California, San Francisco, who first tested a CAR T cell against the virus in the late 1990s.
Drugs work stunningly well to control HIV—but not in everyone, and not without side effects. That’s why a small cadre of patients known as elite controllers has long fascinated researchers: Their immune system alone naturally suppresses HIV for decades without drugs. Now one team, inspired by success in mice, hopes to endow HIV-infected people with tailormade immune cells that target HIV, in effect creating elite controllers in the clinic. The immune strategy has risks, but it builds on increasingly popular cancer treatments with T cells engineered to have surface proteins, called chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), that can recognize markers on the surfaces of tumor cells and destroy the cancer. Such CAR T cells can also be tailored to identify and eliminate HIV-infected cells. This approach was tested in HIV-infected humans long before CAR T cells proved their worth against cancer, but it roundly failed. The field wants “to move what’s been learned from cancer back to HIV, completing the circle,” says Steven Deeks, an HIV/AIDS clinician at the University of California, San Francisco, who first tested a CAR T cell against the virus in the late 1990s. I think it’s very difficult to make the case for an objective morality if you’re using the word ‘objective’ in a strong sense, either to mean a universal morality or a foundational morality that all people everywhere understand and accept in a globalising world.
I think it’s very difficult to make the case for an objective morality if you’re using the word ‘objective’ in a strong sense, either to mean a universal morality or a foundational morality that all people everywhere understand and accept in a globalising world. Fiction shines a light on the human condition by putting people into imaginary situations and envisioning what might happen. Science fiction expands this technique by considering situations in the future, with advanced technology, or with utterly different social contexts. Seth MacFarlane’s show The Orville is good old-fashioned space opera, but it’s also a laboratory for exploring the intricacies of human behavior. There are interpersonal conflicts, sexual politics, alien perspectives, and grappling with the implications of technology. I talk with Seth about all these issues, and maybe a little bit about whether it’s a good idea to block people on Twitter.
Fiction shines a light on the human condition by putting people into imaginary situations and envisioning what might happen. Science fiction expands this technique by considering situations in the future, with advanced technology, or with utterly different social contexts. Seth MacFarlane’s show The Orville is good old-fashioned space opera, but it’s also a laboratory for exploring the intricacies of human behavior. There are interpersonal conflicts, sexual politics, alien perspectives, and grappling with the implications of technology. I talk with Seth about all these issues, and maybe a little bit about whether it’s a good idea to block people on Twitter. The mass shootings over the weekend in El Paso, Texas, and Dayton, Ohio, killed at least 31 people and wounded scores more. Those incidents were just the latest such deadly attacks in the United States, which has tallied more than 250 since Jan. 1, according to a new report by
The mass shootings over the weekend in El Paso, Texas, and Dayton, Ohio, killed at least 31 people and wounded scores more. Those incidents were just the latest such deadly attacks in the United States, which has tallied more than 250 since Jan. 1, according to a new report by  But there is a catch. This groundbreaking research is relevant
But there is a catch. This groundbreaking research is relevant  F
F Today, many science books are full of detailed photos that reveal the intricate parts of plant life, but prior to the invention of photography (and macro photography), it was up to
Today, many science books are full of detailed photos that reveal the intricate parts of plant life, but prior to the invention of photography (and macro photography), it was up to  During the three years that Billy Budd took shape, Britten and Forster occasionally disagreed about just how brazen the piece should be. In one instance, Forster complained that one of Claggart’s arias was just not hot-blooded enough. “I want passion—love constricted, perverted, poisoned, but nevertheless flowing down its agonising channel; a sexual discharge gone evil,” Forster wrote. “Not soggy depression or growling remorse.” Britten—who had largely been circumspect about his own homosexuality, publicly avoiding the subject of his long relationship with the tenor Peter Pears—strongly disagreed, and as a consequence, a rift opened up between librettist and composer, the one a daring idealist, the other a more cautious realist.
During the three years that Billy Budd took shape, Britten and Forster occasionally disagreed about just how brazen the piece should be. In one instance, Forster complained that one of Claggart’s arias was just not hot-blooded enough. “I want passion—love constricted, perverted, poisoned, but nevertheless flowing down its agonising channel; a sexual discharge gone evil,” Forster wrote. “Not soggy depression or growling remorse.” Britten—who had largely been circumspect about his own homosexuality, publicly avoiding the subject of his long relationship with the tenor Peter Pears—strongly disagreed, and as a consequence, a rift opened up between librettist and composer, the one a daring idealist, the other a more cautious realist. This past April, Mount Sinai oncologist
This past April, Mount Sinai oncologist 
 DANIEL ELLSBERG
DANIEL ELLSBERG Noam Chomsky: Trump’s diatribes successfully inflame his audience, many of whom apparently feel deeply threatened by diversity, cultural change, or simply the recognition that the White Christian nation of their collective imagination is changing before their eyes. White supremacy is nothing new in the U.S. The late George Frederickson’s
Noam Chomsky: Trump’s diatribes successfully inflame his audience, many of whom apparently feel deeply threatened by diversity, cultural change, or simply the recognition that the White Christian nation of their collective imagination is changing before their eyes. White supremacy is nothing new in the U.S. The late George Frederickson’s  Born in an Ohio steel town in the depths of the Great Depression, Morrison carved out a literary home for the voices of African Americans, first as an acclaimed editor and then with novels such as The Bluest Eye,
Born in an Ohio steel town in the depths of the Great Depression, Morrison carved out a literary home for the voices of African Americans, first as an acclaimed editor and then with novels such as The Bluest Eye,  ‘We have already exited the state of environmental conditions that allowed the human animal to evolve in the first place,’ Wallace-Wells writes, ‘in an unsure and unplanned bet on just what that animal can endure. The climate system that raised us, and raised everything we now know as human civilisation, is now, like a parent, dead.’ He is not a climate scientist, so is perhaps less circumspect than he might be: the data here is designed to scare us. ‘I am alarmed,’ he writes. Who isn’t? We know exactly where we are, despite the continuous chatter of doubt and denial. Wallace-Wells is scathing about the oil industry, whose disinformation clogs public discourse and waylays political processes: ‘A more grotesque performance of corporate evilness is hardly imaginable, and, a generation from now, oil-backed denial will likely be seen as among the most heinous conspiracies against human health and well-being as have been perpetrated in the modern world.’
‘We have already exited the state of environmental conditions that allowed the human animal to evolve in the first place,’ Wallace-Wells writes, ‘in an unsure and unplanned bet on just what that animal can endure. The climate system that raised us, and raised everything we now know as human civilisation, is now, like a parent, dead.’ He is not a climate scientist, so is perhaps less circumspect than he might be: the data here is designed to scare us. ‘I am alarmed,’ he writes. Who isn’t? We know exactly where we are, despite the continuous chatter of doubt and denial. Wallace-Wells is scathing about the oil industry, whose disinformation clogs public discourse and waylays political processes: ‘A more grotesque performance of corporate evilness is hardly imaginable, and, a generation from now, oil-backed denial will likely be seen as among the most heinous conspiracies against human health and well-being as have been perpetrated in the modern world.’ The laughter of Morrison’s characters disguises pain, deprivation and violation. It is laughter at a series of bad, cruel jokes. The real joke in naming Sula’s neighbourhood “The Bottom”, when it perches on barren Ohio uplands is that, in many senses it really is “the bottom” after all. Nothing is what it seems; no appearance, no relationship, can be trusted to endure.
The laughter of Morrison’s characters disguises pain, deprivation and violation. It is laughter at a series of bad, cruel jokes. The real joke in naming Sula’s neighbourhood “The Bottom”, when it perches on barren Ohio uplands is that, in many senses it really is “the bottom” after all. Nothing is what it seems; no appearance, no relationship, can be trusted to endure.